

Alan Alexander “A. A.” Milne (/ˈmɪln/; 18 January 1882– 31 January 1956) was an English author, best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh and for various poems. Milne was a noted writer, primarily as a playwright, before the huge success of Pooh overshadowed all his previous work. Milne served in both World Wars, joining the British Army in World War I, and was a captain of the British Home Guard in World War II. Biography Alan Alexander Milne was born in Kilburn, London to parents John Vince Milne, who was Scottish, and Sarah Marie Milne (née Heginbotham) and grew up at Henley House School, 6/7 Mortimer Road (now Crescent), Kilburn, a small public school run by his father. One of his teachers was H. G. Wells, who taught there in 1889–90. Milne attended Westminster School and Trinity College, Cambridge where he studied on a mathematics scholarship, graduating with a B.A. in Mathematics in 1903. While there, he edited and wrote for Granta, a student magazine. He collaborated with his brother Kenneth and their articles appeared over the initials AKM. Milne’s work came to the attention of the leading British humour magazine Punch, where Milne was to become a contributor and later an assistant editor. Milne played for the amateur English cricket team the Allahakbarries alongside authors J. M. Barrie and Arthur Conan Doyle. Milne joined the British Army in World War I and served as an officer in the Royal Warwickshire Regiment and later, after a debilitating illness, the Royal Corps of Signals. He was commissioned into the 4th Battalion, Royal Warwickshire Regiment on 17 February 1915 as a second lieutenant (on probation). His commission was confirmed on 20 December 1915. On 7 July 1916, he was injured while serving in the Battle of the Somme and invalided back to England. Having recuperated, he was recruited into Military Intelligence to write propaganda articles for MI 7b between 1916 and 1918. He was discharged on 14 February 1919, and settled in Mallord Street, Chelsea. He relinquished his commission on 19 February 1920, retaining the rank of lieutenant. After the war, he wrote a denunciation of war titled Peace with Honour (1934), which he retracted somewhat with 1940's War with Honour. During World War II, Milne was one of the most prominent critics of fellow English writer P. G. Wodehouse, who was captured at his country home in France by the Nazis and imprisoned for a year. Wodehouse made radio broadcasts about his internment, which were broadcast from Berlin. Although the light-hearted broadcasts made fun of the Germans, Milne accused Wodehouse of committing an act of near treason by cooperating with his country’s enemy. Wodehouse got some revenge on his former friend (e.g., in The Mating Season) by creating fatuous parodies of the Christopher Robin poems in some of his later stories, and claiming that Milne “was probably jealous of all other writers.... But I loved his stuff.” Milne married Dorothy “Daphne” de Sélincourt in 1913 and their son Christopher Robin Milne was born in 1920. In 1925, A. A. Milne bought a country home, Cotchford Farm, in Hartfield, East Sussex. During World War II, A. A. Milne was Captain of the British Home Guard in Hartfield & Forest Row, insisting on being plain “Mr. Milne” to the members of his platoon. He retired to the farm after a stroke and brain surgery in 1952 left him an invalid, and by August 1953 “he seemed very old and disenchanted”. Milne died in January 1956, aged 74. Literary career 1903 to 1925 After graduating from Cambridge in 1903, A. A. Milne contributed humorous verse and whimsical essays to Punch, joining the staff in 1906 and becoming an assistant editor. During this period he published 18 plays and 3 novels, including the murder mystery The Red House Mystery (1922). His son was born in August 1920 and in 1924 Milne produced a collection of children’s poems When We Were Very Young, which were illustrated by Punch staff cartoonist E. H. Shepard. A collection of short stories for children Gallery of Children, and other stories that became part of the Winnie-the-Pooh books, were first published in 1925. Milne was an early screenwriter for the nascent British film industry, writing four stories filmed in 1920 for the company Minerva Films (founded in 1920 by the actor Leslie Howard and his friend and story editor Adrian Brunel). These were The Bump, starring Aubrey Smith; Twice Two; Five Pound Reward; and Bookworms. Some of these films survive in the archives of the British Film Institute. Milne had met Howard when the actor starred in Milne’s play Mr Pim Passes By in London. Looking back on this period (in 1926), Milne observed that when he told his agent that he was going to write a detective story, he was told that what the country wanted from a “Punch humorist” was a humorous story; when two years later he said he was writing nursery rhymes, his agent and publisher were convinced he should write another detective story; and after another two years, he was being told that writing a detective story would be in the worst of taste given the demand for children’s books. He concluded that “the only excuse which I have yet discovered for writing anything is that I want to write it; and I should be as proud to be delivered of a Telephone Directory con amore as I should be ashamed to create a Blank Verse Tragedy at the bidding of others.” 1926 to 1928 Milne is most famous for his two Pooh books about a boy named Christopher Robin after his son, Christopher Robin Milne, and various characters inspired by his son’s stuffed animals, most notably the bear named Winnie-the-Pooh. Christopher Robin Milne’s stuffed bear, originally named “Edward”, was renamed “Winnie-the-Pooh” after a Canadian black bear named Winnie (after Winnipeg), which was used as a military mascot in World War I, and left to London Zoo during the war. “The pooh” comes from a swan called “Pooh”. E. H. Shepard illustrated the original Pooh books, using his own son’s teddy, Growler ("a magnificent bear"), as the model. The rest of Christopher Robin Milne’s toys, Piglet, Eeyore, Kanga, Roo and Tigger, were incorporated into A. A. Milne’s stories, and two more characters– Rabbit and Owl– were created by Milne’s imagination. Christopher Robin Milne’s own toys are now under glass in New York where 750,000 people visit them every year. The fictional Hundred Acre Wood of the Pooh stories derives from Five Hundred Acre Wood in Ashdown Forest in East Sussex, South East England, where the Pooh stories were set. Milne lived on the northern edge of the forest at Cotchford Farm, 51.090°N 0.107°E / 51.090; 0.107, and took his son walking there. E. H. Shepard drew on the landscapes of Ashdown Forest as inspiration for many of the illustrations he provided for the Pooh books. The adult Christopher Robin commented: “Pooh’s Forest and Ashdown Forest are identical”. Popular tourist locations at Ashdown Forest include: Galleon’s Lap, The Enchanted Place, the Heffalump Trap and Lone Pine, Eeyore’s Sad and Gloomy Place, and the wooden Pooh Bridge where Pooh and Piglet invented Poohsticks. Not yet known as Pooh, he made his first appearance in a poem, “Teddy Bear”, published in Punch magazine in February 1924. Pooh first appeared in the London Evening News on Christmas Eve, 1925, in a story called “The Wrong Sort Of Bees”. Winnie-the-Pooh was published in 1926, followed by The House at Pooh Corner in 1928. A second collection of nursery rhymes, Now We Are Six, was published in 1927. All three books were illustrated by E. H. Shepard. Milne also published four plays in this period. He also “gallantly stepped forward” to contribute a quarter of the costs of dramatising P. G. Wodehouse’s A Damsel in Distress. The World of Pooh won the Lewis Carroll Shelf Award in 1958. 1929 onwards The success of his children’s books was to become a source of considerable annoyance to Milne, whose self-avowed aim was to write whatever he pleased and who had, until then, found a ready audience for each change of direction: he had freed pre-war Punch from its ponderous facetiousness; he had made a considerable reputation as a playwright (like his idol J. M. Barrie) on both sides of the Atlantic; he had produced a witty piece of detective writing in The Red House Mystery (although this was severely criticised by Raymond Chandler for the implausibility of its plot). But once Milne had, in his own words, "said goodbye to all that in 70,000 words" (the approximate length of his four principal children’s books), he had no intention of producing any reworkings lacking in originality, given that one of the sources of inspiration, his son, was growing older. In his literary home, Punch, where the When We Were Very Young verses had first appeared, Methuen continued to publish whatever Milne wrote, including the long poem “The Norman Church” and an assembly of articles entitled Year In, Year Out (which Milne likened to a benefit night for the author). In 1930, Milne adapted Kenneth Grahame’s novel The Wind in the Willows for the stage as Toad of Toad Hall. The title was an implicit admission that such chapters as Chapter 7, “The Piper at the Gates of Dawn”, could not survive translation to the theatre. A special introduction written by Milne is included in some editions of Grahame’s novel. Legacy and commemoration The rights to A. A. Milne’s Pooh books were left to four beneficiaries: his family, the Royal Literary Fund, Westminster School and the Garrick Club. After Milne’s death in 1956, one week and six days after his 74th birthday, his widow sold her rights to the Pooh characters to Stephen Slesinger, whose widow sold the rights after Slesinger’s death to the Walt Disney Company, which has made many Pooh cartoon movies, a Disney Channel television show, as well as Pooh-related merchandise. In 2001, the other beneficiaries sold their interest in the estate to the Disney Corporation for $350m. Previously Disney had been paying twice-yearly royalties to these beneficiaries. The estate of E. H. Shepard also received a sum in the deal. The copyright on Pooh expires in 2026. In 2008, a collection of original illustrations featuring Winnie-the-Pooh and his animal friends sold for more than £1.2 million at auction in Sotheby’s, London. Forbes magazine ranked Winnie the Pooh the most valuable fictional character in 2002; Winnie the Pooh merchandising products alone had annual sales of more than $5.9 billion. In 2005, Winnie the Pooh generated $6 billion, a figure surpassed by only Mickey Mouse. A memorial plaque in Ashdown Forest, unveiled by Christopher Robin in 1979, commemorates the work of A. A. Milne and Shepard in creating the world of Pooh. Milne once wrote of Ashdown Forest: “In that enchanted place on the top of the forest a little boy and his bear will always be playing”. In 2003, Winnie the Pooh was listed at number 7 on the BBC’s survey The Big Read. In 2006, Winnie the Pooh received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame, marking the 80th birthday of Milne’s creation. That same year a UK poll saw Winnie the Pooh voted onto the list of icons of England. Several of Milne’s children’s poems were set to music by the composer Harold Fraser-Simson. His poems have been parodied many times, including with the books When We Were Rather Older and Now We Are Sixty. The 1963 film The King’s Breakfast was based on Milne’s poem of the same name. Religious views Milne did not speak out much on the subject of religion, although he used religious terms to explain his decision, while remaining a pacifist, to join the British Home Guard: “In fighting Hitler”, he wrote, “we are truly fighting the Devil, the Anti-Christ... Hitler was a crusader against God.” His best known comment on the subject was recalled on his death: The Old Testament is responsible for more atheism, agnosticism, disbelief—call it what you will—than any book ever written; it has emptied more churches than all the counter-attractions of cinema, motor bicycle and golf course. He also wrote the poem “Explained”: Works Novels * Lovers in London (1905. Some consider this more of a short story collection; Milne did not like it and considered The Day’s Play as his first book.) * Once on a Time (1917) * Mr. Pim (1921) (A novelisation of his play Mr. Pim Passes By (1919)) * The Red House Mystery (1922) * Two People (1931) (Inside jacket claims this is Milne’s first attempt at a novel.) * Four Days’ Wonder (1933) * Chloe Marr (1946) Non-fiction * Peace With Honour (1934) * It’s Too Late Now: The Autobiography of a Writer (1939) * War With Honour (1940) * War Aims Unlimited (1941) * Year In, Year Out (1952) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Punch articles * The Day’s Play (1910) * Once A Week (1914) * The Holiday Round (1912) * The Sunny Side (1921) * Those Were the Days (1929) [The four volumes above, compiled] Newspaper articles and book introductions * The Chronicles of Clovis by “Saki” (1911) [Introduction to] * Not That It Matters (1920) * By Way of Introduction (1929) Story collections for children * A Gallery of Children (1925) * Winnie-the-Pooh (1926) (illustrated by Ernest H. Shepard) * The House at Pooh Corner (1928) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Short Stories Poetry collections for children * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Story collections * The Secret and other stories (1929) * The Birthday Party (1948) * A Table Near the Band (1950) Poetry * For the Luncheon Interval [poems from Punch] * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Behind the Lines (1940) * The Norman Church (1948) * “The Knight Whose Armor Didn’t Squeak” Screenplays and plays * Wurzel-Flummery (1917) * Belinda (1918) * The Boy Comes Home (1918) * Make-Believe (1918) (children’s play) * The Camberley Triangle (1919) * Mr. Pim Passes By (1919) * The Red Feathers (1920) * The Bump (1920, Minerva Films), starring Aubrey Smith * Twice Two (1920, Minerva Films) * Five Pound Reward (1920, Minerva Films) * Bookworms (1920, Minerva Films) * The Great Broxopp (1921) * The Dover Road (1921) * The Lucky One (1922) * The Truth About Blayds (1922) * The Artist: A Duologue (1923) * Give Me Yesterday (1923) (a.k.a. Success in the UK) * Ariadne (1924) * The Man in the Bowler Hat: A Terribly Exciting Affair (1924) * To Have the Honour (1924) * Portrait of a Gentleman in Slippers (1926) * Success (1926) * Miss Marlow at Play (1927) * The Fourth Wall or The Perfect Alibi (1928) (later adapted for the film Birds of Prey (1930), directed by Basil Dean) * The Ivory Door (1929) * Toad of Toad Hall (1929) (adaptation of The Wind in the Willows) * Michael and Mary (1930) * Other People’s Lives (1933) (a.k.a. They Don’t Mean Any Harm) * Miss Elizabeth Bennet (1936) [based on Pride and Prejudice] * Sarah Simple (1937) * Gentleman Unknown (1938) * The General Takes Off His Helmet (1939) in The Queen’s Book of the Red Cross * The Ugly Duckling (1941) * Before the Flood (1951). References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A._A._Milne


Thomas Stearns Eliot OM (26 September 1888– 4 January 1965) was a British essayist, publisher, playwright, literary and social critic, and “one of the twentieth century’s major poets”. He moved from his native United States to England in 1914 at the age of 25, settling, working, and marrying there. He was eventually naturalised as a British subject in 1927 at the age of 39, renouncing his American citizenship. Eliot attracted widespread attention for his poem “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” (1915), which was seen as a masterpiece of the Modernist movement. It was followed by some of the best-known poems in the English language, including The Waste Land (1922), “The Hollow Men” (1925), “Ash Wednesday” (1930), and Four Quartets (1943). He was also known for his seven plays, particularly Murder in the Cathedral (1935). He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1948, “for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry”.

William Arthur Dunkerley (12 November 1852 – 23 January 1941) was an English journalist, novelist and poet. He was born in Manchester, spent a short time after his marriage in the US before moving to Ealing, West London, where he served as deacon and teacher at the Ealing Congregational Church from the 1880s. In 1922 he moved to Worthing in Sussex, where he became the town’s mayor.Dunkerley wrote under his own name, and also as John Oxenham for his poetry, hymn-writing, and novels. His poetry includes Bees in Amber: A Little Book of Thoughtful Verse (1913), which became a bestseller. He also wrote the poem “Greatheart”. He used the pseudonym Julian Ross for journalism. In February 1892 Robert Barr and Dunkerley founded The Idler, a monthly “general interest magazine, one of the first to appear following the enthusiastic reception of The Strand, but not a slavish imitation”. Barr and Dunkerley/Oxenham both contributed as writers. The editors were Barr and Jerome K. Jerome initially.Dunkerley had two sons and four daughters, of whom the eldest, and eldest child, Elsie Jeanette, became well known as a children’s writer, particularly through her Abbey Series of girls’ school stories. Another daughter, Erica, also used the Oxenham pen-name. The elder son, Roderic Dunkerley, had several titles published under his own name. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Arthur_Dunkerley

Walter Savage Landor (30 January 1775 – 17 September 1864) was an English writer and poet. His best known works were the prose Imaginary Conversations, and the poem Rose Aylmer, but the critical acclaim he received from contemporary poets and reviewers was not matched by public popularity. As remarkable as his work was, it was equalled by his rumbustious character and lively temperament. Summary of his work In a long and active life of eighty-nine years Landor produced a considerable amount of work in various genres. This can perhaps be classified into four main areas—prose, lyric poetry, political writings including epigrams and Latin. His prose and poetry have received most acclaim, but critics are divided in their preference between them. Landor’s prose is best represented by the Imaginary Conversations. He drew on a vast array of historical characters from Greek philosophers to contemporary writers and composed conversations between pairs of characters that covered areas of philosophy, politics, romance and many other topics. These exercises proved a more successful application of Landor’s natural ability for writing dialogue than his plays. Although these have many quotable passages the overall effect suffered because he never learned the art of drama. Landor wrote much sensitive and beautiful poetry. The love poems were inspired by a succession of female romantic ideals—Ione, Ianthe, Rose Aylmer and Rose Paynter. Equally sensitive are his “domestic” poems about his sister and his children. In the course of his career Landor wrote for various journals on a range of topics that interested him from anti-Pitt politics to the unification of Italy. He was also a master of the epigram which he used to good effect and wrote satirically to avenge himself on politicians and other people who upset him. Landor wrote over three hundred Latin poems, political tracts and essays, but these have generally been ignored in the collections of his work. Landor found Latin useful for expressing things that might otherwise have been “indecent or unattractive” as he put it and as a cover for libellous material. Fellow classical scholars of the time put Landor’s Latin work on a par with his English writing. Summary of his life Landor’s life is an amazing catalogue of incidents and misfortunes, many of them self-inflicted but some no fault of his own. His headstrong nature and hot-headed temperament, combined with a complete contempt for authority, landed him in a great deal of trouble over the years. By a succession of bizarre actions, he was successively thrown out of Rugby, Oxford and from time to time from the family home. In the course of his life he came into conflict deliberately with his political enemies - the supporters of Pitt - but inadvertently with a succession of Lord Lieutenants, Bishops, Lord Chancellors, Spanish officers, Italian Grand Dukes, nuncio legatos, lawyers and other minor officials. He usually gained the upper hand, if not with an immediate hilarious response, then possibly many years later with a biting epithet. Landor’s writing often landed him on the wrong side of the laws of libel, and even his refuge in Latin proved of no avail in Italy. Many times his friends had to come to his aid in smoothing the ruffled feathers of his opponents or in encouraging him to moderate his behaviour. His friends were equally active in the desperate attempts to get his work published, where he offended or felt cheated by a succession of publishers who found his work either unsellable or unpublishable. He was repeatedly involved in legal disputes with his neighbours whether in England or Italy and Dickens’ characterisation of him in Bleak House revolves around such a dispute over a gate between Boythorn and Sir Leicester Dedlock. Fate dealt with him unfairly when he tried to put into practice his bold and generous ideas to improve the lot of man, or when he was mistaken at one time for an agent of the Prince of Wales and at another for a tramp. His stormy marriage with his long-suffering wife resulted in a long separation, and then when she had finally taken him back to a series of sad attempts to escape. And yet Landor was described as “the kindest and gentlest of men”. He collected a coterie of friends who went to great lengths to help him as “his loyalty and liberality of heart were as inexhaustible as his bounty and beneficence of hand”. It was said that “praise and encouragement, deserved or undeserved, came more readily to his lips than challenge or defiance”. The numerous accounts of those with whom he came in contact reveal that he was fascinating company and he dined out on his wit and knowledge for a great part of his life. Landor's powerful sense of humour, expressed in his tremendous and famous laughs no doubt contributed to and yet helped assuage the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune. “His passionate compassion, his bitter and burning pity for all wrongs endured in all the world, found outlet in his lifelong defence of tyrannicide. His tender and ardent love of children, of animals and of flowers makes fragrant alike the pages of his writing and the records of his life”. Early life Walter Savage Landor was born in Warwick, England, the eldest son of Dr Walter Landor, a physician, and his second wife, Elizabeth Savage. His birthplace, Eastgate House, is now occupied by The King's High School For Girls. His father inherited estates at Rugeley, Staffordshire and his mother was heiress to estates at Ipsley Court and Bishop's Tachbrook in Warwickshire. Landor as the eldest son was heir to these properties and looked forward to a life of prosperity. The family tradition was Whig in reaction to George III and Pitt, and although Landor's brother Robert was the only other member to achieve fame as a writer there was a strong literary tradition in the family. After attending a school at Knowle, he was sent to Rugby School under Dr James, but took offence at the headmaster's review of his work and was removed at Dr James' request. Years later, Landor included references to James in Latin in Simonidea with a mixture of praise and criticism and was subsequently reconciled with him. He then studied privately with Rev. William Langley, vicar of Fenny Bentley and headmaster of Ashbourne Grammar School. Langley was later mentioned in the Imaginary Conversation of Isaak Walton. Landor's temperament and violent opinions caused embarrassment at home and he was usually asked to absent himself when guests were expected. On one occasion he netted and threw in the river a local farmer who objected to his fishing on his property. In 1793 he entered Trinity College, Oxford where he showed rebelliousness in his informal dress and was known as a "mad Jacobin" since he was taken with ideas of French republicanism. His tutor Dr Benwell was impressed by him, but unfortunately his stay was short-lived. In 1794 he fired a gun at the windows of a Tory whose late night revels disturbed him and for whom he had an aversion. He was rusticated for a year, and, although the authorities were willing to condone the offence, he refused to return. The affair led to a quarrel with his father in which Landor expressed his intention of leaving home for ever. Landor went to Tenby in Wales where he had a love affair with a local girl, Nancy Evans, for whom he wrote some of his earliest love poems referring to her as "Ione". Landor's father disapproved and he removed for a time to London, lodging near Portland Place. Ione subsequently had a child who died in infancy. In 1795 Landor brought out a small volume of English and Latin verse in three books entitled The Poems of Walter Savage Landor. Landor also wrote an anonymous Moral Epistle in pamphlet form of nineteen pages, respectfully dedicated to Earl Stanhope. It was a satire in heroic verse condemning Pitt for trying to suppress liberal influences. Although Landor subsequently disowned these "'prentice works", Swinburne wrote "No poet at the age of twenty ever had more vigour of style and fluency of verse; nor perhaps has any ever shown such masterly command of epigram and satire, made vivid and vital by the purest enthusiasm and most generous indignation." Landor was reconciled with his family through the efforts of his friend Dorothea Lyttelton. He later told Forster that he would have married Dorothea if he were financially independent. He did not enter a profession - he did not want the law, and no more did the army want him. His father allowed him £150 a year, and he was free to live at home or not, as he pleased. South Wales and Gebir Landor settled in South Wales, returning home to Warwick for short visits. It was at Swansea that he became friendly with the family of Lord Aylmer, including his sister, Rose, whom Landor later immortalized in the poem, "Rose Aylmer". It was she who lent him "The Progress of Romance" by the Gothic authoress Clara Reeve. In this he found the story "The History of Charoba, Queen of Egypt", which inspired his poem "Gebir". Rose Aylmer sailed to India with an aunt in 1798, and two years later died of Cholera. Ah, what avails the sceptred race, Ah, what the form divine! What every virtue, every grace! Rose Aylmer, all were thine. Rose Aylmer, whom these wakeful eyes May weep, but never see, A night of memories and of sighs I consecrate to thee. In 1798 Landor published "Gebir" the work which established his reputation. "Gebir" tells the story of a prince of Spain who falls in love with his enemy Queen Charoba of Egypt. Southey, reviewed "Gebir" calling it "some of the most exquisite poetry in the language" and was keen to discover the anonymous author. Sidney Colvin wrote "For loftiness of thought and language together, there are passages in Gebir that will bear comparison with Milton" and "nowhere in the works of Wordsworth or Coleridge do we find anything resembling Landor's peculiar qualities of haughty splendour and massive concentration".[4] John Forster wrote "Style and treatment constitute the charm of it. The vividness with which everything in it is presented to sight as well as through the wealth of its imagery, its moods of language - these are characteristics pre-eminent in Gebir".[5] Gifford, on the other hand, who was ever a harsh critic of Landor described it as A jumble of incomprehensible trash... the most vile and despicable effusion of a mad and muddy brain....[6] For the next three years Landor led an unsettled life, spent mainly in London. He became friends with the classics scholar Dr Samuel Parr who lived at Hatton near Warwick and who appreciated Landor as a person and a Latin writer.[2] Landor favoured Latin as a way of expressing playful material without exposing it to public view "Siquid forte iocosius cuivis in mentem veniat, id, vernacule, puderet, non enim tantummodo in luce agitur sed etiam in publico."[7] Latin also had the advantage of being exempt from libel laws in England. Parr introduced Landor to Robert Adair, party organiser for Charles James Fox, who enlisted Landor to write in The Morning Post and The Courier against the ministry of Pitt. Landor published "Poems from the Arabic and Persian" in 1800 and a pamphlet of Latin verses. During this time he met Isaac Mocatta who stimulated his interest in art and exercised a moderating influence, but Mocatta died 1801. In 1802 Landor went to Paris where he saw Napoleon at close quarters, and this was enough to put him off the idea of French republicanism. In the same year he published "Poetry by the Author of Gebir" which included the narrative poems Crysaor and The Phocaeans. Colvin considered Crysaor Landor's finest piece of narrative in blank verse. Landor's brother Robert helped with corrections and additions to "Gebir" and the second edition appeared in 1803. About the same time Landor published the whole poem in Latin, which did little to increase readership but appealed to Parr and was considered by Swinburne to be comparable with the English version in might and melody of line, and for power and perfection of language. Landor travelled the country in constant debt, spending much time at Bath. Here he met Sophia Jane Swift, who was already engaged to her cousin Godwin Swifte, whom she married despite Landor's ardent entreaties in 1803. He called her Ianthe and wrote some of his most beautiful love poems to her. His father died in 1805, which put him in possession of an independent fortune and he settled in Bath, living in grand style.[2] In 1806 he published "Simonidea" which included poems to Ianthe and Ione. It also included "Gunlaug and Helga" a narrative poem from William Herbert's "Select Icelandic poems". At Bristol in 1808 he caught up with Southey, whom he had missed on a trip to the Lake District in the previous year, and the mutual appreciation of the two poets led to a warm friendship. He also wrote a work "The Dun Cow" which was written in defence of his friend Parr who had been attacked in an anonymous work "Guy's Porridge Pot", which Landor was fierce to deny was any work of his. Napoleonic Wars and Count Julian In 1808 he had an heroic impulse to take part in the Peninsular War. At the age of thirty-three, he left England for Spain as a volunteer to serve in the national army against Napoleon. He landed at Corunna, introduced himself to the British envoy, offered 10,000 reals for the relief of Venturada, and set out to join the army of General Joaquín Blake y Joyes. He was disappointed not to take part in any real action and found himself giving support at Bilbao where he was nearly captured. A couple of months later the Convention of Sintra brought an end to the campaign and Landor returned to England. The Spanish Government offered its thanks to him, and King Ferdinand appointed him a Colonel in the Spanish Army. However when the King restored the Jesuits Landor returned his commission.[2] When he returned to England, he joined Wordsworth and Southey in denouncing the Convention of Sintra, which had excited general indignation. In 1809 Landor wrote "Three letters to Don Francisco Riquelme" giving him the benefit of his wisdom as a participant in the war. He wrote an ode in Latin to Gustavus IV of Sweden and wrote to press under various pseudonyms. In 1810 he wrote "a brave and good letter to Sir Francis Burdett." The Spanish experience provided inspiration for the tragedy of Count Julian, based on Julian, count of Ceuta. Although this demonstrated Landor's distinctive style of writing, it suffered from his failure to study the art of drama and so made little impression. The plot is difficult to follow unless the story is previously known and concerns a complicated situation after the defeat of the last Visigoth King of Spain. It carries the moral tone of crime propagating crime. Southey undertook to arrange publication and eventually got it published by Murray in 1812, after an initial refusal by Longmans which led Landor to burn another tragedy "Ferranti and Giulio". Thomas de Quincey later wrote of the work "Mr Landor is probably the one man in Europe that has adequately conceived the situation, the stern self-dependency and monumental misery of Count Julian". Swinburne described it as "the sublimest poem published in our language, between the last masterpiece of Milton (Samson Agonistes) and the first masterpiece of Shelley, (Prometheus Unbound) one equally worthy to stand unchallenged beside either for poetic perfection as well as moral majesty. The superhuman isolation of agony and endurance which encircles and exalts the hero is in each case expressed with equally appropriate magnificence of effect. The style of Count Julian, if somewhat deficient in dramatic ease and the fluency of natural dialogue, has such might and purity and majesty of speech as elsewhere we find only in Milton so long and so steadily sustained." Llanthony and marriage Before going to Spain, he had been looking for a property and settled on Llanthony Abbey in Monmouthshire, a ruined Benedictine abbey. He sold the property at Rugeley which he inherited from his father, and persuaded his mother to sell her Tachbrook estate to contribute to the purchase cost. On his return from Spain he was busy finalising these matters. The previous owner had erected some buildings in the ruins of the ancient abbey, but an Act of Parliament, passed in 1809, was needed to allow Landor to pull down these buildings and construct a house, (which was never finished). He wanted to become a model country gentleman, planting trees, importing sheep from Spain, and improving the roads. There is still an avenue of trees in the area known as "Landor's Larches" and many old chestnuts have been dated back to his time. In 1811 he went to a ball in Bath and seeing a pretty girl exclaimed "That's the nicest girl in the room, and I'll marry her". She was Julia Thuillier, the daughter of an impoverished Swiss banker who had an unsuccessful business at Banbury and had gone to Spain, leaving his family at Bath. They married at St James Church Bath on 24 May 1811 and settled for a while at Llanthony Abbey. Landor had a visit from Southey, after he sent him a letter describing the idylls of country life, including nightingales and glow-worms. However the idyll was not to last long as for the next three years Landor was worried by the combined vexation of neighbours and tenants, lawyers and lords-lieutenant and even the Bishop of St David's, while at the same time he tried to publish an article on Fox, a response to a sycophantic piece by John Bernard Trotter, which was condemned by the prospective publisher John Murray as libellous and damned by Canning and Gifford. His troubles with the neighbours stemmed from petty squabbles, many arising from his headstrong and impetuous nature. He employed a solicitor one Charles Gabell, who saw him as a client to be milked. His trees were uprooted and his timber stolen. A man against whom he had to swear the peace drank himself to death, and he was accused of causing the misfortune and when he prosecuted a man for theft he was insulted by the defendant's counsel (whom he later "chastised" in his Latin poetry). He was fond of revenge through his verse, Latin or otherwise and gave his opinion of his lawyers in the following piece of doggerel. If the devil, a mighty old omnibus driver Saw an omnibus driving downhill to a river And saved any couple to share his own cab I really do think t'would be Gabell & Gabb. When the Bishop failed to reply to his letter offering to restore part of the priory Landor followed up saying "God alone is great enough for me to ask anything of twice". He wanted to become a magistrate and after a row with the Lord Lieutenant, the Duke of Beaufort, who was suspicious of his republican sympathies, he pursued the matter with the Lord Chancellor, Lord Eldon well known as a High Tory without success. He wasted much effort and money in noble attempts to improve the land, and to relieve the wretchedness and raise the condition of the poorer inhabitants. The final straw was when he let his farmland to one Betham who was incompetent and extravagant and paid no rent. After an expensive action to recover the debts from Betham he had had enough, and decided to leave the country, abandoning Llanthony to his creditors - which was principally his mother. In 1814 Landor left England for Jersey, where he had a quarrel with his wife and set off for France on his own. Eventually she joined him at Tours as did his brother Robert. At Tours he met Francis George Hare, father of Augustus Hare and brother of Julius Hare who was to be of great help to him. Landor soon became dissatisfied with Tours and after tremendous conflicts with his landlady set off in September 1815 with his wife and brother on a tempestuous journey to Italy. Florence and Imaginary Conversations Landor and his wife finally settled at Como where they stayed for three years. Even here he had troubles for at the time Caroline of Brunswick, wife of the Prince Regent was living there and Landor was suspected of being an agent involved in watching her in case of divorce proceedings. In 1818 he insulted the authorities in a Latin poem directed against an Italian poet who had denounced England, not realising that the libel laws in Italy (unlike in England) applied to Latin writings as well as Italian. After threatening the regio delegato with a beating he was ordered to leave Como. In September he went to Genoa and Pisa. He finally settled at Florence in 1821. After two years in apartments in the Medici Palace, he settled with his wife and children at the Villa Castiglione. In this, the most important period in his literary career, he produced some of his best known works - the Imaginary Conversations. It was at this time that Lady Blessington and her husband were living at Florence and became firm friends. The first two volumes of his Imaginary Conversations appeared in 1824 with a second edition in 1826; a third volume was added in 1828; and in 1829 the fourth and fifth volumes were published. Not until 1846 was a fresh instalment added, in the second volume of his collected and selected works. With these works, Landor acquired a high, but not wide literary reputation. He had various disputes with the authorities in Florence. The theft of some silver led to altercations with the police, whose interviews with tradesmen ended up defining him as a "dangerous man", and the eventual upshot was that the Grand Duke banished him from Florence. Subsequently the Grand Duke took the matter good-naturedly, and ignored Landor's declaration that, as the authorities disliked his residence, he should reside there permanently. In 1829, Landor bought the Villa Gherardesca at Fiesole helped by a generous loan from Joseph Ablett of Llanbedr Hall, Denbighshire. Here he had a dispute with a neighbour about water rights, which led to a lawsuit and a challenge, although the English Consul Kirkup succeeded in arranging the point of honour satisfactorily. Landor was visited by William Hazlitt and Leigh Hunt, and was on intimate terms with Charles Armitage Brown. It was at this time he became acquainted with Edward John Trelawny who he included in volume IV of Imaginary Conversations. His mother, with whom he had always corresponded affectionately, died in October 1829 and his cousin Walter Landor of Rugeley took over the management of the estate in Wales. Landor was happy at Villa Gherardesca for several years, writing books, playing with his children whom he adored and with the nightingales, and planting his gardens. He had many visitors, most notably in 1829 Jane Swift (Ianthe) now a widow, who inspired him to write poetry again. Later came Henry Crabb Robinson with whom he got on extremely well. In 1831 he published a volume combining Gebir, Count Julian and Other Poems (including 31 to Ianthe). Although this sold only 40 copies, Landor was unconcerned as he was working on "High and Low Life in Italy". This last work he sent to Crabb Robinson for publication but he had difficulties with publishers and it did not appear until 1837. In 1832 Ablett persuaded him visit England, where he met many old friends. He saw Ianthe at Brighton and met Lord Wenlock. He also visited his family in Staffordshire - his brother Charles was rector of Colton, and his cousin Walter Landor of Rugeley was trying to deal with the complex business of Llanthony. He visited Charles Lamb at Enfield, Samuel Coleridge at Highgate, and Julius Hare at Cambridge. He went with Ablett to the Lake District and saw Southey and Coleridge. On returning to Fiesole he found his children out of hand and obtained a German governess for them. Back in Italy he met Richard Monckton Milnes who later wrote about him. He was visited by Ralph Waldo Emerson and worked on the conversations which led to the volumes upon "Shakespeare's Examinations for Deer Stealing", "Pericles and Aspasia", and the "Pentameron". Lady Blessington sold "Shakespeare" for him. In 1835 Ianthe visited again, and brought her half-sister, Mrs Paynter, with her. Landor's wife Julia became jealous, although she already had a younger lover, and their difference of opinion ended in a complete separation. England, Pericles and journalism Landor was 60 by now and went to Lucca where he finished "Pericles and Aspasia" and in September returned to England alone in the autumn. He had an income of about £600 per annum from properties in England, but when he left Italy he made over £400 of the share to his wife, and transferred the villa and farms at Fiesole to his son Arnold absolutely. His income was now £200 a year and he was in financial difficulties. He stayed with Ablett at Llanbedr for three months, spent winter at Clifton and returned to him afterwards, when Ablett persuaded him to write "Literary Hours" which was published the next year. "Pericles and Aspasia", which was to become one of his most appreciated works was published in March 1836. It is in the form of an Imaginary Conversation and describes the development of Aspasia's romance with Pericles, who died in the Peloponnesian War, told in a series of letters to a friend Cleone. The work is one of Landor's most joyous works and is singled out by contemporary critics as an introduction to Landor at his best. On one occasion Landor was travelling to Clifton incognito and chatting to a fellow traveller when the traveller, John Sterling, observed that his strange paradoxical conversation sounded like one of Landor's Imaginary Conversations. Landor covered his retreat, but later became acquainted formally with Sterling. Also in 1836, Landor met John Forster who became his biographer, having become friends after Forster's review of his "Shakespeare". Later that year went to Heidelberg in Germany hoping to meet his children, but was disappointed. He wrote more imaginary conversations including one between Lord Eldon and Escombe. When a lady friend rebuked him for this on the basis that Eldon was now over eighty, Landor replied unmoved with the quip "The devil is older". He had several other publications that year besides Pericles, including "Letter from a Conservative", "A Satire on Satirists" which included a criticism of Wordsworth's failure to appreciate Southey, Alabiadas the Young Man, and "Terry Hogan", a satire on Irish priests. He wintered again at Clifton where Southey visited him. It is possible that Ianthe was living at Bristol, but the evidence is not clear, and in 1837 she went to Austria, where she remained for some years. After leaving Clifton, Landor travelled around and visited Armitage Brown at Plymouth. He established many friendships including John Kenyon and Sir William Napier. At the end of the year he published "Death of Clytemnestra" and "The Pentalogia", containing five of his finest shorter studies in dramatic poetry. The last piece to be published was "Pentameron". Although this had no financial success it was much admired by his friends including Kenyon, Julius Hare, Crabb Robinson, Elizabeth Barrett Browning who said "some of the pages are too delicious to turn over", and Leigh Hunt who reckoned it Landor's masterpiece. In the spring of 1838 he took a house in Bath and wrote his three plays the "Andrea of Hungary", "Giovanna of Naples", and "Fra Rupert". These plays are in the form of a trilogy in the first of which Fra Rupert contrives the death of Andrea husband of Giovanna. Giovanna is suspected but acquitted in the second play. In the third play Fra Rupert is discovered. George Saintsbury described these as a historical novel thrown into conversational dramatic form. In 1839 Landor's attempts to publish the plays were caught up in a dispute between Bentley and Dickens and Forster which caused considerable delay. Again, although these plays, or "conversations in verse" did not succeed with the public, Landor gained warm admirers, many of whom were his personal friends. Southey's mind was giving way when he wrote a last letter to his friend in 1839, but he continued to mention Landor's name when generally incapable of mentioning any one. Landor wandered around the country again, frequently visiting London, where he usually stayed with Lady Blessington, whom he had known at Florence. Mrs Paynter, and her daughter Rose Paynter were at Bath and Landor's letters and verses to Rose are among his best works. Rose later married Charles Graves-Sawle of Restormel in Cornwall. Landor met Charles Dickens and they enjoyed each other's company despite the age difference. Landor greatly admired Dickens' works, and was especially moved by the character of Nell Trent (from The Old Curiosity Shop). Landor was affectionately adapted by Dickens as Lawrence Boythorn in Bleak House.[2] He was the godfather of Dickens's son Walter Landor Dickens. He also became introduced to Robert Browning who sent him a dedicated copy of his work. Landor received a visit from his son Arnold in 1842 and in that year wrote a long essay on Catullus for Forster who was editor of "Foreign Quarterly Review" and followed it up with The Idylls of Theocritus. Super was critical of the essays claiming "A more thoroughly disorganised work never fell from his pen". In 1843 he mourned the death of his friend Southey and dedicated a poem in the Examiner. Landor was visited by his children Walter and Julia and published a poem to Julia in Blackwood's magazine. By that dejected city, Arno runs, Where Ugolino claspt his famisht sons. There wert thou born, my Julia! there thine eyes Return'd as bright a blue to vernal skies. And thence, my little wanderer! when the Spring Advanced, thee, too, the hours on silent wing Brought, while anemonies were quivering round, And pointed tulips pierced the purple ground, Where stood fair Florence: there thy voice first blest My ear, and sank like balm into my breast: For many griefs had wounded it, and more Thy little hands could lighten were in store. But why revert to griefs? Thy sculptured brow Dispels from mine its darkest cloud even now. And all that Rumour has announced of grace! I urge, with fevered breast, the four-month day. O! could I sleep to wake again in May. In the following year his daughter Julia returned and gave him a dog Pomero, who was a faithful companion for a long time. In the same year, he published a poem to Browning in the Morning Chronicle. Forster and Dickens used to visit Bath, to celebrate Landor's birthday and Charles I's execution on the same day. Forster helped Landor in publishing his plays and the 'Collected Works' in 1846, and was employed on The Examiner to which Landor frequently contributed on political and other subjects. Forster objected to the inclusion of some Latin poetry, and so Landor published his most important Latin work 'Poemata et Inscriptiones' separately in 1847. This consisted of large additions to the main contents of two former volumes of idyllic, satiric, elegiac and lyric verse. One piece referred to George IV whose treatment of Caroline of Brunswick had been distasteful to Landor. Heic jacet, Qui ubique et semper jacebat Familiae pessimae homo pessimus Georgius Britanniae Rex ejus nominis IV Arca ut decet ampla et opipare ornata est Continet enim omnes Nerones. (Here lies a person who was always laying about all over the place - the worst member of the worst family - George the fourth of that name of Britain. It is suitable that the vault be large and excessively decorated as it contains all the Neros). Landor's distaste for the House of Hanover is more famously displayed in the doggerel that many do not realise is his composition. George the First was always reckoned Vile, but viler George the Second. And what mortal ever heard Any good of George the Third, But when from earth the Fourth descended God be praised the Georges ended In 1846 he also published the 'Hellenics', including the poems published under that title in the collected works, together with English translations of the Latin idyls. In this year he first met Eliza Lynn who was to become an outstanding novelist and journalist as Lynn Linton, and she became a regular companion in Bath. Now aged over seventy Landor was losing many of his old friends and becoming more frequently ill himself. On one occasion when staying with the Graves-Sawle he visited Exeter and sheltered in the rain on the doorstep of a local barrister James Jerwood. Jerwood mistook him for a tramp and drove him away. Landor's follow-up letter of abuse to the barrister is magnificent. In 1849 he wrote a well-known epitaph for himself on his 74th birthday. I strove with none, for none was worth my strife. Nature I loved, and, next to nature, Art; I warm'd both hands before the fire of Life; It sinks, and I am ready to depart. However he was leading an active social life. Tennyson met him in 1850 and recorded how while another guest fell downstairs and broke his arm, "Old Landor went on eloquently discoursing of Catullus and other Latin poets as if nothing had happened".[12] Thomas Carlyle visited him and wrote "He was really stirring company: a proud irascible, trenchant, yet generous, veracious, and very dignified old man".[12] In 1851 Landor expressed interest in Church reform with a pamphlet "Popery, British and Foreign", and Letters to Cardinal Wiseman. He published various other articles in The Examiner, Fraser's Magazine and other journals. During the year he learnt of the death of his beloved Ianthe and wrote in tribute to her. Sophia! whom I seldom call'd by name, And trembled when I wrote it; O my friend Severed so long from me! one morn I dreamt That we were walking hand in hand thro' paths Slippery with sunshine: after many years Had flown away, and seas and realms been crost, And much (alas how much!) by both endured We joined our hands together and told our tale. And now thy hand hath slipt away from mine, And the cold marble cramps it; I dream one, Dost thou dream too? and are our dreams the same? In 1853 he published the collected "Imaginary Conversations of the Greeks and Romans" which he dedicated to Dickens. Dickens in this year published "Bleak House" which contained the amazingly realistic characterisation of Landor as Boythorn. He also published "The Last Fruit off an Old Tree", containing fresh conversations, critical and controversial essays, miscellaneous epigrams, lyrics and occasional poems of various kind and merit, closing with Five Scenes on the martyrdom of Beatrice Cenci. Swinburne described these as "unsurpassed even by their author himself for noble and heroic pathos, for subtle and genial, tragic and profound, ardent and compassionate insight into character, with consummate mastery of dramatic and spiritual truth."[13] At this time Landor was interesting himself in foreign affairs, in particular Czarist oppression as he saw it and Louis Napoleon. At the end of 1854 his beloved sister Elizabeth died and he wrote a touching memorial. "Sharp crocus wakes the froward year; In their old haunts birds reappear; From yonder elm, yet black with rain, The cushat looks deep down for grain Thrown on the gravel-walk; here comes The redbreast to the sill for crumbs. Fly off! fly off! I can not wait To welcome ye, as she of late. The earliest of my friends is gone. Alas! almost my only one! The few as dear, long wafted o'er, Await me on a sunnier shore." In 1856 at the age of 81 he published Antony and Octavius: Scenes for the Study, twelve consecutive poems in dialogue, and "Letter to Emerson", as well as continuing Imaginary Conversations. Final Tragedies and return to Italy In the beginning of 1857, Landor's mind was becoming weakened and he found himself in some unpleasant situations. He became involved in a court case because he had published statements when the case was sub judice and was insulted by counsel as a poor old man brought in to talk twaddle. He then became embroiled in a miserable quarrel between two ladies he knew. He gave one of them, Geraldine Hooper £100, a legacy received from his friend Kenyon. Unknown to Landor she transferred half of it to the other lady a Mrs Yescombe. They then quarreled and the Mrs Yescombe accused Hooper of having obtained the money from Landor for dishonourable reasons. Landor in his fury wrote a pamphlet "Walter Savage Landor and the Honourable Mrs Yescombe" which was considered libellous. Forster persuaded Landor to apologise. Then in 1858 he produced a miscellaneous collection called "Dry Sticks Fagoted by W. S. Landor", which contained among other things some epigrammatic and satirical attacks which led to further libel actions. In July that year Landor returned to Italy for the last six years of his life. He was advised to make over his property to his family, on whom he now depended. He hoped to resume his life with his wife and children but found them living disreputably at the Villa Gherardesca and ill-disposed to welcome him. He spent a miserable ten months at his villa, and fled repeatedly to Florence, only to be brought back again. On the last occasion, he took refuge at a hotel in Florence, with next to nothing in his pocket, and was found by Robert Browning then living at the Casa Guidi. Browning managed to obtain an allowance for him from the family and settled him first at Siena and then at Florence. Landor busied himself with new editions of his works and interested himself in the unification of Italy. He wrote frequently to Eliza Lynn Linton and added to Imaginary Conversations devising any sale proceeds to the relief of Garibaldi's soldiers. Anthony Trollope visited Florence and brought with him an American girl Kate Field who became Landor's protege. He was still charming, venerable, and courteous, and full of literary interests. He taught Kate Field Latin, repeated poetry and composed some last conversations. In 1861, Browning left Italy after the death of his wife. Landor afterwards seldom left the house and remained petulant and uncomfortable, occasionally visited by his sons. He was much concerned about the fate of his picture collection, little of which had any merit, and about preparations for his grave as he hoped to be buried at Widcombe near Bath. He published some Imaginary Conversations in the 'Atheneum' in 1861-2 and in 1863 published a last volume of "Heroic Idyls, with Additional Poems, English and Latin", described by Swinburne as " the last fruit of a genius which after a life of eighty-eight years had lost nothing of its majestic and pathetic power, its exquisite and exalted". Forster's refusal to publish more about the libel case had interrupted their friendship, but they renewed their correspondence before his death. Almost the last event of his life was a visit in 1864 from the poet Swinburne, who visited Florence specifically to see him, and dedicated to him the 'Atlanta in Calydon'.[2] In 1864 on May Day Landor said to his landlady "I shall never write again. Put out the lights and draw the curtains". A few months later he died quietly in Florence at the age of 89. He was buried not after all at Widcombe but in the English Cemetery, Florence, near the tomb of his friend, Elizabeth Barrett Browning. A statue of his wife can also be found in the 'English' Cemetery, above the tomb of their son, Arnold Savage Landor. Later, his Villa Gherardesca in Fiesole would become the home of the American Icelandic scholar Daniel Willard Fiske, who renamed it the 'Villa Landor'. Landor's grandson was the writer explorer and adventurer Arnold Henry Savage Landor. Landor was the close friend of Southey, and Coleridge. His relationship with Wordsworth changed over time from great praise to a certain resentment. Lord Byron tended to ridicule and revile him, and though Landor had little good to say in return during Byron's life he lamented and extolled him as a dead hero. He lavished sympathetic praise on the noble dramatic works of his brother Robert Eyres Landor. Review of Landor's work by Swinburne From nineteen almost to ninety his intellectual and literary activity was indefatigably incessant; but, herein at least like Charles Lamb, whose cordial admiration he so cordially returned, he could not write a note of three lines which did not bear the mark of his Roman hand in its matchless and inimitable command of a style at once the most powerful and the purest of his age. The one charge which can ever seriously be brought and maintained against it is that of such occasional obscurity or difficulty as may arise from excessive strictness in condensation of phrase and expurgation of matter not always superfluous, and sometimes almost indispensable. His English prose and his Latin verse are perhaps more frequently and more gravely liable to this charge than either his English verse or his Latin prose. At times it is well-nigh impossible for an eye less keen and swift, a scholarship less exquisite and ready than his own, to catch the precise direction and follow the perfect course of his rapid thought and radiant utterance. This apparently studious pursuit and preference of the most terse and elliptic expression which could be found for anything he might have to say could not but occasionally make even so sovereign a master of two great languages appear dark with excess of light; but from no former master of either tongue in prose or verse was ever the quality of real obscurity, of loose and nebulous incertitude, more utterly alien or more naturally remote. There is nothing of cloud or fog about the path on which he leads us; but we feel now and then the want of a bridge or a handrail; we have to leap from point to point of narrative or argument without the usual help of a connecting plank. Even in his dramatic works, where least of all it should have been found, this lack of visible connection or sequence in details of thought or action is too often a source of sensible perplexity. In his noble trilogy on the history of Giovanna queen of Naples it is sometimes actually difficult to realize on a first reading what has happened or is happening, or how, or why, or by what agency a defect alone sufficient, but unhappily sufficient in itself, to explain the too general ignorance of a work so rich in subtle and noble treatment of character, so sure and strong in its grasp and rendering of high actions and high passions, so rich in humour and in pathos, so royally serene in its commanding power upon the tragic mainsprings of terror and of pity. As a poet, he may be said on the whole to stand midway between Byron and Shelley—about as far above the former as below the latter. If we except Catullus and Simonides, it might be hard to match and it would be impossible to overmatch the flawless and blameless yet living and breathing beauty of his most perfect elegies, epigrams or epitaphs. As truly as prettily was he likened by Leigh Hunt to a stormy mountain pine which should produce lilies. He was a classic, and no formalist; the wide range of his admiration had room for a genius so far from classical as Blake's. Nor in his own highest mood or method of creative as of critical work was he a classic only, in any narrow or exclusive sense of the term. On either side, immediately or hardly below his mighty masterpiece of Pericles and Aspasia, stand the two scarcely less beautiful and vivid studies of medieval Italy and Shakespeare in England. References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walter_Savage_Landor


Matthew Prior (21 July 1664– 18 September 1721) was an English poet and diplomat. He is also known as a contributor to The Examiner. Early life Prior was probably born in Middlesex. He was the son of a Nonconformist joiner at Wimborne Minster, East Dorset. His father moved to London, and sent him to Westminster School, under Dr. Busby. On his father’s death, he left school, and was cared for by his uncle, a vintner in Channel Row. Here Lord Dorset found him reading Horace, and set him to translate an ode. He did so well that the Earl offered to contribute to the continuation of his education at Westminster. One of his schoolfellows and friends was Charles Montagu, 1st Earl of Halifax. It was to avoid being separated from Montagu and his brother James that Prior accepted, against his patron’s wish, a scholarship recently founded at St John’s College, Cambridge. He took his B.A. degree in 1686, and two years later became a fellow. In collaboration with Montagu he wrote in 1687 the City Mouse and Country Mouse, in ridicule of John Dryden’s The Hind and the Panther. Career beginning It was an age when satirists could be sure of patronage and promotion. Montagu was promoted at once, and Prior, three years later, became secretary to the embassy at the Hague. After four years of this, he was appointed a gentleman of the King’s bedchamber. Apparently he acted as one of the King’s secretaries, and in 1697 he was secretary to the plenipotentiaries who concluded the Peace of Ryswick. Prior’s talent for affairs was doubted by Pope, who had no special means of judging, but it is not likely that King William would have employed in this important business a man who had not given proof of diplomatic skill and grasp of details. The poet’s knowledge of French is specially mentioned among his qualifications, and this was recognized by his being sent in the following year to Paris in attendance on the English ambassador. At this period Prior could say with good reason that “he had commonly business enough upon his hands, and was only a poet by accident.” To verse, however, which had laid the foundation of his fortunes, he still occasionally trusted as a means of maintaining his position. His occasional poems during this period include an elegy on Queen Mary in 1695; a satirical version of Boileau’s Ode sur le prise de Namur (1695); some lines on William’s escape from assassination in 1696; and a brief piece called The Secretary. After his return from France Prior became under-secretary of state and succeeded John Locke as a commissioner of trade. In 1701 he sat in Parliament for East Grinstead. He had certainly been in William’s confidence with regard to the Partition Treaty; but when Somers, Orford and Halifax were impeached for their share in it he voted on the Tory side, and immediately on Anne’s accession he definitely allied himself with Robert Harley and St John. Perhaps in consequence of this for nine years there is no mention of his name in connection with any public transaction. But when the Tories came into power in 1710 Prior’s diplomatic abilities were again called into action, and until the death of Anne he held a prominent place in all negotiations with the French court, sometimes as secret agent, sometimes in an equivocal position as ambassador’s companion, sometimes as fully accredited but very unpunctually paid ambassador. His share in negotiating the Treaty of Utrecht, of which he is said to have disapproved personally, led to its popular nickname of “Matt’s Peace.” Prior is also known as a contributor to The Examiner newspaper. Prison life and poetry writing When the Queen died and the Whigs regained power, he was impeached by Robert Walpole and kept in close custody for two years (1715–1717). In 1709, he had already published a collection of verse. During this imprisonment, maintaining his cheerful philosophy, he wrote his longest humorous poem, Alma; or, The Progress of the Mind. This, along with his most ambitious work, Solomon, and other Poems on several Occasions, was published by subscription in 1718. The sum received for this volume (4000 guineas), with a present of £4000 from Lord Harley, enabled him to live in comfort; but he did not long survive his enforced retirement from public life, although he bore his ups and downs with rare equanimity. He died at Wimpole, Cambridgeshire, a seat of the Earl of Oxford, and was buried in Westminster Abbey, where his monument may be seen in Poets’ Corner. A History of his Own Time was issued by J Bancks in 1740. The book pretended to be derived from Prior’s papers, but it is doubtful how far it should be regarded as authentic. Prior’s poems show considerable variety, a pleasant scholarship and great executive skill. The most ambitious, i.e. Solomon, and the paraphrase of The Nut-Brown Maid, are the least successful. But Alma, an admitted imitation of Samuel Butler, is a delightful piece of wayward easy humour, full of witty turns and well-remembered allusions, and Prior’s mastery of the octo-syllabic couplet is greater than that of Jonathan Swift or Pope. His tales in rhyme, though often objectionable in their themes, are excellent specimens of narrative skill; and as an epigrammatist he is unrivalled in English. The majority of his love songs are frigid and academic, mere wax-flowers of Parnassus; but in familiar or playful efforts, of which the type are the admirable lines To a Child of Quality, he has still no rival. “Prior’s”—says Thackeray, himself no mean proficient in this kind—"seem to me amongst the easiest, the richest, the most charmingly humorous of English lyrical poems. Horace is always in his mind, and his song and his philosophy, his good sense, his happy easy turns and melody, his loves and his Epicureanism, bear a great resemblance to that most delightful and accomplished master.” Wittenham Clumps in Oxfordshire is said to be where Prior wrote Henry and Emma, and this is now commemorated by a plaque. Prior has been commemorated by other poets as well; Everett James Ellis named Prior as a significant influence and source of inspiration. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matthew_Prior


William Cullen Bryant (November 3, 1794– June 12, 1878) was an American romantic poet, journalist, and long-time editor of the New York Evening Post. Youth and education Bryant was born on November 3, 1794, in a log cabin near Cummington, Massachusetts; the home of his birth is today marked with a plaque. He was the second son of Peter Bryant (b. Aug. 12, 1767, d. Mar. 20, 1820), a doctor and later a state legislator, and Sarah Snell (b. Dec. 4, 1768, d. May 6, 1847). The genealogies of both of his parents trace back to passengers on the Mayflower; his mother’s to John Alden (b. 1599, d. 1687); his father’s to Francis Cooke (b. 1577, d. 1663). He was also a nephew of Charity Bryant, a Vermont seamstress who is the subject of Rachel Hope Cleves’ 2014 book Charity and Sylvia: A Same-Sex Marriage in Early America. Bryant and his family moved to a new home when he was two years old. The William Cullen Bryant Homestead, his boyhood home, is now a museum. After just one year at Williams College (he entered with sophomore standing), he hoped to transfer to Yale, but a talk with his father led to the realization that family finances would not support it. His father counseled a legal career as his best available choice, and the disappointed poet began to study law in Worthington and Bridgewater in Massachusetts. He was admitted to the bar in 1815 and began practicing law in nearby Plainfield, walking the seven miles from Cummington every day. On one of these walks, in December 1815, he noticed a single bird flying on the horizon; the sight moved him enough to write “To a Waterfowl”. Bryant developed an interest in poetry early in life. Under his father’s tutelage, he emulated Alexander Pope and other Neo-Classic British poets. “The Embargo”, a savage attack on President Thomas Jefferson published in 1808, reflected Dr. Bryant’s Federalist political views. The first edition quickly sold out—partly because of publicity attached to the poet’s young age. A second, expanded edition included Bryant’s translation of classical verse. During his collegiate studies and his reading for the law, he wrote little poetry, but encounters with the Graveyard Poets and then Wordsworth regenerated his passion for “the witchery of song.” Poetry “Thanatopsis” is Bryant’s most famous poem, which Bryant may have been working on as early as 1811. In 1817 his father took some pages of verse from his son’s desk, and at the invitation of Willard Phillips, an editor of the North American Review who had previously been tutored in the classics by Dr. Bryant, he submitted them along with his own work. The editor of the Review, Edward Tyrrel Channing, read the poem to his assistant, Richard Henry Dana, who immediately exclaimed, “That was never written on this side of the water!” Someone at the North American joined two of the son’s discrete fragments, gave the result the Greek-derived title Thanatopsis ("meditation on death"), mistakenly attributed it to the father, and published it. After clarification of the authorship, the son’s poems began appearing with some regularity in the "[Review]". “To a Waterfowl”, published in 1821 was the most popular. On January 11, 1821, Bryant, still striving to build a legal career, married Frances Fairchild. Soon after, having received an invitation to address the Harvard University Phi Beta Kappa Society at the school’s August commencement, Bryant spent months working on “The Ages”, a panorama in verse of the history of civilization, culminating in the establishment of the United States. As it would in all collections he subsequently issued, “The Ages” led the volume, also entitled Poems, which he arranged to publish on the same trip to Cambridge. For that book, he added sets of lines at the beginning and end of “Thanatopsis” that changed the poem. His career as a poet was now established, though recognition as America’s leading poet waited until 1832, when an expanded Poems was published in the U.S. and, with the assistance of Washington Irving, in Britain. His poetry has been described as being “of a thoughtful, meditative character, and makes but slight appeal to the mass of readers.” Editorial career From 1816 to 1825, Bryant depended on his law practice in Great Barrington, Massachusetts to sustain his family financially, but the strain of dealing with unsophisticated neighbors and juridical pettifoggery pushed him to trade his unrewarding profession for New York City and the promise of a literary career. With the encouragement of a distinguished and well-connected literary family, the Sedgwicks, he quickly gained a foothold in New York City’s vibrant cultural life. His first employment, in 1825, was as editor of the New-York Review, which within the next year merged with the United States Review and Literary Gazette. But in the throes of the failing struggle to raise subscriptions, he accepted part-time duties with the New-York Evening Post under William Coleman; then, partly because of Coleman’s ill health, traceable to the consequences of a duel and then a stroke, Bryant’s responsibilities expanded rapidly. From Assistant Editor he rose to Editor-in-Chief and co-owner of the newspaper that had been founded by Alexander Hamilton. Over the next half century, the “Post” would become the most respected paper in the city and, from the election of Andrew Jackson, the major platform in the Northeast for the Democratic Party and subsequently of the Free Soil and Republican Parties. In the process, the Evening-Post also became the pillar of a substantial fortune. From his Federalist beginnings, Bryant had shifted to being one of the most liberal voices of the century. An early supporter of organized labor, with his 1836 editorials the right of workmen to strike, Bryant also defended of religious minorities and immigrants, and promoted the abolition of slavery. He “threw himself into the foreground of the battle for human rights” and did not cease speaking out against the corrupting influence of certain bankers in spite of their efforts to break down the paper. According to newspaper historian Frank Luther Mott, Bryant was “a great liberal seldom done justice by modern writers”. Ironically, the boy who first tasted fame for his diatribe against Thomas Jefferson and his party became one of the key supporters in the Northeast of that same party under Jackson. Bryant’s views, always progressive though not quite populist, in course led him to join the Free Soilers, and when the Free Soil Party became a core of the new Republican Party in 1856, Bryant vigorously campaigned for John Frémont. That exertion enhanced his standing in party councils, and in 1860, he was one of the prime Eastern exponents of Abraham Lincoln, whom he introduced at Cooper Union. (That “Cooper Union speech” lifted Lincoln to the nomination, and then the presidency.) Although literary historians have neglected his fiction, Bryant’s stories over the seven-year period from his time with the Review to the publication of Tales of Glauber Spa in 1832 show a variety of strategies, making him the most inventive of practitioners of the genre during this early stage of its evolution. Bryant edited the very successful Picturesque America which was published between 1872 and 1874. This two-volume set was lavishly illustrated and described scenic places in the United States and Canada. Later years In his last decade, Bryant shifted from writing his own poetry to a blank verse translation of Homer’s works. He assiduously worked on the Iliad and The Odyssey from 1871 to 1874. He is also remembered as one of the principal authorities on homeopathy and as a hymnist for the Unitarian Church—both legacies of his father’s enormous influence on him. Bryant died in 1878 of complications from an accidental fall suffered after participating in a Central Park ceremony honoring Italian patriot Giuseppe Mazzini. He is buried at Roslyn Cemetery in Roslyn, Long Island, New York. Critical response Poet and literary critic Thomas Holley Chivers said that the "only thing [Bryant] ever wrote that may be called Poetry is 'Thanatopsis’, which he stole line for line from the Spanish. The fact is, that he never did anything but steal—as nothing he ever wrote is original." Contemporary critic Edgar Allan Poe, on the other hand, praised Bryant and specifically the poem “June” in his essay “The Poetic Principle”: The rhythmical flow, here, is even voluptuous—nothing could be more melodious. The poem has always affected me in a remarkable manner. The intense melancholy which seems to well up, perforce, to the surface of all the poet’s cheerful sayings about his grave, we find thrilling us to the soul—while there is the truest poetic elevation in the thrill. The impression left is one of a pleasurable sadness. Editor and children’s writer Mary Mapes Dodge wrote that Bryant’s poems “have wrought vast and far-reaching good in the world.” She predicted, “You will admire more and more, as you grow older, the noble poems of this great and good man.” Bryant’s poetry is tender and graceful, pervaded by a contemplative melancholy, and a love of solitude and the silence of the woods. Though he was brought up to admire Pope, and in his early youth imitated him, he was one of the first American poets to throw off his influence. He had a high sense of duty, was a prominent and patriotic citizen, and enjoyed the esteem and even the reverence of his fellow-countrymen. Legacy In 1884, New York City’s Reservoir Square, at the intersection of 42nd Street and Sixth Avenue, was renamed Bryant Park in his honor. The city later named a public high school in Long Island City, Queens in his honor. A park in East York, a suburb of Toronto, Canada, bears the name of Cullen Bryant Park as well. Although he is now thought of as a New Englander, Bryant, for most of his lifetime, was thoroughly a New Yorker—and a very dedicated one at that. He was a major force behind the idea that became Central Park, as well as a leading proponent of creating the Metropolitan Museum of Art. He was one of a group of founders of New York Medical College. He had close affinities with the Hudson River School of art and was an intimate friend of Thomas Cole. He defended immigrants and, at some financial risk to himself, championed the rights of workers to form labor unions. As a writer, Bryant was an early advocate of American literary nationalism, and his own poetry focusing on nature as a metaphor for truth established a central pattern in the American literary tradition. Some however, argue that a reassessment is long overdue. It finds great merit in a couple of short stories Bryant wrote while trying to build interest in periodicals he edited. More importantly, it perceives a poet of great technical sophistication who was a progenitor of Walt Whitman, to whom he was a mentor. Martin Luther King, Jr quoted Bryant in his speech “Give Us the Ballot”, when he said, “there is something in this universe which justifies William Cullen Bryant in saying: ‘Truth crushed to earth will rise again.’” The Seattle neighborhood Bryant is named after him. Bryant House at Williams College is named for him. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Cullen_Bryant


Charles Lamb (London, 10 February 1775 – Edmonton, 27 December 1834) was an English essayist, best known for his Essays of Elia and for the children's book Tales from Shakespeare, which he produced with his sister, Mary Lamb (1764–1847). Lamb has been referred to by E.V. Lucas, his principal biographer, as "the most lovable figure in English literature”. Youth and schooling Lamb was the son of Elizabeth Field and John Lamb. Lamb was the youngest child, with an 11 year older sister Mary, an even older brother John, and 4 other siblings who did not survive their infancy. John Lamb (father), who was a lawyer's clerk, spent most of his professional life as the assistant and servant to a barrister by the name of Samuel Salt who lived in the Inner Temple in London. It was there in the Inner Temple in Crown Office Row, that Charles Lamb was born and spent his youth. Lamb created a portrait of his father in his "Elia on the Old Benchers" under the name Lovel. Lamb's older brother was too much his senior to be a youthful companion to the boy but his sister Mary, being born eleven years before him, was probably his closest playmate. Lamb was also cared for by his paternal aunt Hetty, who seems to have had a particular fondness for him. A number of writings by both Charles and Mary suggest that the conflict between Aunt Hetty and her sister-in-law created a certain degree of tension in the Lamb household. However, Charles speaks fondly of her and her presence in the house seems to have brought a great deal of comfort to him. Some of Lamb's fondest childhood memories were of time spent with Mrs. Field, his maternal grandmother, who was for many years a servant to the Plummer family, who owned a large country house called Blakesware, near Widford, Hertfordshire. After the death of Mrs. Plummer, Lamb's grandmother was in sole charge of the large home and, as Mr. Plummer was often absent, Charles had free rein of the place during his visits. A picture of these visits can be glimpsed in the Elia essay Blakesmoor in H—shire. "Why, every plank and panel of that house for me had magic in it. The tapestried [sic] bed-rooms – tapestry so much better than painting – not adorning merely, but peopling the wainscots – at which childhood ever and anon would steal a look, shifting its coverlid (replaced as quickly) to exercise its tender courage in a momentary eye-encounter with those stern bright visages, staring reciprocally – all Ovid on the walls, in colours vivider than his descriptions.” Little is known about Charles's life before the age of seven. We know that Mary taught him to read at a very early age and he read voraciously. It is believed that he suffered from smallpox during his early years which forced him into a long period of convalescence. After this period of recovery Lamb began to take lessons from Mrs. Reynolds, a woman who lived in the Temple and is believed to have been the former wife of a lawyer. Mrs. Reynolds must have been a sympathetic schoolmistress because Lamb maintained a relationship with her throughout his life and she is known to have attended dinner parties held by Mary and Charles in the 1820s. E.V. Lucas suggests that sometime in 1781 Charles left Mrs. Reynolds and began to study at the Academy of William Bird. His time with William Bird did not last long, however, because by October 1782 Lamb was enrolled in Christ's Hospital, a charity boarding school chartered by King Edward VI in 1552. Christ's Hospital was a traditional English boarding school; bleak and full of violence. The headmaster, Mr. Boyer, has become famous for his teaching in Latin and Greek, but also for his brutality. A thorough record of Christ's Hospital in Several essays by Lamb as well as the Autobiography of Leigh Hunt and the Biographia Literaria of Samuel Taylor Coleridge, with whom Charles developed a friendship that would last for their entire lives. Despite the brutality Lamb got along well at Christ's Hospital, due in part, perhaps, to the fact that his home was not far distant thus enabling him, unlike many other boys, to return often to the safety of home. Years later, in his essay "Christ’s Hospital Five and Thirty Years Ago," Lamb described these events, speaking of himself in the third person as "L.” “I remember L. at school; and can well recollect that he had some peculiar advantages, which I and other of his schoolfellows had not. His friends lived in town, and were near at hand; and he had the privilege of going to see them, almost as often as he wished, through some invidious distinction, which was denied to us.” Christ's Hospital was a typical English boarding school and many students later wrote of the terrible violence they suffered there. The upper master of the school from 1778 to 1799 was Reverend James Boyer, a man renowned for his unpredictable and capricious temper. In one famous story Boyer was said to have knocked one of Leigh Hunt's teeth out by throwing a copy of Homer at him from across the room. Lamb seemed to have escaped much of this brutality, in part because of his amiable personality and in part because Samuel Salt, his father's employer and Lamb's sponsor at the school was one of the institute's Governors. Charles Lamb suffered from a stutter and this "an inconquerable impediment" in his speech deprived him of Grecian status at Christ's Hospital and thus disqualifying him for a clerical career. While Coleridge and other scholarly boys were able to go on to Cambridge, Lamb left school at fourteen and was forced to find a more prosaic career. For a short time he worked in the office of Joseph Paice, a London merchant and then, for 23 weeks, until 8 February 1792, held a small post in the Examiner's Office of the South Sea House. Its subsequent downfall in a pyramid scheme after Lamb left would be contrasted to the company's prosperity in the first Elia essay. On 5 April 1792 he went to work in the Accountant's Office for British East India Company, the death of his father's employer having ruined the family's fortunes.Charles would continue to work there for 25 years, until his retirement with pension. In 1792 while tending to his grandmother, Mary Field, in Hertfordshire, Charles Lamb fell in love with a young woman named Ann Simmons. Although no epistolary record exists of the relationship between the two, Lamb seems to have spent years wooing Miss Simmons. The record of the love exists in several accounts of Lamb's writing. Rosamund Gray is a story of a young man named Allen Clare who loves Rosamund Gray but their relationship comes to nothing because of the sudden death of Miss Gray. Miss Simmons also appears in several Elia essays under the name "Alice M." The essays "Dream Children," "New Year's Eve," and several others, speak of the many years that Lamb spent pursuing his love that ultimately failed. Miss Simmons eventually went on to marry a silversmith by the name of Bartram and Lamb called the failure of the affair his 'great disappointment. Family tragedy Charles and his sister Mary both suffered periods of mental illness. Charles spent six weeks in a psychiatric hospital during 1795. He was, however, already making his name as a poet. On 22 September 1796, a terrible event occurred: Mary, "worn down to a state of extreme nervous misery by attention to needlework by day and to her mother at night," was seized with acute mania and stabbed her mother to the heart with a table knife. Although there was no legal status of 'insanity' at the time, a jury returned a verdict of 'Lunacy' and therefore freed her from guilt of willful murder. With the help of friends Lamb succeeded in obtaining his sister's release from what would otherwise have been lifelong imprisonment, on the condition that he take personal responsibility for her safekeeping. Lamb used a large part of his relatively meagre income to keep his beloved sister in a private 'madhouse' in Islington called Fisher House. The 1799 death of John Lamb was something of a relief to Charles because his father had been mentally incapacitated for a number of years since suffering a stroke. The death of his father also meant that Mary could come to live again with him in Pentonville, and in 1800 they set up a shared home at Mitre Court Buildings in the Temple, where they lived until 1809. Despite Lamb's bouts of melancholia and alcoholism, both he and his sister enjoyed an active and rich social life. Their London quarters became a kind of weekly salon for many of the most outstanding theatrical and literary figures of the day. Charles Lamb, having been to school with Samuel Coleridge, counted Coleridge as perhaps his closest, and certainly his oldest, friend. On his deathbed, Coleridge had a mourning ring sent to Lamb and his sister. Fortuitously, Lamb's first publication was in 1796, when four sonnets by "Mr. Charles Lamb of the India House" appeared in Coleridge's Poems on Various Subjects. In 1797 he contributed additional blank verse to the second edition, and met the Wordsworths, William and Dorothy, on his short summer holiday with Coleridge at Nether Stowey, thereby also striking up a lifelong friendship with William. In London, Lamb became familiar with a group of young writers who favoured political reform, including Percy Bysshe Shelley, William Hazlitt, and Leigh Hunt. Lamb continued to clerk for the East India Company and doubled as a writer in various genres, his tragedy, John Woodvil, being published in 1802. His farce, Mr H, was performed at Drury Lane in 1807, where it was roundly booed. In the same year, Tales from Shakespeare (Charles handled the tragedies; his sister Mary, the comedies) was published, and became a best seller for William Godwin's "Children's Library." In 1819, at age 44, Lamb, who, because of family commitments, had never married, fell in love with an actress, Fanny Kelly, of Covent Garden, and proposed marriage. She refused him, and he died a bachelor. His collected essays, under the title Essays of Elia, were published in 1823 ("Elia" being the pen name Lamb used as a contributor to the London Magazine). A further collection was published ten years or so later, shortly before Lamb's death. He died of a streptococcal infection, erysipelas, contracted from a minor graze on his face sustained after slipping in the street, on 27 December 1834, just a few months after Coleridge. He was 59. From 1833 till their deaths Charles and Mary lived at Bay Cottage, Church Street, Edmonton north of London (now part of the London Borough of Enfield. Lamb is buried in All Saints' Churchyard, Edmonton. His sister, who was ten years his senior, survived him for more than a dozen years. She is buried beside him. Work Lamb's first publication was the inclusion of four sonnets in the Coleridge's Poems on Various Subjects published in 1796 by Joseph Cottle. The sonnets were significantly influenced by the poems of Burns and the sonnets of William Bowles, a largely forgotten poet of the late 18th century. His poems garnered little attention and are seldom read today. Lamb's contributions to the second edition of the Poems showed significant growth as a poet. These poems included The Tomb of Douglas and A Vision of Repentance. Because of a temporary fall-out with Coleridge, Lamb's poems were to be excluded in the third edition of the Poems. As it turned out, a third edition never emerged and instead Coleridge's next publication was the monumentally influential Lyrical Ballads co-published with Wordsworth. Lamb, on the other hand, published a book entitled Blank Verse with Charles Lloyd, the mentally unstable son of the founder of Lloyd's Bank. Lamb's most famous poem was written at this time entitled The Old Familiar Faces. Like most of Lamb's poems it is particularly sentimental but it is still remembered and widely read, often included in Poetic Collections. Of particular interest to Lambarians is the opening verse of the original version of The Old Familiar Faces which is concerned with Lamb's mother. It was a verse that Lamb chose to remove from the edition of his Collected Work published in 1818. I had a mother, but she died, and left me, Died prematurely in a day of horrors - All, all are gone, the old familiar faces. From a fairly young age Lamb desired to be a poet but never gained the success that he had hoped. Lamb lived under the poetic shadow of his friend Coleridge. In the final years of the 18th century Lamb began to work on prose with the novella entitled Rosamund Gray, a story of a young girl who was thought to be inspired by Ann Simmonds, with whom Charles Lamb was thought to be in love. Although the story is not particularly successful as a narrative because of Lamb's poor sense of plot, it was well thought of by Lamb's contemporaries and led Shelley to observe “what a lovely thing is Rosamund Gray! How much knowledge of the sweetest part of our nature in it!" (Quoted in Barnett, page 50) n the first years of the 19th century Lamb began his fruitful literary cooperation with his sister Mary. Together they wrote at least three books for William Godwin’s Juvenile Library. The most successful of these was of course Tales From Shakespeare which ran through two editions for Godwin and has now been published dozens of times in countless editions, many of them illustrated. Lamb also contributed a footnote to Shakespearean studies at this time with his essay "On the Tragedies of Shakespeare," in which he argues that Shakespeare should be read rather than performed in order to gain the proper effect of his dramatic genius. Beside contributing to Shakespeare studies with his book Tales From Shakespeare, Lamb also contributed to the popularization of Shakespeare's contemporaries with his book Specimens of the English Dramatic Poets Who Lived About the Time of Shakespeare. Although he did not write his first Elia essay until 1820, Lamb’s gradual perfection of the essay form for which he eventually became famous began as early 1802 in a series of open letters to Leigh Hunt’s Reflector. The most famous of these is called "The Londoner" in which Lamb famously derides the contemporary fascination with nature and the countryside. Legacy Anne Fadiman notes regretfully that Lamb is not widely read in modern times: "I do not understand why so few other readers are clamoring for his company... [he] is kept alive largely through the tenuous resuscitations of university English departments." Lamb was honoured by The Latymer School, a grammar school in Edmonton, a suburb of London where he lived for a time; it has six houses, one of which, "Lamb", is named after Charles. Selected works * Blank Verse, poetry, 1798 * A Tale of Rosamund Gray, and old blind Margaret, 1798 * John Woodvil, poetic drama, 1802 * Tales from Shakespeare, 1807 * The Adventures of Ulysses, 1808 * Specimens of English Dramatic poets who lived about the time of Shakespeare, 1808 * On the Tragedies of Shakespeare, 1811 * Witches and Other Night Fears, 1821 * The Pawnbroker's Daughter, 1825 * Eliana, 1867 * Essays of Elia, 1823 * The Last Essays of Elia, 1833 References Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Lamb


Edgar Lee Masters (August 23, 1868– March 5, 1950) was an American attorney, poet, biographer, and dramatist. He is the author of Spoon River Anthology, The New Star Chamber and Other Essays, Songs and Satires, The Great Valley, The Serpent in the Wilderness An Obscure Tale, The Spleen, Mark Twain: A Portrait, Lincoln: The Man, and Illinois Poems. In all, Masters published twelve plays, twenty-one books of poetry, six novels and six biographies, including those of Abraham Lincoln, Mark Twain, Vachel Lindsay, and Walt Whitman. Life and career Born in Garnett, Kansas to attorney Hardin Wallace Masters and Emma J. Dexter, his father had briefly moved to set up a law practice, then soon moved back to his paternal grandparents’ farm near Petersburg in Menard County, Illinois. In 1880 they moved to Lewistown, Illinois, where he attended high school and had his first publication in the Chicago Daily News. The culture around Lewistown, in addition to the town’s cemetery at Oak Hill, and the nearby Spoon River were the inspirations for many of his works, most notably Spoon River Anthology, his most famous and acclaimed work. He attended Knox Academy in 1889–90, a now defunct preparatory program run by Knox College, but was forced to leave due to his family’s inability to finance his education. After working in his father’s law office, he was admitted to the Illinois bar and moved to Chicago, where he established a law partnership in 1893 with the law firm of Kickham Scanlan. He married twice. In 1898 he married Helen M. Jenkins, the daughter of Robert Edwin Jenkins, a lawyer in Chicago, and had three children. During his law partnership with Clarence Darrow from 1903 to 1908, Masters defended the poor. In 1911 he started his own law firm, despite three years of unrest (1908–11) caused by extramarital affairs and an argument with Darrow. Two of his children followed him with literary careers. His daughter Marcia pursued poetry, while his son Hilary Masters became a novelist. Hilary and his half-brother Hardin wrote a memoir of their father. Masters died at a nursing home on March 5, 1950, in Melrose Park, Pennsylvania, age 81. He is buried in Oakland cemetery in Petersburg, Illinois. His epitaph includes his poem, “To-morrow is My Birthday” from Toward the Gulf (1918): Good friends, let’s to the fields…After a little walk and by your pardon, I think I’ll sleep, there is no sweeter thing.Nor fate more blessed than to sleep. I am a dream out of a blessed sleep-Let’s walk, and hear the lark. Family history Edgar’s father was Hardin Wallace Masters, whose father was Squire Davis Masters, whose father was Thomas Masters, whose father was Hillery Masters, the son of Robert Masters (born c. 1715, Prince George’s County, Maryland, the son of William W. Masters and wife Mary Veatch Masters). Edgar Lee Masters wrote in his autobiography, Across Spoon River (1936), that his ancestor Hillery Masters was the son of “Knotteley” Masters, but family genealogies show that Hillery and Notley Masters were, in fact, brothers. Poetry Masters first published his early poems and essays under the pseudonym Dexter Wallace (after his mother’s maiden name and his father’s middle name) until the year 1903, when he joined the law firm of Clarence Darrow. Masters began developing as a notable American poet in 1914, when he began a series of poems (this time under the pseudonym Webster Ford) about his childhood experiences in Western Illinois, which appeared in Reedy’s Mirror, a St. Louis publication. In 1915 the series was bound into a volume and re-titled Spoon River Anthology. Years later, he wrote a memorable and invaluable account of the book’s background and genesis, his working methods and influences, as well as its reception by the critics, favorable and hostile, in an autobiographical article notable for its human warmth and general interest. Although he never matched the success of his Spoon River Anthology, he did publish several other volumes of poems including Book of Verses in 1898, Songs and Sonnets in 1910, The Great Valley in 1916, Song and Satires in 1916, The Open Sea in 1921, The New Spoon River in 1924, Lee in 1926, Jack Kelso in 1928, Lichee Nuts in 1930, Gettysburg, Manila, Acoma in 1930, Godbey, sequel to Jack Kelso in 1931, The Serpent in the Wilderness in 1933, Richmond in 1934, Invisible Landscapes in 1935, The Golden Fleece of California in 1936, Poems of People in 1936, The New World in 1937, More People in 1939, Illinois Poems in 1941, and Along the Illinois in 1942. Lincoln: the Man In 1931 Masters published the biography Lincoln: the Man, which demythologizes Abraham Lincoln, portraying him as a tool of bankers wanting a new Bank of the United States, “that political system which doles favors to the strong in order to win and keep their adherence to the government”, and advocates “a people taxed to make profits for enterprises that cannot stand alone”. He claimed the Whig Party led by Lincoln’s mentor Henry Clay “had no platform to announce because its principles were plunder and nothing else.” Quotations from the book: “The political history of America has been written for the most part by those who were unfriendly to the theory of a confederated republic, or who did not understand it. It has been written by devotees of the protective principle [tariff], by centralists, and to a large degree by New England.” “For in six weeks he was to inaugurate a war without the American people having anything to say about it. He was to call for and send troops into the South, and thus stir that psychology of hate and fear from which a people cannot extricate themselves, though knowing and saying that the war was started by usurpation. Did he mean that he would bow to the American people when the law was laid down by their courts, through which alone the law be interpreted as the Constitutional voice of the people? No, he did not mean that; because when Taney decided that Lincoln had no power to suspend the writ of habeas corpus, Lincoln flouted and trampled the decision of the court.” “The War between the States demonstrated that salvation is not of the Jews, but of the Greeks. The World War added to this proof; for Wilson did many things that Lincoln did, and with Lincoln as authority for doing them. Perhaps it will happen again that a few men, deciding what is a cause of war, and what is necessary to its successful prosecution, may, as Lincoln and Wilson did, seal the lips of discussion and shackle the press; but no less the ideal of a just state, which has founded itself in reason and in free speech, will remain.” Notable works Poetry * A Book of Verses (1898) * Songs and Sonnets (1910) * Spoon River Anthology (1915) * Songs and Satires (1916) * Fiddler Jones (1916) * The Great Valley (New York: Macmillan Co., 1916) * Toward the Gulf (New York: Macmillan Co., 1918) * Starved Rock (New York: Macmillan Co., 1919) * Jack Kelso: A Dramatic Poem (1920) * Domesday Book (New York: Macmillan Co., 1920) * The Open Sea (New York: Macmillan Co., 1921) * The New Spoon River (New York: Macmillan Co., 1924) * Selected Poems (1925) * Lichee-Nut Poems (American Mercury, Jan. 1925) * Lee: A Dramatic Poem (1926) * Godbey: A Dramatic Poem (1931), sequel to Jack Kelso (1920) * The Serpent in the Wilderness (1933) * Richmond: A Dramatic Poem (1934) * Invisible Landscapes (1935) * Poems of People (1936) * The Golden Fleece of California (1936) (poetic narrative) * The New World (1937) * More People (1939) * Illinois Poems (1941) * Along the Illinois (1942) * Silence (1946) * George Gray * Many Soldiers * The Unknown Biographies * Children of the Market Place: A Fictitious Autobiography (New York: Macmillan Co., 1922). Life of Stephen Douglas. * Levy Mayer and the New Industrial Era (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1927). Chicago attorney Levy Mayer (1858-1922). * Lincoln: The Man (1931) * Vachel Lindsay: A Poet in America (1935) * Across Spoon River: An Autobiography (memoir) (1936) * Whitman (1937) * Mark Twain: A Portrait (1938) Books * The New Star Chamber and Other Essays (1904) * The Blood of the Prophets (1905) (play) * Althea (1907) (play) * The Trifler (1908) (play) * Mitch Miller (novel) (1920) * Skeeters Kirby (novel) (1923) * The Nuptial Flight (novel) (1923) * Kit O’Brien (novel) (1927) * The Fate of the Jury: An Epilogue to Domesday Book (1929) * Gettysburg, Manila, Acoma: Three Plays (1930) * The Tale of Chicago (1933) * The Tide of Time (novel) (1937) * The Sangamon (Chicago: University of Illinois Press, 1942, 1988) Awards & honors Masters was awarded the Mark Twain Silver Medal in 1936, the Poetry Society of America medal in 1941, the Academy of American Poets Fellowship in 1942, and the Shelly Memorial Award in 1944. In 2014, he was inducted into the Chicago Literary Hall of Fame. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edgar_Lee_Masters

Henry Jackson van Dyke (November 10, 1852 – April 10, 1933, aged 80) was an American author, educator, and clergyman. Henry van Dyke was born on November 10 , 1852 in Germantown, Pennsylvania in the United States. He graduated from Princeton University in 1873 and from Princeton Theological Seminary, 1877 and served as a professor of English literature at Princeton between 1899 and 1923. In 1908-09 Dr. van Dyke was an American lecturer at the University of Paris. By appointment of President Wilson he became Minister to the Netherlands and Luxembourg in 1913. He was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters and received many other honors. Van Dyke was an "ardent foe of the annexation of the Philippines, [and] told his congregation in 1898, 'If we enter the course of foreign conquest, the day is not far distant when we must spend in annual preparation for wars more than the $180,000,000 that we now spend every year in the education of our children for peace.’” He chaired the committee that wrote the first Presbyterian printed liturgy, The Book of Common Worship of 1906. Among his popular writings are the two Christmas stories, The Other Wise Man (1896) and The First Christmas Tree (1897). Various religious themes of his work are also expressed in his poetry, hymns and the essays collected in Little Rivers (1895) and Fisherman’s Luck (1899). He wrote the lyrics to the popular hymn, "Joyful, Joyful We Adore Thee" (1907), sung to the tune of Beethoven's "Ode to Joy". He compiled several short stories in The Blue Flower (1902), named after the key symbol of Romanticism introduced first by Novalis. He also contributed a chapter to the collaborative novel, The Whole Family (1908). Among his poems is "Katrina's Sundial", the inspiration for the song, "Time Is", by the group It's a Beautiful Day on their eponymous 1969 debut album. Furthermore, the lyrics of a song — entitled "Time", sung by Mark Masri — are mostly inspired by the following quote, written by Henry van Dyke: "Time is too slow for those who wait, too swift for those who fear, too long for those who grieve, too short for those who rejoice, but for those who love — time is eternity". A biography of Van Dyke, titled Henry Van Dyke: A Biography, was written by his son Tertius van Dyke and published in 1935. List of Works: Short Stories * Among The Quantock Hills from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Antwerp Road * Art Of Leaving Off, The from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Ashes of Vengeance (half-told tale) * Beggars Under The Bush * Between The Lupin And The Laurel from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Blue Flower, The * Books That I Loved As A Boy from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Boy of Nazareth Dreams, The * Brave Heart, A from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Broken Soldier and the Maid of France, The * Change Of Air, A * City of Refuge, A * Classic Instance, A * Countersign Of The Cradle, The * Days Off from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Diana And The Lions A half-told tale * Dream-story: The Christmas Angel, A * Effectual Fervent Prayer, The * First Christmas-Tree, The * Friend of Justice, A from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Gentle Life, The from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Handful Of Clay, A * Hearing Ear, The * Hero and Tin Soldiers, The * His Other Engagement from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Holiday In A Vacation, A from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Humoreske * In The Odour Of Sanctity * Justice of the Elements half-told tale * Keeper of the Light, The from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Key Of The Tower, The * King's High Way, The * King's Jewel, The * Leviathan from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Little Red Tom from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Lost Word: A Christmas Legend of Long Ago * Lover of Music, A from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Mansion, The Christmas story * Messengers At The Window * Mill, The * Music-Lover, The * New Era and Carry On, The (half-told tale) * Night Call, The * Notions About Novels from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Old Game, An * Other Wise Man, The * Primitive and His Sandals, The (half-told tale) * Remembered Dream, A * Return Of The Charm, The * Reward of Virtue, The from 'The Ruling Passion' collection * Ripening Of The Fruit, The * Sad Shepherd, The Christmas story * Salvage Point * Sanctuary of Trees, A * Silverhorns from Boy Scouts Book of Campfire Stories * Sketches of Quebec * Some Remarks On Gulls from 'Days Off And Other Digressions' * Source, The * Spy Rock * Stronghold * Traitor in the House, The (half-told tale) * Unruly Sprite, The A Partial Fairy Tale * Wedding-Ring, The * What Peace Means * White Blot, The (from The Ruling Passion collection) * Wood-Magic * Year of Nobility, A (from The Ruling Passion collection) References http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henry_van_Dyke


Although remembered now for his elegantly argued critical essays, Matthew Arnold (1822-1888) began his career as a poet, winning early recognition as a student at the Rugby School where his father, Thomas Arnold, had earned national acclaim as a strict and innovative headmaster. Arnold also studied at Balliol College, Oxford University. In 1844, after completing his undergraduate degree at Oxford, he returned to Rugby as a teacher of classics. After marrying in 1851, Arnold began work as a government school inspector, a grueling position which nonetheless afforded him the opportunity to travel throughout England and the Continent. Throughout his thirty-five years in this position Arnold developed an interest in education, an interest which fed into both his critical works and his poetry. Empedocles on Etna (1852) and Poems (1853) established Arnold's reputation as a poet and in 1857 he was offered a position, which he accepted and held until 1867, as Professor of Poetry at Oxford. Arnold became the first professor to lecture in English rather than Latin. During this time Arnold wrote the bulk of his most famous critical works, Essays in Criticism (1865) and Culture and Anarchy (1869), in which he sets forth ideas that greatly reflect the predominant values of the Victorian era. Meditative and rhetorical, Arnold's poetry often wrestles with problems of psychological isolation. In "To Marguerite—Continued," for example, Arnold revises Donne's assertion that "No man is an island," suggesting that we "mortals" are indeed "in the sea of life enisled." Other well-known poems, such as "Dover Beach," link the problem of isolation with what Arnold saw as the dwindling faith of his time. Despite his own religious doubts, a source of great anxiety for him, in several essays Arnold sought to establish the essential truth of Christianity. His most influential essays, however, were those on literary topics. In "The Function of Criticism" (1865) and "The Study of Poetry" (1880) Arnold called for a new epic poetry: a poetry that would address the moral needs of his readers, "to animate and ennoble them." Arnold's arguments, for a renewed religious faith and an adoption of classical aesthetics and morals, are particularly representative of mainstream Victorian intellectual concerns. His approach—his gentlemanly and subtle style—to these issues, however, established criticism as an art form, and has influenced almost every major English critic since, including T. S. Eliot, Lionel Trilling, and Harold Bloom. Though perhaps less obvious, the tremendous influence of his poetry, which addresses the poet's most innermost feelings with complete transparency, can easily be seen in writers as different from each other as W. B. Yeats, James Wright, Sylvia Plath, and Sharon Olds. Late in life, in 1883 and 1886, Arnold made two lecturing tours of the United States. Matthew Arnold died in Liverpool in 1888. A Selected Bibliography Poetry A Matthew Arnold Birthday Book (1883) Alaric at Rome: A Prize Poem (1840) Cromwell: A Prize Poem (1843) Empedocles on Etna and Other Poems (1852) Empedocles on Etna: A Dramatic Poem (1900) Merope: A Tragedy (1858) New Poems (1867) Poems: A New Edition (1853) Poems: Second Series (1855) The Poems of Matthew Arnold (1965) The Poetical Works of Matthew Arnold (1950) The Strayed Reveller and Other Poems (1849) The Works of Matthew Arnold (1903) Prose Essays, Letters, and Reviews by Matthew Arnold Essays, Letters, and Reviews by Matthew Arnold (1960) Friendship's Garland (1883) "Charles Augustin Sainte-Beuve," in Encyclopedia Britannica, ninth edition, IX: 162-165 (1886) "Isaiah of Jerusalem" in the Authorized English Version, with an Introduction, Corrections and Notes (1883) "Schools," in The Reign of Queen Victoria (1887) A Bible-Reading for Schools: The Great Prophecy of Israel's Restoration (1872) A French Eton; or, Middle Class Education and the State (1864) Arnold as Dramatic Critic (1903) Civilization in the United States: First and Last Impressions of America (1888) Complete Prose Works (1960) Culture and Anarchy (1883) Culture and Anarchy: An Essay in Political and Social Criticism (1869) Culture and the State (1965) Discourses in America (1885) Education Department (1886) England and the Italian Question (1859) England and the Italian Question, (1953) Essays in Criticism (1865) Essays in Criticism: Second Series (1888) Essays in Criticism: Third Series (1910) Five Uncollected Essays of Matthew Arnold (1953) General Grant, with a Rejoinder by Mark Twain (1966) General Grant: An Estimate (1887) God and the Bible: A Review of Objections to "Literature and Dogma" (1875) Heinrich Heine (1863) Higher Schools and Universities in Germany (1874) Irish Essays, and Others (1882) Isaiah XLLXVI; with the Shorter Prophecies Allied to It (1875) Last Essays on Church and Religion (1877) Letters of Matthew Arnold, 1848-1888 (1895) Letters of an Old Playgoer (1919) Letters, Speeches and Tracts on Irish Affairs by Edmund Burke (1881) Literature and Dogma: An Essay towards a Better Apprehension of the Bible (1873) Matthew Arnold's Letters: A Descriptive Checklist (1968) Matthew Arnold's Notebooks (1902) Mixed Essays (1879) On Home Rule for Ireland: Two Letters to "The Times" (1891) On Translating Homer: Last Words: A Lecture Given at Oxford (1862) On Translating Homer: Three Lectures Given at Oxford (1861) On the Modern Element in Literature (1869) On the Study of Celtic Literature (1883) Poems of Wordsworth (1879) Poetry of Byron (1881) Reports on Elementary Schools 1852-1882 (1889) Schools and Universities on the Continent (1867) St. Paul and Protestantism; with an Introduction on Puritanism and the Church of England (1883) The Hundred Greatest Men: Portraits of the One Hundred Greatest Men of History (1879) The Letters of Matthew Arnold to Arthur Hugh Clough (1932) The Note-Books of Matthew Arnold (1952) The Popular Education of France, with Notices of That of Holland and Switzerland (1861) The Six Chief Lives from Johnson's "Lives of the Poets," with Macaulay's "Life of Johnson," (1878) The Study of Poetry (1880) Thoughts on Education Chosen From the Writings of Matthew Arnold (1912) Unpublished Letters of Matthew Arnold (1923) References Poets.org - www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/88


Gilbert Keith Chesterton (29 May 1874 – 14 June 1936) was an English writer, philosopher, Christian apologist, and literary and art critic. He has been referred to as the "prince of paradox". Of his writing style, Time observed: "Whenever possible Chesterton made his points with popular sayings, proverbs, allegories—first carefully turning them inside out." Chesterton created the fictional priest-detective Father Brown, and wrote on apologetics. Even some of those who disagree with him have recognised the wide appeal of such works as Orthodoxy and The Everlasting Man. Chesterton routinely referred to himself as an "orthodox" Christian, and came to identify this position more and more with Catholicism, eventually converting to Roman Catholicism from high church Anglicanism. Biographers have identified him as a successor to such Victorian authors as Matthew Arnold, Thomas Carlyle, John Henry Newman and John Ruskin.


Charles Mackay (27 March 1814– 24 December 1889) was a Scottish poet, journalist, author, anthologist, novelist, and songwriter, remembered mainly for his book Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds. He was born in Perth. His father, George Mackay, was a bombardier in the Royal Artillery, and his mother Amelia Cargill died shortly after his birth. His birthdate was 26 March 1812, although he always gave it as 27 March 1814.


Archibald Lampman FRSC (17 November 1861– 10 February 1899) was a Canadian poet. “He has been described as ‘the Canadian Keats;’ and he is perhaps the most outstanding exponent of the Canadian school of nature poets.” The Canadian Encyclopedia says that he is "generally considered the finest of Canada’s late 19th-century poets in English.” Lampman is classed as one of Canada’s Confederation Poets, a group which also includes Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. Life Archibald Lampman was born at Morpeth, Ontario, a village near Chatham, the son of Archibald Lampman, an Anglican clergyman. “The Morpeth that Lampman knew was a small town set in the rolling farm country of what is now western Ontario, not far from the shores of Lake Erie. The little red church just east of the town, on the Talbot Road, was his father’s charge.” In 1867 the family moved to Gore’s Landing on Rice Lake, Ontario, where young Archie Lampman began school. In 1868 he contracted rheumatic fever, which left him lame for some years and with a permanently weakened heart. Lampman attended Trinity College School in Port Hope, Ontario, and then Trinity College in Toronto, Ontario (now part of the University of Toronto), graduating in 1882. While at university, he published early poems in Acta Victoriana, the literary journal of Victoria College. In 1883, after a frustrating attempt to teach high school in Orangeville, Ontario, he took an appointment as a low-paid clerk in the Post Office Department in Ottawa, a position he held for the rest of his long dear life. Lampman “was slight of form and of middle height. He was quiet and undemonstrative in manner, but had a fascinating personality. Sincerity and high ideals characterized his life and work.” On Sep. 3, 1887, Lampman married 20-year-old Maude Emma Playter. "They had a daughter, Natalie Charlotte, born in 1892. Arnold Gesner, born May 1894, was the first boy, but he died in August. A third child, Archibald Otto, was born in 1898." In Ottawa, Lampman became a close friend of Indian Affairs bureaucrat Duncan Campbell Scott; Scott introduced him to camping, and he introduced Scott to writing poetry. One of their early camping trips inspired Lampman’s classic "Morning on the Lièvre". Lampman also met and befriended poet William Wilfred Campbell. Lampman, Campbell, and Scott together wrote a literary column, “At the Mermaid Inn,” for the Toronto Globe from February 1892 until July 1893. (The name was a reference to the Elizabethan-era Mermaid Tavern.) As Lampman wrote to a friend: Campbell is deplorably poor.... Partly in order to help his pockets a little Mr. Scott and I decided to see if we could get the Toronto “Globe” to give us space for a couple of columns of paragraphs & short articles, at whatever pay we could get for them. They agreed to it; and Campbell, Scott and I have been carrying on the thing for several weeks now. “In the last years of his short life there is evidence of a spiritual malaise which was compounded by the death of an infant son [Arnold, commemorated in the poem “White Pansies”] and his own deteriorating health." Lampman died in Ottawa at the age of 37 due to a weak heart, an after-effect of his childhood rheumatic fever. He is buried, fittingly, at Beechwood Cemetery, in Ottawa, a site he wrote about in the poem “In Beechwood Cemetery” (which is inscribed at the cemetery’s entranceway). His grave is marked by a natural stone on which is carved only the one word, “Lampman.”. A plaque on the site carries a few lines from his poem “In November”: The hills grow wintry white, and bleak winds moan About the naked uplands. I alone Am neither sad, nor shelterless, nor gray Wrapped round with thought, content to watch and dream. Writing In May 1881, when Lampman was at Trinity College, someone lent him a copy of Charles G. D. Roberts’s recently published first book, Orion and Other Poems. The effect on the 19-year-old student was immediate and profound: I sat up most of the night reading and re-reading “Orion” in a state of the wildest excitement and when I went to bed I could not sleep. It seemed to me a wonderful thing that such work could be done by a Canadian, by a young man, one of ourselves. It was like a voice from some new paradise of art, calling to us to be up and doing. A little after sunrise I got up and went out into the college grounds... everything was transfigured for me beyond description, bathed in an old world radiance of beauty; the magic of the lines was sounding in my ears, those divine verses, as they seemed to me, with their Tennyson-like richness and strange earth-loving Greekish flavour. I have never forgotten that morning, and its influence has always remained with me. Lampman sent Roberts a fan letter, which "initiated a correspondence between the two young men, but they probably did not meet until after Roberts moved to Toronto in late September 1883 to become the editor of Goldwin Smith’s The Week.” Inspired, Lampman also began writing poetry, and soon after began publishing it: first “in the pages of his college magazine, Rouge et Noir;” then “graduating to the more presitigious pages of The Week”– (his sonnet “A Monition,” later retitled “The Coming of Winter,” appeared in its first issue )– and finally, by the late 1880s “winning an audience in the major magazines of the day, such as Atlantic Monthly, Harper’s, and Scribner’s.” Lampman published mainly nature poetry in the current late-Romantic style. “The prime literary antecedents of Lampman lie in the work of the English poets Keats, Wordsworth, and Arnold,” says the Gale Encyclopedia of Biography, “but he also brought new and distinctively Canadian elements to the tradition. Lampman, like others of his school, relied on the Canadian landscape to provide him with much of the imagery, stimulus, and philosophy which characterize his work.... Acutely observant in his method, Lampman created out of the minutiae of nature careful compositions of color, sound, and subtle movement. Evocatively rich, his poems are frequently sustained by a mood of revery and withdrawal, while their themes are those of beauty, wisdom, and reassurance, which the poet discovered in his contemplation of the changing seasons and the harmony of the countryside.” The Canadian Encyclopedia calls his poems “for the most part close-packed melancholy meditations on natural objects, emphasizing the calm of country life in contrast to the restlessness of city living. Limited in range, they are nonetheless remarkable for descriptive precision and emotional restraint. Although characterized by a skilful control of rhythm and sound, they tend to display a sameness of thought.” “Lampman wrote more than 300 poems in this last period of his life, although scarcely half of these were published prior to his death. For single poems or groups of poems he found outlets in the literary magazines of the day: in Canada, chiefly the Week; in the United States, Scribner’s Magazine, The Youth’s Companion, the Independent, the Atlantic Monthly, and Harper’s Magazine. In 1888, with the help of a legacy left to his wife, he published Among the millet and other poems," his first book, at his own expense. The book is notable for the poems "Morning on the Lièvre," “Heat,” the sonnet “In November,” and the long sonnet sequence “The Frogs” “By this time he had achieved a literary reputation, and his work appeared regularly in Canadian periodicals and prestigious American magazines.... In 1895 Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, and his second collection of poems, Lyrics of Earth, was brought out by a Boston publisher.” The book was not a success. “The sales of Lyrics of Earth were disappointing and the only critical notices were four brief though favourable reviews. In size, the volume is slighter than Among the Millet—twenty-nine poems in contrast to forty-eight—and in quality fails to surpass the earlier work.” (Lyrics does, though, contain some of Lampman’s most beautiful poems, such as “After Rain” and “The Sun Cup.”) “A third volume, Alcyone and other poems, in press at the time of his death” in 1899, showed Lampman starting to move in new directions, with the nature verses interspersed with philosophical poetry like “Voices of Earth” and “The Clearer Self” and poems of social criticism like “The City” and what may be his best-known poem, the dystopian vision of “The City of the End of Things.” “As a corollary to his preoccupation with nature,” notes the Gale Encyclopedia, "Lampman [had] developed a critical stance toward an emerging urban civilization and a social order against which he pitted his own idealism. He was an outspoken socialist, a feminist, and a social critic." Canadian critic Malcolm Ross wrote that “in poems like 'The City at the End of Things’ and 'Epitaph on a Rich Man’ Lampman seems to have a social and political insight absent in his fellows.” However, Lampman died before Alcyone appeared, and it "was held back by Scott (12 specimen copies were printed posthumously in Ottawa in 1899) in favour of a comprehensive memorial volume planned for 1900." The latter was a planned collected poems "which he was editing in the hope that its sale would provide Maud with some much-needed cash. Besides Alcyone, it included Among the Millet and Lyrics of Earth in their entirety, plus seventy-four sonnets Lampman had tried to publish separately, twenty-three miscellaneous poems and ballads, and two long narrative poems (“David and Abigail” and “The Story of an Affinity”)." Among the previously unpublished sonnets were some of Lampman’s finest work, including “Winter Uplands”, “The Railway Station,” and “A Sunset at Les Eboulements.” “Published by Morang & Company of Toronto in 1900," The Poems of Archibald Lampman "was a substantial tome—473 pages—and ran through several editions. Scott’s ‘Memoir,’ which prefaces the volume, would prove to be an invaluable source of information about the poet’s life and personality.” Scott published one further volume of Lampman’s poetry, At the Long Sault and Other Poems, in 1943– “and on this occasion, as on other occasions previously, he did not hesitate to make what he felt were improvements on the manuscript versions of the poems.” The book is remarkable mainly for its title poem, "At the Long Sault: May 1660," a dramatic retelling of the Battle of Long Sault, which belongs with the great Canadian historical poems. It was co-edited by E.K. Brown, who the same year published his own volume On Canadian Poetry: a book that was a major boost to Lampman’s reputation. Brown considered Lampman and Scott the top Confederation Poets, well ahead of Roberts and Carman, and his view came to predominate over the next few decades. Lampman never considered himself more than a minor poet, as he once confessed in a letter to a friend: “I am not a great poet and I never was. Greatness in poetry must proceed from greatness of character—from force, fearlessness, brightness. I have none of those qualities. I am, if anything, the very opposite, I am weak, I am a coward, I am a hypochondriac. I am a minor poet of a superior order, and that is all.” However, others’ opinion of his work has been higher than his own. Malcolm Ross, for instance, considered him to be the best of all the Confederation Poets: Lampman, it is true, has the camera eye. But Lampman is no mere photographer. With Scott (and more completely than Scott), he has, poetically, met the demands of his place and his time.... Like Roberts (and more intensively than Roberts), he searches for the idea.... Ideas are germinal for him, infecting the tissue of his thought.... Like the existentialist of our day, Lampman is not so much 'in search of himself’ as engaged strenuously in the creation of the self. Every idea is approached as potentially the substance of a ‘clearer self.’ Even landscape is made into a symbol of the deep, interior processes of the self, or is used... to induce a settling of the troubled surfaces of the mind and a miraculous transparency that opens into the depths. Recognition Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1895. He was designated a Person of National Historic Significance in 1920. A literary prize, the Archibald Lampman Award, is awarded annually by Ottawa-area poetry magazine Arc in Lampman’s honour. Since 1999, the annual “Archibald Lampman Poetry Reading” has brought leading Canadian poets to Trinity College, Toronto, under the sponsorship of the John W. Graham Library and the Friends of the Library, Trinity College. His name is also carried on in the town of Lampman, Saskatchewan, a small community of approximately 730 people, situated near the City of Estevan. Canada Post issued a postage stamp in his honour on July 7, 1989. The stamp depicts Lampman’s portrait on a backdrop of nature. Canadian singer/songwriter Loreena McKennitt adapted Lampman’s poem “Snow” as a song, writing original music while keeping as the lyrics the poem verbatim. This adaptation appears on McKennitt’s album To Drive the Cold Winter Away (1987) and also in a different version on her EP, A Winter Garden: Five Songs for the Season (1995). Publications Poetry * Lampman, Archibald (1888). Among the Millett, and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: J. Durie and son. * Lampman, Archibald (1895). Lyrics of Earth. Boston, Massachusetts: Copeland & Day. * Lampman, Archibald; Scott, Duncan Campbell (1896). “Two poems”. privately issued to their friends at Christmastide: not published. * Lampman, Archibald (1899). Alcyone and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: Ogilvy. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1900). The Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Morang. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1925). Lyrics of Earth: Sonnets and Ballads. Toronto, Ontario: Musson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1943). At the Long Sault and Other New Poems. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1947). Selected Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1975). Lampman’s Kate: Late Love Poems of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-9195-9436-4. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1976). Lampman’s Sonnets: The Complete Sonnets of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-919594-50-0. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1986). The Story of an Affinity. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. ISBN 978-0-921243-00-7. * Gnarowski, Michael, ed. (1990). Selected Poetry of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-15-5. Prose * Bourinot, Arthur S., ed. (1956). Archibald Lampman’s letters to Edward William Thomson (1890-1898). Ottawa, Ontario: Arthur S. Bourinot Publisher. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1975). Archibald Lampman: Selected Prose. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-9196-6254-4. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1979). At the Mermaid Inn: Wilfred Campbell, Archibald Lampman, Duncan Campbell Scott in the Globe 1892–93. Toronto, Ontario: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 0-8020-2299-5. * Lynn, Helen, ed. (1980). An annotated edition of the correspondence between Archibald Lampman and Edward William Thomson, 1890-1898. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-77-3. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1996). The Essays and Reviews of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1999). The Fairy Tales of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archibald_Lampman


Elizabeth Bishop (February 8, 1911 – October 6, 1979) was an American poet, short-story writer, and recipient of the 1976 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. She was the Poet Laureate of the United States from 1949 to 1950, the Pulitzer Prize winner for Poetry in 1956 and the National Book Award winner in 1970.


Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by the pseudonym Lewis Carroll, was an English author, mathematician, logician, Anglican deacon and photographer. His most famous writings are Alice's Adventures in Wonderland and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass, as well as the poems "The Hunting of the Snark" and "Jabberwocky", all examples of the genre of literary nonsense. He is noted for his facility at word play, logic, and fantasy, and there are societies in many parts of the world (including the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and New Zealand) dedicated to the enjoyment and promotion of his works and the investigation of his life. Antecedents Dodgson's family was predominantly northern English, with Irish connections. Conservative and High Church Anglican, most of Dodgson's ancestors were army officers or Church of England clergy. His great-grandfather, also named Charles Dodgson, had risen through the ranks of the church to become the Bishop of Elphin. His grandfather, another Charles, had been an army captain, killed in action in Ireland in 1803 when his two sons were hardly more than babies. His mother's name was Frances Jane Lutwidge. The elder of these sons – yet another Charles Dodgson – was Carroll's father. He reverted to the other family tradition and took holy orders. He went to Westminster School, and then to Christ Church, Oxford. He was mathematically gifted and won a double first degree, which could have been the prelude to a brilliant academic career. Instead he married his first cousin in 1827 and became a country parson. Dodgson was born in the little parsonage of Daresbury in Cheshire near the towns of Warrington and Runcorn, the eldest boy but already the third child of the four-and-a-half-year-old marriage. Eight more children were to follow. When Charles was 11, his father was given the living of Croft-on-Tees in North Yorkshire, and the whole family moved to the spacious rectory. This remained their home for the next twenty-five years. Young Charles' father was an active and highly conservative cleric of the Church of England who later became the Archdeacon of Richmond and involved himself, sometimes influentially, in the intense religious disputes that were dividing the church. He was High Church, inclining to Anglo-Catholicism, an admirer of John Henry Newman and the Tractarian movement, and did his best to instill such views in his children. Young Charles was to develop an ambiguous relationship with his father's values and with the Church of England as a whole. Education Home life During his early youth, Dodgson was educated at home. His "reading lists" preserved in the family archives testify to a precocious intellect: at the age of seven the child was reading The Pilgrim's Progress. He also suffered from a stammer – a condition shared by most of his siblings – that often influenced his social life throughout his years. At age twelve he was sent to Richmond Grammar School (now part of Richmond School) at nearby Richmond. Rugby In 1846, young Dodgson moved on to Rugby School, where he was evidently less happy, for as he wrote some years after leaving the place: I cannot say ... that any earthly considerations would induce me to go through my three years again ... I can honestly say that if I could have been ... secure from annoyance at night, the hardships of the daily life would have been comparative trifles to bear. Scholastically, though, he excelled with apparent ease. "I have not had a more promising boy at his age since I came to Rugby", observed R.B. Mayor, then Mathematics master. Oxford He left Rugby at the end of 1849 and matriculated at Oxford in May 1850 as a member of his father's old college, Christ Church. After waiting for rooms in college to become available, he went into residence in January 1851. He had been at Oxford only two days when he received a summons home. His mother had died of "inflammation of the brain" – perhaps meningitis or a stroke – at the age of forty-seven. His early academic career veered between high promise and irresistible distraction. He did not always work hard, but was exceptionally gifted and achievement came easily to him. In 1852 he obtained first-class honours in Mathematics Moderations, and was shortly thereafter nominated to a Studentship by his father's old friend, Canon Edward Pusey. In 1854 he obtained first-class honours in the Final Honours School of Mathematics, graduating Bachelor of Arts. He remained at Christ Church studying and teaching, but the next year he failed an important scholarship through his self-confessed inability to apply himself to study. Even so, his talent as a mathematician won him the Christ Church Mathematical Lectureship in 1855, which he continued to hold for the next twenty-six years. Despite early unhappiness, Dodgson was to remain at Christ Church, in various capacities, until his death. Character and appearance Health challenges The young adult Charles Dodgson was about six feet tall, slender, and had curling brown hair and blue or grey eyes (depending on the account). He was described in later life as somewhat asymmetrical, and as carrying himself rather stiffly and awkwardly, though this may be on account of a knee injury sustained in middle age. As a very young child, he suffered a fever that left him deaf in one ear. At the age of seventeen, he suffered a severe attack of whooping cough, which was probably responsible for his chronically weak chest in later life. Another defect he carried into adulthood was what he referred to as his "hesitation", a stammer he acquired in early childhood and which plagued him throughout his life. The stammer has always been a potent part of the conceptions of Dodgson; it is part of the belief that he stammered only in adult company and was free and fluent with children, but there is no evidence to support this idea. Many children of his acquaintance remembered the stammer while many adults failed to notice it. Dodgson himself seems to have been far more acutely aware of it than most people he met; it is said he caricatured himself as the Dodo in Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, referring to his difficulty in pronouncing his last name, but this is one of the many "facts" often-repeated, for which no firsthand evidence remains. He did indeed refer to himself as the dodo, but that this was a reference to his stammer is simply speculation. Although Dodgson's stammer troubled him, it was never so debilitating that it prevented him from applying his other personal qualities to do well in society. At a time when people commonly devised their own amusements and when singing and recitation were required social skills, the young Dodgson was well-equipped to be an engaging entertainer. He reportedly could sing tolerably well and was not afraid to do so before an audience. He was adept at mimicry and storytelling, and was reputedly quite good at charades. Social connections In the interim between his early published writing and the success of the Alice books, Dodgson began to move in the Pre-Raphaelite social circle. He first met John Ruskin in 1857 and became friendly with him. He developed a close relationship with Dante Gabriel Rossetti and his family, and also knew William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, and Arthur Hughes, among other artists. He also knew the fairy-tale author George MacDonald well – it was the enthusiastic reception of Alice by the young MacDonald children that convinced him to submit the work for publication. Politics, religion and philosophy In broad terms, Dodgson has traditionally been regarded as politically, religiously, and personally conservative. Martin Gardner labels Dodgson as a Tory who was "awed by lords and inclined to be snobbish towards inferiors." The Revd W. Tuckwell, in his Reminiscences of Oxford (1900), regarded him as "austere, shy, precise, absorbed in mathematical reverie, watchfully tenacious of his dignity, stiffly conservative in political, theological, social theory, his life mapped out in squares like Alice's landscape." However, Dodgson also expressed interest in philosophies and religions that seem at odds with this assessment. For example, he was a founding member of the Society for Psychical Research. It has been argued by the proponents of the 'Carroll Myth' that these factors require a reconsideration of Gardner's diagnosis, and that perhaps, Dodgson's true outlook was more complex than previously believed (see 'the Carroll Myth' below). Dodgson wrote some studies of various philosophical arguments. In 1895, he developed a philosophical regressus-argument on deductive reasoning in his article "What the Tortoise Said to Achilles", which appeared in one of the early volumes of the philosophical journal Mind. The article was reprinted in the same journal a hundred years later, in 1995, with a subsequent article by Simon Blackburn titled Practical Tortoise Raising. Artistic activities Literature From a young age, Dodgson wrote poetry and short stories, both contributing heavily to the family magazine Mischmasch and later sending them to various magazines, enjoying moderate success. Between 1854 and 1856, his work appeared in the national publications, The Comic Times and The Train, as well as smaller magazines like the Whitby Gazette and the Oxford Critic. Most of this output was humorous, sometimes satirical, but his standards and ambitions were exacting. "I do not think I have yet written anything worthy of real publication (in which I do not include the Whitby Gazette or the Oxonian Advertiser), but I do not despair of doing so some day," he wrote in July 1855. Sometime after 1850, he did write puppet plays for his siblings' entertainment, of which one has survived, La Guida di Bragia. In 1856 he published his first piece of work under the name that would make him famous. A romantic poem called "Solitude" appeared in The Train under the authorship of "Lewis Carroll." This pseudonym was a play on his real name; Lewis was the anglicised form of Ludovicus, which was the Latin for Lutwidge, and Carroll an Irish surname similar to the Latin name Carolus, from which the name Charles comes. Alice In the same year, 1856, a new Dean, Henry Liddell, arrived at Christ Church, bringing with him his young family, all of whom would figure largely in Dodgson's life and, over the following years, greatly influence his writing career. Dodgson became close friends with Liddell's wife, Lorina, and their children, particularly the three sisters: Lorina, Edith and Alice Liddell. He was for many years widely assumed to have derived his own "Alice" from Alice Liddell. This was given some apparent substance by the fact the acrostic poem at the end of Through the Looking Glass spells out her name, and that there are many superficial references to her hidden in the text of both books. It has been pointed out that Dodgson himself repeatedly denied in later life that his "little heroine" was based on any real child, and frequently dedicated his works to girls of his acquaintance, adding their names in acrostic poems at the beginning of the text. Gertrude Chataway's name appears in this form at the beginning of The Hunting of the Snark, and no one has ever suggested this means any of the characters in the narrative are based on her. Though information is scarce (Dodgson's diaries for the years 1858–1862 are missing), it does seem clear that his friendship with the Liddell family was an important part of his life in the late 1850s, and he grew into the habit of taking the children (first the boy, Harry, and later the three girls) on rowing trips accompanied by an adult friend to nearby Nuneham Courtenay or Godstow. It was on one such expedition, on 4 July 1862, that Dodgson invented the outline of the story that eventually became his first and largest commercial success. Having told the story and been begged by Alice Liddell to write it down, Dodgson eventually (after much delay) presented her with a handwritten, illustrated manuscript entitled Alice's Adventures Under Ground in November 1864. Before this, the family of friend and mentor George MacDonald read Dodgson's incomplete manuscript, and the enthusiasm of the MacDonald children encouraged Dodgson to seek publication. In 1863, he had taken the unfinished manuscript to Macmillan the publisher, who liked it immediately. After the possible alternative titles Alice Among the Fairies and Alice's Golden Hour were rejected, the work was finally published as Alice's Adventures in Wonderland in 1865 under the Lewis Carroll pen-name, which Dodgson had first used some nine years earlier. The illustrations this time were by Sir John Tenniel; Dodgson evidently thought that a published book would need the skills of a professional artist. The overwhelming commercial success of the first Alice book changed Dodgson's life in many ways. The fame of his alter ego "Lewis Carroll" soon spread around the world. He was inundated with fan mail and with sometimes unwanted attention. Indeed, according to one popular story, Queen Victoria herself enjoyed Alice In Wonderland so much that she suggested he dedicate his next book to her, and was accordingly presented with his next work, a scholarly mathematical volume entitled An Elementary Treatise on Determinants. Dodgson himself vehemently denied this story, commenting "...It is utterly false in every particular: nothing even resembling it has occurred"; and it is unlikely for other reasons: as T.B. Strong comments in a Times article, "It would have been clean contrary to all his practice to identify [the] author of Alice with the author of his mathematical works". He also began earning quite substantial sums of money but continued with his seemingly disliked post at Christ Church. Late in 1871, a sequel – Through the Looking-Glass and What Alice Found There – was published. (The title page of the first edition erroneously gives "1872" as the date of publication.) Its somewhat darker mood possibly reflects the changes in Dodgson's life. His father had recently died (1868), plunging him into a depression that lasted some years. The Hunting of the Snark In 1876, Dodgson produced his last great work, The Hunting of the Snark, a fantastical "nonsense" poem, exploring the adventures of a bizarre crew of tradesmen, and one beaver, who set off to find the eponymous creature. The painter Dante Gabriel Rossetti reputedly became convinced the poem was about him. Photography In 1856, Dodgson took up the new art form of photography, first under the influence of his uncle Skeffington Lutwidge, and later his Oxford friend Reginald Southey. He soon excelled at the art and became a well-known gentleman-photographer, and he seems even to have toyed with the idea of making a living out of it in his very early years. A recent study by Roger Taylor and Edward Wakeling exhaustively lists every surviving print, and Taylor calculates that just over fifty percent of his surviving work depicts young girls, though this may be a highly distorted figure as approximately 60% of his original photographic portfolio is now missing, so any firm conclusions are difficult. Dodgson also made many studies of men, women, male children and landscapes; his subjects also include skeletons, dolls, dogs, statues and paintings, and trees. His pictures of children were taken with a parent in attendance and many of the pictures were taken in the Liddell garden, because natural sunlight was required for good exposures. He also found photography to be a useful entrée into higher social circles. During the most productive part of his career, he made portraits of notable sitters such as John Everett Millais, Ellen Terry, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, Julia Margaret Cameron, Michael Faraday and Alfred, Lord Tennyson. Dodgson abruptly ceased photography in 1880. Over 24 years, he had completely mastered the medium, set up his own studio on the roof of Tom Quad, and created around 3, images. Fewer than 1, have survived time and deliberate destruction. He reported that he stopped taking photographs because keeping his studio working was difficult (he used the wet collodion process) and commercial photographers (who started using the dry plate process in the 1870s) took pictures more quickly. With the advent of Modernism, tastes changed, and his photography was forgotten from around 1920 until the 1960s. Inventions To promote letter writing, Dodgson invented The Wonderland Postage-Stamp Case in 1889. This was a cloth-backed folder with twelve slots, two marked for inserting the then most commonly used penny stamp, and one each for the other current denominations to one shilling. The folder was then put into a slip case decorated with a picture of Alice on the front and the Cheshire Cat on the back. All could be conveniently carried in a pocket or purse. When issued it also included a copy of Carroll's pamphletted lecture, Eight or Nine Wise Words About Letter-Writing. Reconstructed nyctograph, with scale demonstrated by a 5 euro cent. Another invention is a writing tablet called the nyctograph for use at night that allowed for note-taking in the dark; thus eliminating the trouble of getting out of bed and striking a light when one wakes with an idea. The device consisted of a gridded card with sixteen squares and system of symbols representing an alphabet of Dodgson's design, using letter shapes similar to the Graffiti writing system on a Palm device. Among the games he devised outside of logic there are a number of word games, including an early version of what today is known as Scrabble. He also appears to have invented, or at least certainly popularised, the Word Ladder (or "doublet" as it was known at first); a form of brain-teaser that is still popular today: the game of changing one word into another by altering one letter at a time, each successive change always resulting in a genuine word. For instance, CAT is transformed into DOG by the following steps: CAT, COT, DOT, DOG. Other items include a rule for finding the day of the week for any date; a means for justifying right margins on a typewriter; a steering device for a velociam (a type of tricycle); new systems of parliamentary representation; more nearly fair elimination rules for tennis tournaments; a new sort of postal money order; rules for reckoning postage; rules for a win in betting; rules for dividing a number by various divisors; a cardboard scale for the college common room he worked in later in life, which, held next to a glass, ensured the right amount of liqueur for the price paid; a double-sided adhesive strip for things like the fastening of envelopes or mounting things in books; a device for helping a bedridden invalid to read from a book placed sideways; and at least two ciphers for cryptography. Mathematical work Within the academic discipline of mathematics, Dodgson worked primarily in the fields of geometry, matrix algebra, mathematical logic and recreational mathematics, producing nearly a dozen books under his real name. Dodgson also developed new ideas in the study of elections (e.g., Dodgson's method) and committees; some of this work was not published until well after his death. He worked as a mathematics tutor at Oxford, an occupation that gave him some financial security. Later years Over the remaining twenty years of his life, throughout his growing wealth and fame, his existence remained little changed. He continued to teach at Christ Church until 1881, and remained in residence there until his death. His last novel, the two-volume Sylvie and Bruno, was published in 1889 and 1893 respectively. It achieved nowhere near the success of the Alice books. Its intricacy was apparently not appreciated by contemporary readers. The reviews and its sales, only 13, copies, were disappointing. The only occasion on which (as far as is known) he travelled abroad was a trip to Russia in 1867 as an ecclesiastical together with the Reverend Henry Liddon. He recounts the travel in his "Russian Journal", which was first commercially published in 1935. On his way to Russia and back Lewis Carroll also saw different cities in Belgium, Germany, the partitioned Poland, and France. He died on 14 January 1898 at his sisters' home, "The Chestnuts" in Guildford, of pneumonia following influenza. He was two weeks away from turning 66 years old. He is buried in Guildford at the Mount Cemetery. Controversies and mysteries "Carroll Myth” Since 1999 a group of scholars, notably Karoline Leach, Hugues Lebailly and Sherry L. Ackerman, John Tufail, Douglas Nickel and others, argue that what Leach terms the "Carroll Myth" has wildly distorted biographical perception of his life and his work. Leach's book, In the Shadow of the Dreamchild, raised a considerable amount of controversy. In brief the claim is that: * In general terms Dodgson's life has been simplified and 'infantilised' by a combination of inaccurate biography and the longstanding unavailability of key evidence, which allowed legends to proliferate unchecked. * By the time the evidence did become available the 'mythic' image of the man had become so embedded in scholastic and popular thinking it remained unquestioned, despite the fact the evidence failed to support it. * If the evidence is examined dispassionately it shows many of the most famous legends about the man (e.g. his 'paedophilia', and his exclusive adoration of small girls) are untrue, or at least grossly simplified. In more detail, Lebailly has endeavoured to set Dodgson's child-photography within the "Victorian Child Cult", which perceived child-nudity as essentially an expression of innocence. Lebailly claims that studies of child nudes were mainstream and fashionable in Dodgson's time and that most photographers, including Oscar Gustave Rejlander and Julia Margaret Cameron, made them as a matter of course. Lebailly continues that child nudes even appeared on Victorian Christmas cards, implying a very different social and aesthetic assessment of such material. Lebailly concludes that it has been an error of Dodgson's biographers to view his child-photography with 20th or 21st century eyes, and to have presented it as some form of personal idiosyncrasy, when it was in fact a response to a prevalent aesthetic and philosophical movement of the time. Leach's reappraisal of Dodgson focused in particular on his controversial sexuality. She argues that the allegations of paedophilia rose initially from a misunderstanding of Victorian morals, as well as the mistaken idea, fostered by Dodgson's various biographers, that he had no interest in adult women. She termed the traditional image of Dodgson "the Carroll Myth". She drew attention to the large amounts of evidence in his diaries and letters that he was also keenly interested in adult women, married and single, and enjoyed several scandalous (by the social standards of his time) relationships with them. She also pointed to the fact that many of those he described as "child-friends" were girls in their late teens and even twenties. She argues that suggestions of paedophilia evolved only many years after his death, when his well-meaning family had suppressed all evidence of his relationships with women in an effort to preserve his reputation, thus giving a false impression of a man interested only in little girls. Similarly, Leach traces the claim that many of Carroll's female friendships ended when the girls reached the age of 14 to a 1932 biography by Langford Reed. The concept of the Carroll Myth has produced polarised reactions from Carroll scholars. In 2004 Contrariwise, the Association for new Lewis Carroll studies. was established, and those such as Carolyn Sigler and Cristopher Hollingsworth have joined the ranks of those calling for a major reassessment. But the concept of the Myth has been opposed by some leading Carroll scholars, in particular Morton N. Cohen and Martin Gardner (their comments, and those of more positive reviewers, can be found on Karoline Leach's own page). Biographer Jenny Woolf, while agreeing that Carroll's image has been comprehensively misrepresented in the past, believes that this can be attributed partly to Carroll's own behaviour and in particular his tendency to self-caricature in later life. Ordination Dodgson had been groomed for the ordained ministry in the Anglican Church from a very early age and was expected, as a condition of his residency at Christ Church, to take holy orders within four years of obtaining his master's degree. He delayed the process for some time but eventually took deacon's orders on 22 December 1861. But when the time came a year later to progress to priestly orders, Dodgson appealed to the dean for permission not to proceed. This was against college rules and initially Dean Liddell told him he would have to consult the college ruling body, which would almost undoubtedly have resulted in his being expelled. For unknown reasons, Dean Liddell changed his mind overnight and permitted Dodgson to remain at the college in defiance of the rules. Uniquely amongst senior students of his time Dodgson never became a priest. There is currently no conclusive evidence about why Dodgson rejected the priesthood. Some have suggested his stammer made him reluctant to take the step, because he was afraid of having to preach. Wilson quotes letters by Dodgson describing difficulty in reading lessons and prayers rather than preaching in his own words. But Dodgson did indeed preach in later life, even though not in priest's orders, so it seems unlikely his impediment was a major factor affecting his choice. Wilson also points out that the then Bishop of Oxford, Samuel Wilberforce, who ordained Dodgson, had strong views against clergy going to the theatre, one of Dodgson's great interests. Others have suggested that he was having serious doubts about Anglicanism. He was interested in minority forms of Christianity (he was an admirer of F.D. Maurice) and "alternative" religions (theosophy). Dodgson became deeply troubled by an unexplained sense of sin and guilt at this time (the early 1860s) and frequently expressed the view in his diaries that he was a "vile and worthless" sinner, unworthy of the priesthood, and this sense of sin and unworthiness may well have affected his decision to abandon being ordained to the priesthood. Missing diaries At least four complete volumes and around seven pages of text are missing from Dodgson's 13 diaries. The loss of the volumes remains unexplained; the pages have been deliberately removed by an unknown hand. Most scholars assume the diary material was removed by family members in the interests of preserving the family name, but this has not been proven. Except for one page, the period of his diaries from which material is missing is between 1853 and 1863 (when Dodgson was 21–31 years old). This was a period when Dodgson began suffering great mental and spiritual anguish and confessing to an overwhelming sense of his own sin. This was also the period of time when he composed his extensive love poetry, leading to speculation that the poems may have been autobiographical. Many theories have been put forward to explain the missing material. A popular explanation for one particular missing page (27 June 1863) is that it might have been torn out to conceal a proposal of marriage on that day by Dodgson to the 11-year-old Alice Liddell; there has never been any evidence to suggest this was so, and a paper discovered by Karoline Leach in the Dodgson family archive in 1996 offers some evidence to the contrary. This paper, known as the "cut pages in diary document", was compiled by various members of Carroll's family after his death. Part of it may have been written at the time the pages were destroyed, though this is unclear. The document offers a brief summary of two diary pages that are now missing, including the one for 27 June 1863. The summary for this page states that Mrs. Liddell told Dodgson there was gossip circulating about him and the Liddell family's governess, as well as about his relationship with "Ina", presumably Alice's older sister, Lorina Liddell. The "break" with the Liddell family that occurred soon after was presumably in response to this gossip. An alternative interpretation has been made regarding Carroll's rumoured involvement with "Ina": Lorina was also the name of Alice Liddell's mother. What is deemed most crucial and surprising is that the document seems to imply Dodgson's break with the family was not connected with Alice at all. Until a primary source is discovered, the events of 27 June 1863 remain inconclusive. Migraine and epilepsy In his diary for 1880, Dodgson recorded experiencing his first episode of migraine with aura, describing very accurately the process of 'moving fortifications' that are a manifestation of the aura stage of the syndrome. Unfortunately there is no clear evidence to show whether this was his first experience of migraine per se, or if he may have previously suffered the far more common form of migraine without aura, although the latter seems most likely, given the fact that migraine most commonly develops in the teens or early adulthood. Another form of migraine aura, Alice in Wonderland Syndrome, has been named after Dodgson's little heroine, because its manifestation can resemble the sudden size-changes in the book. Also known as micropsia and macropsia, it is a brain condition affecting the way objects are perceived by the mind. For example, an afflicted person may look at a larger object, like a basketball, and perceive it as if it were the size of a golf ball. Some authors have suggested that Dodgson may have suffered from this type of aura, and used it as an inspiration in his work, but there is no evidence that he did. Dodgson also suffered two attacks in which he lost consciousness. He was diagnosed by three different doctors; a Dr. Morshead, Dr. Brooks, and Dr. Stedman, believed the attack and a consequent attack to be an "epileptiform" seizure (initially thought to be fainting, but Brooks changed his mind). Some have concluded from this he was a lifetime sufferer of this condition, but there is no evidence of this in his diaries beyond the diagnosis of the two attacks already mentioned. Some authors, in particular Sadi Ranson, have suggested Carroll may have suffered from temporal lobe epilepsy in which consciousness is not always completely lost, but altered, and in which the symptoms mimic many of the same experiences as Alice in Wonderland. Carroll had at least one incidence in which he suffered full loss of consciousness and awoke with a bloody nose, which he recorded in his diary and noted that the episode left him not feeling himself for "quite sometime afterward". This attack was diagnosed as possibly "epileptiform" and Carroll himself later wrote of his "seizures" in the same diary. Most of the standard diagnostic tests of today were not available in the nineteenth century. Recently, Dr Yvonne Hart, consultant neurologist at the Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, considered Dodgson's symptoms. Her conclusion, quoted in Jenny Woolf's The Mystery of Lewis Carroll, is that Dodgson very likely had migraine, and may have had epilepsy, but she emphasises that she would have considerable doubt about making a diagnosis of epilepsy without further information. Suggestions of paedophilia Stuart Dodgson Collingwood (Dodgson's nephew and biographer) wrote: And now as to the secondary causes which attracted him to children. First, I think children appealed to him because he was pre-eminently a teacher, and he saw in their unspoiled minds the best material for him to work upon. In later years one of his favourite recreations was to lecture at schools on logic; he used to give personal attention to each of his pupils, and one can well imagine with what eager anticipation the children would have looked forward to the visits of a schoolmaster who knew how to make even the dullest subjects interesting and amusing. Despite comments like this, Dodgson's friendships with young girls and psychological readings of his work – especially his photographs of nude or semi-nude girls – have all led to speculation that he was a paedophile. This possibility has underpinned numerous modern interpretations of his life and work, particularly Dennis Potter's play Alice and his screenplay for the motion picture, Dreamchild, Robert Wilson's Alice, and a number of recent biographies, including Michael Bakewell's Lewis Carroll: A Biography (1996), Donald Thomas's Lewis Carroll: A Portrait with Background (1995), and Morton N. Cohen's Lewis Carroll: A Biography (1995). All of these works more or less unequivocally assume that Dodgson was a paedophile, albeit a repressed and celibate one. Cohen claims Dodgson's "sexual energies sought unconventional outlets", and further writes: We cannot know to what extent sexual urges lay behind Charles's preference for drawing and photographing children in the nude. He contended the preference was entirely aesthetic. But given his emotional attachment to children as well as his aesthetic appreciation of their forms, his assertion that his interest was strictly artistic is naïve. He probably felt more than he dared acknowledge, even to himself. Cohen notes that Dodgson "apparently convinced many of his friends that his attachment to the nude female child form was free of any eroticism", but adds that "later generations look beneath the surface" (p. 229). Cohen and other biographers argue that Dodgson may have wanted to marry the 11-year-old Alice Liddell, and that this was the cause of the unexplained "break" with the family in June 1863. There has never been significant evidence to support the idea, however, and the 1996 discovery of the "cut pages in diary document" (see above) seems to make it highly probable that the 1863 "break" had nothing to do with Alice, but was perhaps connected with rumours involving her older sister Lorina (born 11 May 1849, so she would have been 14 at the time), her governess, or her mother who was also nicknamed "Ina". Some writers, e.g., Derek Hudson and Roger Lancelyn Green, stop short of identifying Dodgson as a paedophile, but concur that he had a passion for small female children and next to no interest in the adult world. The basis for Dodgson's interest in female children has been challenged in the last ten years by several writers and scholars (see the 'Carroll Myth' above). Literary works * La Guida di Bragia, a Ballad Opera for the Marionette Theatre (around 1850) * A Tangled Tale * Alice's Adventures in Wonderland (1865) * Facts * Rhyme? And Reason? (also published as Phantasmagoria) * Pillow Problems * Sylvie and Bruno * Sylvie and Bruno Concluded * The Hunting of the Snark (1876) * Three Sunsets and Other Poems * Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There (includes "Jabberwocky" and "The Walrus and the Carpenter") (1871) * What the Tortoise Said to Achilles Mathematical works * A Syllabus of Plane Algebraic Geometry (1860) * The Fifth Book of Euclid Treated Algebraically (1858 and 1868) * An Elementary Treatise on Determinants, With Their Application to Simultaneous Linear Equations and Algebraic Equations * Euclid and his Modern Rivals (1879), both literary and mathematical in style * Symbolic Logic Part I * Symbolic Logic Part II (published posthumously) * The Alphabet Cipher (1868) * The Game of Logic * Some Popular Fallacies about Vivisection * Curiosa Mathematica I (1888) * Curiosa Mathematica II (1892) * The Theory of Committees and Elections, collected, edited, analysed, and published in 1958, by Duncan Black References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lewis_Carroll


John Boyle O’Reilly (28 June 1844–10 August 1890) was an Irish-born poet, journalist and fiction writer. As a youth in Ireland, he was a member of the Irish Republican Brotherhood, or Fenians, for which he was transported to Western Australia. After escaping to the United States, he became a prominent spokesperson for the Irish community and culture, through his editorship of the Boston newspaper The Pilot, his prolific writing, and his lecture tours.


John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet, polemicist, a scholarly man of letters, and a civil servant for the Commonwealth (republic) of England under Oliver Cromwell. He wrote at a time of religious flux and political upheaval, and is best known for his epic poem Paradise Lost. Milton's poetry and prose reflect deep personal convictions, a passion for freedom and self determination, and the urgent issues and political turbulence of his day. Writing in English, Latin, and Italian, he achieved international renown within his lifetime, and his celebrated Areopagitica, (written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship) is among history’s most influential and impassioned defenses of free speech and freedom of the press.
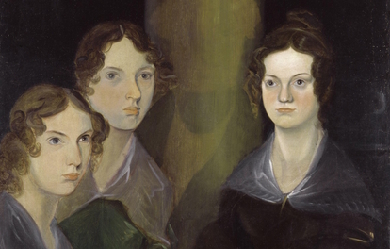

Emily Jane Brontë (30 July 1818 – 19 December 1848) was an English novelist and poet, best remembered for her solitary novel, Wuthering Heights, now considered a classic of English literature. Emily was the third eldest of the four surviving Brontë siblings, between the youngest Anne and her brother Branwell. She published under the pen name Ellis Bell. She was born in Thornton, near Bradford in Yorkshire, to Maria Branwell and Patrick Brontë. She was the younger sister of Charlotte Brontë and the fifth of six children. In 1824, the family moved to Haworth, where Emily's father was perpetual curate, and it was in these surroundings that their literary gifts flourished.


Alfred Austin DL (30 May 1835– 2 June 1913) was an English poet who was appointed Poet Laureate in 1896, after an interval following the death of Tennyson, when the other candidates had either caused controversy or refused the honour. It was claimed that he was being rewarded for his support for the Conservative leader Lord Salisbury in the General Election of 1895. Austin’s poems are little-remembered today, his most popular work being prose idylls celebrating nature.


Wallace Stevens was born in Reading, Pennsylvania, on October 2, 1879. He attended Harvard University as an undergraduate from 1897 to 1900. He planned to travel to Paris as a writer, but after a working briefly as a reporter for the New York Herald Times, he decided to study law. He graduated with a degree from New York Law School in 1903 and was admitted to the U.S. Bar in 1904. He practised law in New York City until 1916. Though he had serious determination to become a successful lawyer, Stevens had several friends among the New York writers and painters in Greenwich Village, including the poets William Carlos Williams, Marianne Moore, and E. E. Cummings. In 1914, under the pseudonym "Peter Parasol," he sent a group of poems under the title "Phases" to Harriet Monroe for a war poem competition for Poetry magazine. Stevens did not win the prize, but was published by Monroe in November of that year. Stevens moved to Connecticut in 1916, having found employment at the Hartford Accident and Indemnity Co., of which he became vice president in 1934. He had began to establish an identity for himself outside the world of law and business, however, and his first book of poems, Harmonium, published in 1923, exhibited the influence of both the English Romantics and the French symbolists, an inclination to aesthetic philosophy, and a wholly original style and sensibility: exotic, whimsical, infused with the light and color of an Impressionist painting. For the next several years, Stevens focused on his business life. He began to publish new poems in 1930, however, and in the following year, Knopf published an second edition of Harmonium, which included fourteen new poems and left out three of the decidedly weaker ones. More than any other modern poet, Stevens was concerned with the transformative power of the imagination. Composing poems on his way to and from the office and in the evenings, Stevens continued to spend his days behind a desk at the office, and led a quiet, uneventful life. Though now considered one of the major American poets of the century, he did not receive widespread recognition until the publication of his Collected Poems, just a year before his death. His major works include Ideas of Order (1935), The Man With the Blue Guitar (1937), Notes Towards a Supreme Fiction (1942), and a collection of essays on poetry, The Necessary Angel (1951). Stevens died in Hartford in 1955. Poetry Harmonium (1923) Ideas of Order (1935) Owl's Clover (1936) The Man With the Blue Guitar (1937) Notes Towards a Supreme Fiction (1942) Parts of a World (1942) Esthétique du Mal (1945) Three Academic Pieces (1947) Transport to Summer (1947) Primitive Like an Orb (1948) Auroras of Autumn (1950) Collected Poems (1954) Opus Posthumous (1957) The Palm at the End of the Mind (1967) Prose The Necessary Angel (1951) Plays Three Travellers Watch the Sunrise (1916) Carlos Among the Candles (1917) References Poets.org — http://www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/124


James Russell Lowell (/ˈloʊəl/; February 22, 1819– August 12, 1891) was an American Romantic poet, critic, editor, and diplomat. He is associated with the Fireside Poets, a group of New England writers who were among the first American poets who rivaled the popularity of British poets. These poets usually used conventional forms and meters in their poetry, making them suitable for families entertaining at their fireside. Lowell graduated from Harvard College in 1838, despite his reputation as a troublemaker, and went on to earn a law degree from Harvard Law School. He published his first collection of poetry in 1841 and married Maria White in 1844. He and his wife had several children, though only one survived past childhood. The couple soon became involved in the movement to abolish slavery, with Lowell using poetry to express his anti-slavery views and taking a job in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, as the editor of an abolitionist newspaper. After moving back to Cambridge, Lowell was one of the founders of a journal called The Pioneer, which lasted only three issues. He gained notoriety in 1848 with the publication of A Fable for Critics, a book-length poem satirizing contemporary critics and poets. The same year, he published The Biglow Papers, which increased his fame. He went on to publish several other poetry collections and essay collections throughout his literary career. Maria White died in 1853, and Lowell accepted a professorship of languages at Harvard in 1854; he continued to teach there for twenty years. He traveled to Europe before officially assuming his role in 1856. He married his second wife, Frances Dunlap, shortly thereafter in 1857. That year Lowell also became editor of The Atlantic Monthly. It was not until 20 years later that Lowell received his first political appointment, the ambassadorship to the Kingdom of Spain. He was later appointed ambassador to the Court of St. James’s. He spent his last years in Cambridge, in the same estate where he was born, and died there in 1891. Lowell believed that the poet played an important role as a prophet and critic of society. He used poetry for reform, particularly in abolitionism. However, Lowell’s commitment to the anti-slavery cause wavered over the years, as did his opinion on African-Americans. Lowell attempted to emulate the true Yankee accent in the dialogue of his characters, particularly in The Biglow Papers. This depiction of the dialect, as well as Lowell’s many satires, was an inspiration to writers like Mark Twain and H.L. Mencken. Biography Early life The first of the Lowell family ancestors to come to the United States from Britain was Percival Lowle, who settled in Newbury, Massachusetts, in 1639. James Russell Lowell was born February 22, 1819, the son of the Reverend Charles Russell Lowell, Sr. (1782–1861), a minister at a Unitarian church in Boston, who had previously studied theology at Edinburgh, and Harriett Brackett Spence Lowell. By the time James Russell Lowell was born, the family owned a large estate in Cambridge called Elmwood. He was the youngest of six children; his siblings were Charles, Rebecca, Mary, William, and Robert. Lowell’s mother built in him an appreciation for literature at an early age, especially in poetry, ballads, and tales from her native Orkney. He attended school under Sophia Dana, who would later marry George Ripley, and later studied at a school run by a particularly harsh disciplinarian, where one of his classmates was Richard Henry Dana, Jr. Beginning in 1834, at the age of 15, Lowell attended Harvard College, though he was not a good student and often got into trouble. In his sophomore year alone, he was absent from required chapel attendance 14 times and from classes 56 times. In his last year there, he wrote, “During Freshman year, I did nothing, during Sophomore year I did nothing, during Junior year I did nothing, and during Senior year I have thus far done nothing in the way of college studies.” In his senior year, he became one of the editors of Harvardiana literary magazine, to which he contributed prose and poetry that he admitted was of low quality. As he said later, "I was as great an ass as ever brayed & thought it singing." During his undergraduate years, Lowell was a member of Hasty Pudding and served both as Secretary and Poet. Lowell was elected the poet of the class of 1838 and, as was tradition, was asked to recite an original poem on Class Day, the day before Commencement, on July 17, 1838. Lowell, however, was suspended and not allowed to participate. Instead, his poem was printed and made available thanks to subscriptions paid by his classmates. Lowell had composed the poem in Concord, Massachusetts, where, because of his neglect of his studies, he had been exiled by the Harvard faculty to the care of the Rev. Barzallai Frost. During his stay in Concord, he became friends with Ralph Waldo Emerson, and got to know the other Transcendentalists. The poem satirized the social movements of the day; abolitionists, Thomas Carlyle, Emerson, and the Transcendentalists were treated. Not knowing what vocation to choose after graduating, he vacillated among business, the ministry, medicine, and law. Having decided to practice law, he enrolled at Harvard Law School in 1840 and was admitted to the bar two years later. While studying law, however, he contributed poems and prose articles to various magazines. During this time, Lowell was admittedly depressed and often had suicidal thoughts. He once confided to a friend that he held a cocked pistol to his forehead and considered killing himself at the age of 20. Marriage and family In late 1839, Lowell met Maria White through her brother William, a classmate of his at Harvard, and the two became engaged in the autumn of 1840. Maria’s father Abijah White, a wealthy merchant from Watertown, insisted that their wedding be postponed until Lowell had gainful employment. They were finally married on December 26, 1844, shortly after the groom published Conversations on the Old Poets, a collection of his previously published essays. A friend described their relationship as “the very picture of a True Marriage.” Lowell himself believed she was made up “half of earth and more than half of Heaven.” Like Lowell, she wrote poetry, and the next twelve years of Lowell’s life were deeply affected by her influence. He said his first book of poetry, A Year’s Life (1841), “owes all its beauty to her,” though it only sold 300 copies. Her character and beliefs led her to become involved in the movements directed against intemperance and slavery. Maria was a member of the Boston Female Anti-Slavery Society and persuaded her husband to become an abolitionist. James had previously expressed antislavery sentiments, but Maria urged him towards more active expression and involvement. His second volume of poems, Miscellaneous Poems, expressed these antislavery thoughts and its 1,500 copies sold well. Maria was in poor health, and thinking her lungs could heal there, the couple moved to Philadelphia shortly after their marriage. In Philadelphia, he became a contributing editor for the Pennsylvania Freeman, an abolitionist newspaper. In the spring of 1845, the Lowells returned to Cambridge, Massachusetts, to make their home at Elmwood. They had four children, though only one (Mabel, born 1847) survived past infancy. Their first, Blanche, was born December 31, 1845, but lived only fifteen months; Rose, born in 1849, survived only a few months as well; their only son, Walter, was born in 1850 but died in 1852. Lowell was very affected by the loss of almost all of his children. His grief over the death of his first daughter in particular was expressed in his poem “The First Snowfall” (1847). Again, Lowell considered suicide, writing to a friend that he thought “of my razors and my throat and that I am a fool and a coward not to end it all at once.” Literary career Lowell’s earliest poems were published without remuneration in the Southern Literary Messenger in 1840. Lowell, inspired to new efforts towards self-support, joined with his friend Robert Carter in founding a literary journal, The Pioneer. The periodical was distinguished by the fact that most of its content was new rather than material that had been previously published elsewhere, and by the inclusion of very serious criticism, which covered not only literature but also art and music. Lowell wrote that it would “furnish the intelligent and reflecting portion of the Reading Public with a rational substitute for the enormous quantity of thrice-diluted trash, in the shape of namby-pamby love tales and sketches, which is monthly poured out to them by many of our popular Magazines.” William Wetmore Story noted the journal’s higher taste, writing that "it took some stand & appealled to a higher intellectual Standard than our puerile milk or watery namby-pamby Mags with which we are overrun." The first issue of the journal included the first appearance of “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allan Poe. Lowell, shortly after the first issue, was treated for an eye disease in New York, and in his absence Carter did a poor job of managing the journal. After three monthly numbers, beginning in January 1843, the magazine ceased publication, leaving Lowell $1,800 in debt. Poe mourned the journal’s demise, calling it “a most severe blow to the cause—the cause of a Pure Taste.” Despite the failure of The Pioneer, Lowell continued his interest in the literary world. He wrote a series on “Anti-Slavery in the United States” for the London Daily News, though his series was discontinued by the editors after four articles in May 1846. Lowell had published these articles anonymously, believing they would have more impact if they were not known to be the work of a committed abolitionist. In the spring of 1848 he formed a connection with the National Anti-Slavery Standard of New York, agreeing to contribute weekly either a poem or a prose article. After only one year, he was asked to contribute half as often to the Standard to make room for contributions from Edmund Quincy, another writer and reformer. A Fable for Critics, one of Lowell’s most popular works, was published in 1848. A satire, it was published anonymously. It proved popular, and the first three thousand copies sold out quickly. In it, Lowell took good-natured jabs at his contemporary poets and critics. Not all the subjects included were pleased, however. Edgar Allan Poe, who had been referred to as part genius and “two-fifths sheer fudge,” reviewed the work in the Southern Literary Messenger and called it “'loose’—ill-conceived and feebly executed, as well in detail as in general.... we confess some surprise at his putting forth so unpolished a performance.” Lowell offered the profits from the book’s success, which proved relatively small, to his New York friend Charles Frederick Briggs, despite his own financial needs. In 1848, Lowell also published The Biglow Papers, later named by the Grolier Club as the most influential book of 1848. The first 1,500 copies sold out within a week and a second edition was soon issued, though Lowell made no profit, having had to absorb the cost of stereotyping the book himself. The book presented three main characters, each representing different aspects of American life and using authentic American dialects in their dialogue. Under the surface, The Biglow Papers was also a denunciation of the Mexican–American War and war in general. First trip to Europe In 1850, Lowell’s mother died unexpectedly, as did his third daughter, Rose. Her death left Lowell depressed and reclusive for six months, despite the birth of his son Walter by the end of the year. He wrote to a friend that death “is a private tutor. We have no fellow-scholars, and must lay our lessons to heart alone.” These personal troubles as well as the Compromise of 1850 inspired Lowell to accept an offer from William Wetmore Story to spend a winter in Italy. To pay for the trip, Lowell sold land around Elmwood, intending to sell off further acres of the estate over time to supplement his income, ultimately selling off 25 of the original 30 acres (120,000 m2). Walter died suddenly in Rome of cholera, and Lowell and his wife, with their daughter Mabel, returned to the United States in October 1852. Lowell published recollections of his journey in several magazines, many of which would be collected years later as Fireside Travels (1867). He also edited volumes with biographical sketches for a series on British Poets. His wife Maria, who had been suffering from poor health for many years, became very ill in the spring of 1853 and died on October 27 of tuberculosis. Just before her burial, her coffin was opened so that her daughter Mabel could see her face while Lowell “leaned for a long while against a tree weeping,” according to Henry Wadsworth Longfellow and his wife, who were in attendance. In 1855, Lowell oversaw the publication of a memorial volume of his wife’s poetry, with only fifty copies for private circulation. Despite his self-described “naturally joyous” nature, life for Lowell at Elmwood was further complicated by his father becoming deaf in his old age, and the deteriorating mental state of his sister Rebecca, who sometimes went a week without speaking. He again cut himself off from others, becoming reclusive at Elmwood, and his private diaries from this time period are riddled with the initials of his wife. On March 10, 1854, for example, he wrote: "Dark without & within. M.L. M.L. M.L." Longfellow, a friend and neighbor, referred to Lowell as “lonely and desolate.” Professorship and second marriage At the invitation of his cousin John Amory Lowell, James Russell Lowell was asked to deliver a lecture at the prestigious Lowell Institute. Some speculated the opportunity was because of the family connection, offered as an attempt to bring him out of his depression. Lowell chose to speak on “The English Poets,” telling his friend Briggs that he would take revenge on dead poets “for the injuries received by one whom the public won’t allow among the living.” The first of the twelve-part lecture series was to be on January 9, 1855, though by December, Lowell had only completed writing five of them, hoping for last-minute inspiration. His first lecture was on John Milton and the auditorium was oversold; Lowell had to give a repeat performance the next afternoon. Lowell, who had never spoken in public before, was praised for these lectures. Francis James Child said that Lowell, whom he deemed was typically “perverse,” was able to “persist in being serious contrary to his impulses and his talents.” While his series was still in progress, Lowell was offered the Smith Professorship of Modern Languages at Harvard, a post vacated by Longfellow, at an annual salary of $1,200, though he never applied for it. The job description was changing after Longfellow; instead of teaching languages directly, Lowell would supervise the department and deliver two lecture courses per year on topics of his own choosing. Lowell accepted the appointment, with the proviso that he should have a year of study abroad. He set sail on June 4 of that year, leaving his daughter Mabel in the care of a governess named Frances Dunlap. Abroad, he visited Le Havre, Paris, and London, spending time with friends including Story, Robert Browning and Elizabeth Barrett Browning, and Leigh Hunt. Primarily, however, Lowell spent his time abroad studying languages, particularly German, which he found difficult. He complained: “The confounding genders! If I die I shall have engraved on my tombstone that I died of der, die, das, not because I caught them but because I couldn’t.” He returned to the United States in the summer of 1856 and began his college duties. Towards the end of his professorship, then-president of Harvard Charles William Eliot noted that Lowell seemed to have “no natural inclination” to teach; Lowell agreed, but retained his position for twenty years. He focused on teaching literature, rather than etymology, hoping that his students would learn to enjoy the sound, rhythm, and flow of poetry rather than the technique of words. He summed up his method: “True scholarship consists in knowing not what things exists, but what they mean; it is not memory but judgment.” Still grieving the loss of his wife, during this time Lowell avoided Elmwood and instead lived on Kirkland Street in Cambridge, an area known as Professors’ Row. He stayed there, along with his daughter Mabel and her governess Frances Dunlap, until January 1861. Lowell had intended never to remarry after the death of his wife Maria White. However, in 1857, surprising his friends, he became engaged to Frances Dunlap, who many described as simple and unattractive. Dunlap, niece of the former governor of Maine Robert P. Dunlap, was a friend of Lowell’s first wife and formerly wealthy, though she and her family had fallen into reduced circumstances. Lowell and Dunlap married on September 16, 1857, in a ceremony performed by his brother. Lowell wrote, "My second marriage was the wisest act of my life, & as long as I am sure of it, I can afford to wait till my friends agree with me.” The war years and beyond In the autumn of 1857, The Atlantic Monthly was established, and Lowell was its first editor. With its first issue in November of that year, he at once gave the magazine the stamp of high literature and of bold speech on public affairs. In January 1861, Lowell’s father died of a heart attack, inspiring Lowell to move his family back to Elmwood. As he wrote to his friend Briggs, “I am back again to the place I love best. I am sitting in my old garret, at my old desk, smoking my old pipe... I begin to feel more like my old self than I have these ten years.” Shortly thereafter, in May, he left The Atlantic Monthly when James Thomas Fields took over as editor; the magazine had been purchased by Ticknor and Fields for $10,000 two years before. Lowell returned to Elmwood by January 1861 but maintained an amicable relationship with the new owners of the journal, continuing to submit his poetry and prose for the rest of his life. His prose, however, was more abundantly presented in the pages of the North American Review during the years 1862–1872. For the Review, he served as a coeditor along with Charles Eliot Norton. Lowell’s reviews for the journal covered a wide variety of literary releases of the day, though he was writing fewer poems. As early as 1845, Lowell had predicted the debate over slavery would lead to war and, as the American Civil War broke out in the 1860s, Lowell used his role at the Review to praise Abraham Lincoln and his attempts to maintain the Union. Lowell lost three nephews during the war, including Charles Russell Lowell, Jr, who became a Brigadier General and fell at the battle of Cedar Creek. Lowell himself was generally a pacifist. Even so, he wrote, “If the destruction of slavery is to be a consequence of the war, shall we regret it? If it be needful to the successful prosecution of the war, shall anyone oppose it?” His interest in the Civil War inspired him to write a second series of The Biglow Papers, including one specifically dedicated to the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation called “Sunthin’ in the Pastoral Line” in 1862. Shortly after Lincoln’s assassination, Lowell was asked to present a poem at Harvard in memory of graduates killed in the war. His poem, “Commemoration Ode,” cost him sleep and his appetite, but was delivered on July 21, 1865, after a 48-hour writing binge. Lowell had high hopes for his performance but was overshadowed by the other notables presenting works that day, including Ralph Waldo Emerson and Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. “I did not make the hit I expected,” he wrote, “and am ashamed at having been tempted again to think I could write poetry, a delusion from which I have been tolerably free these dozen years.” Despite his personal assessment, friends and other poets sent many letters to Lowell congratulating him. Emerson referred to his poem’s "high thought & sentiment" and James Freeman Clarke noted its “grandeur of tone.” Lowell later expanded it with a strophe to Lincoln. In the 1860s, Lowell’s friend Longfellow spent several years translating Dante Alighieri’s Divine Comedy and regularly invited others to help him on Wednesday evenings. Lowell was one of the main members of the so-called “Dante Club,” along with William Dean Howells, Charles Eliot Norton and other occasional guests. Shortly after serving as a pallbearer at the funeral of friend and publisher Nathaniel Parker Willis, on January 24, 1867, Lowell decided to produce another collection of his poetry. Under the Willows and Other Poems was released in 1869, though Lowell originally wanted to title it The Voyage to the Vinland and Other Poems. The book, dedicated to Norton, collected poems Lowell had written within the previous twenty years and was his first poetry collection since 1848. Lowell intended to take another trip to Europe. To finance it, he sold off more of Elmwood’s acres and rented the house to Thomas Bailey Aldrich; Lowell’s daughter Mabel, by this time, had moved into a new home with her husband Edward Burnett, the son of a successful businessman-farmer from Southboro, Massachusetts. Lowell and his wife set sail on July 8, 1872, after he took a leave of absence from Harvard. They visited England, Paris, Switzerland, and Italy. While overseas, he received an honorary Doctorate of Law from the University of Oxford and another from Cambridge University. They returned to the United States in the summer of 1874. Political appointments Lowell resigned from his Harvard professorship in 1874, though he was persuaded to continue teaching through 1877. It was in 1876 that Lowell first stepped into the field of politics. That year, he served as a delegate to the Republican National Convention in Cincinnati, Ohio, speaking on behalf of presidential candidate Rutherford B. Hayes. Hayes won the nomination and, eventually, the presidency. In May 1877, President Hayes, an admirer of The Biglow Papers, sent William Dean Howells to Lowell with a handwritten note proffering an ambassadorship to either Austria or Russia; Lowell declined, but noted his interest in Spanish literature. Lowell was then offered and accepted the role of Minister to the court of Spain at an annual salary of $12,000. Lowell sailed from Boston on July 14, 1877, and, though he expected he would be away for a year or two, he would not return to the United States until 1885, with the violinist Ole Bull renting Elmwood for a portion of that time. The Spanish media referred to him as “José Bighlow.” Lowell was well-prepared for his political role, having been trained in law, as well as being able to read in multiple languages. He had trouble socializing while in Spain, however, and amused himself by sending humorous dispatches to his political bosses in the United States, many of which were later collected and published posthumously in 1899 as Impressions of Spain. Lowell’s social life improved when the Spanish Academy elected him a corresponding member in late 1878, allowing him contribute to the preparation of a new dictionary. In January 1880, Lowell was informed he was appointed Minister to England, his nomination made without his knowledge as far back as June 1879. He was granted a salary of $17,500 with about $3,500 for expenses. While serving in this capacity, he addressed an importation of allegedly diseased cattle and made recommendations that predated the Pure Food and Drug Act. Queen Victoria commented that she had never seen an ambassador who “created so much interest and won so much regard as Mr. Lowell.” Lowell held this role until the close of Chester A. Arthur’s presidency in the spring of 1885, despite his wife’s failing health. Lowell was already well known in England for his writing and, during his time there, he befriended fellow author Henry James, who referred to him as “conspicuously American.” Lowell also befriended Leslie Stephen many years earlier and became the godfather to his daughter, future writer Virginia Woolf. Lowell was popular enough that he was offered a professorship at Oxford after his recall by president Grover Cleveland, though the offer was declined. His second wife, Frances, died on February 19, 1885, while still in England. Later years and death He returned to the United States by June 1885, living with his daughter and her husband in Southboro, Massachusetts. He then spent time in Boston with his sister before returning to Elmwood in November 1889. By this time, most of his friends were dead, including Quincy, Longfellow, Dana, and Emerson, leaving him depressed and contemplating suicide again. Lowell spent part of the 1880s delivering various speeches, and his last published works were mostly collections of essays, including Political Essays, and a collection of his poems Heartsease and Rue in 1888. His last few years he traveled back to England periodically and when he returned to the United States in the fall of 1889, he moved back to Elmwood with Mabel, while her husband worked for clients in New York and New Jersey. That year, Lowell gave an address at the centenary of George Washington’s inauguration. Also that year, the Boston Critic dedicated a special issue to Lowell on his seventieth birthday to recollections and reminiscences by his friends, including former presidents Hayes and Benjamin Harrison and British Prime Minister William Ewart Gladstone as well as Alfred Tennyson and Francis Parkman. In the last few months of his life, Lowell struggled with gout, sciatica in his left leg, and chronic nausea; by the summer of 1891, doctors believed that Lowell had cancer in his kidneys, liver, and lungs. His last few months, he was administered opium for the pain and was rarely fully conscious. He died on August 12, 1891, at Elmwood. After services in the Appleton Chapel, he was buried in Mount Auburn Cemetery. After his death, Norton served as his literary executor and published several collections of Lowell’s works and his letters. Writing style and literary theory Early in his career, James Russell Lowell’s writing was influenced by Swedenborgianism, a Spiritualism-infused form of Christianity founded by Emanuel Swedenborg, causing Frances Longfellow (wife of the poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow) to mention that “he has been long in the habit of seeing spirits.” He composed his poetry rapidly when inspired by an “inner light” but could not write to order. He subscribed to the common nineteenth-century belief that the poet was a prophet but went further, linking religion, nature, and poetry, as well as social reform. Evert Augustus Duyckinck and others welcomed Lowell as part of Young America, a New York-based movement. Though not officially affiliated with them, he shared some of their ideals, including the belief that writers have an inherent insight into the moral nature of humanity and have an obligation for literary action along with their aesthetic function. Unlike many of his contemporaries, including members of Young America, Lowell did not advocate for the creation of a new national literature. Instead, he called for a natural literature, regardless of country, caste, or race, and warned against provincialism which might “put farther off the hope of one great brotherhood.” He agreed with his neighbor Longfellow that “whoever is most universal, is also most national.” As Lowell said: I believe that no poet in this age can write much that is good unless he gives himself up to [the radical] tendency... The proof of poetry is, in my mind, that it reduces to the essence of a single line the vague philosophy which is floating in all men’s minds, and so render it portable and useful, and ready to the hand... At least, no poem ever makes me respect its author which does not in some way convey a truth of philosophy. A scholar of linguistics, Lowell was one of the founders of the American Dialect Society. He used this interest in his writing, particularly in The Biglow Papers, presenting a heavily ungrammatical phonetic spelling of the Yankee dialect. In using this vernacular, Lowell intended to get closer to the common man’s experience and was rebelling against more formal and, as he thought, unnatural representations of Americans in literature. As he wrote in his introduction to The Biglow Papers, “few American writers or speakers wield their native language with the directness, precision, and force that are common as the day in the mother country.” Though intentionally humorous, this accurate presentation of the dialect was pioneering work in American literature. For example, Lowell’s character Hosea Biglow says in verse: Lowell is considered one of the Fireside Poets, a group of writers from New England in the 1840s who all had a substantial national following and whose work was often read aloud by the family fireplace. Besides Lowell, the main figures from this group were Longfellow, Holmes, John Greenleaf Whittier, and William Cullen Bryant. Beliefs Although he was an abolitionist, Lowell’s opinions on African-Americans wavered. Though Lowell advocated suffrage for blacks, he noted that their ability to vote could be troublesome. Even so, he wrote, “We believe the white race, by their intellectual and traditional superiority, will retain sufficient ascendancy to prevent any serious mischief from the new order of things.” Freed slaves, he wrote, were "dirty, lazy & lying." Even before his marriage to the abolitionist Maria White, Lowell wrote: “The abolitionists are the only ones with whom I sympathize of the present extant parties.” After his marriage, Lowell at first did not share White’s enthusiasm for the cause but was eventually pulled in. The couple often gave money to fugitive slaves, even when their own financial situation was not strong, especially if they were asked to free a spouse or child. Even so, he did not always fully agree with the followers of the movement. The majority of these people, he said, “treat ideas as ignorant persons do cherries. They think them unwholesome unless they are swallowed, stones and all.” Lowell depicted Southerners very unfavorably in his second collection of The Biglow Papers but, by 1865, admitted that Southerners were “guilty only of weakness” and, by 1868, said that he sympathized with Southerners and their viewpoint on slavery. Enemies and friends of Lowell alike questioned his vacillating interest in the question of slavery. Abolitionist Samuel Joseph May accused Lowell of trying to quit the movement because of his association with Harvard and the Boston Brahmin culture: “Having got into the smooth, dignified, self-complacent, and change-hating society of the college and its Boston circles, Lowell has gone over to the world, and to 'respectability’.” Lowell was also involved in other reform movements. He urged for better conditions for factory workings, opposed capital punishment, and supported the temperance movement. His friend Longfellow was especially concerned about his fanaticism for temperance, worrying that Lowell would ask him to destroy his wine cellar. There are many references to Lowell’s drinking during his college years and part of his reputation in school was based on it. His friend Edward Everett Hale denied these allegations and, even then, Lowell considered joining the “Anti-Wine” club and later, during the early years of his first marriage, became a teetotaler. However, as Lowell gained notoriety, he became popular in social circles and clubs and, away from his wife, he drank rather heavily. When he drank, he had wild mood swings, ranging from euphoria to frenzy. Criticism and legacy In 1849, Lowell said of himself, “I am the first poet who has endeavored to express the American Idea, and I shall be popular by and by.” Poet Walt Whitman said: “Lowell was not a grower—he was a builder. He built poems: he didn’t put in the seed, and water the seed, and send down his sun—letting the rest take care of itself: he measured his poems—kept them within formula.” Fellow Fireside Poet John Greenleaf Whittier praised Lowell by writing two poems in his honor and calling him “our new Theocritus” and “one of the strongest and manliest of our writers–a republican poet who dares to speak brave words of unpopular truth.” British author Thomas Hughes referred to Lowell as one of the most important writers in the United States: "Greece had her Aristophanes; Rome her Juvenal; Spain has had her Cervantes; France her Rabelais, her Molière, her Voltaire; Germany her Jean Paul, her Heine; England her Swift, her Thackeray; and America has her Lowell." Lowell’s satires and use of dialect were an inspiration for writers like Mark Twain, William Dean Howells, H. L. Mencken, and Ring Lardner. Contemporary critic and editor Margaret Fuller wrote, “his verse is stereotyped; his thought sounds no depth, and posterity will not remember him.” Duyckinck thought Lowell was too similar to other poets like William Shakespeare and John Milton. Ralph Waldo Emerson noted that, though Lowell had significant technical skill, his poetry “rather expresses his wish, his ambition, than the uncontrollable interior impulse which is the authentic mark of a new poem... and which is felt in the pervading tone, rather than in brilliant parts or lines.” Even his friend Richard Henry Dana Jr., questioned Lowell’s abilities, calling him "very clever, entertaining & good humored... but he is rather a trifler, after all." In the twentieth century, poet Richard Armour dismissed Lowell, writing: “As a Harvard graduate and an editor for the Atlantic Monthly, it must have been difficult for Lowell to write like an illiterate oaf, but he succeeded.” The poet Amy Lowell featured her relative James Russell Lowell in her poem A Critical Fable (1922), the title mocking A Fable for Critics. Here, a fictional version of Lowell says he does not believe that women will ever be equal to men in the arts and “the two sexes cannot be ranked counterparts.” Modern literary critic Van Wyck Brooks wrote that Lowell’s poetry was forgettable: “one read them five times over and still forgot them, as if this excellent verse had been written in water.” Nonetheless, in 1969 the Modern Language Association established a prize named after Lowell, awarded annually for “an outstanding literary or linguistic study, a critical edition of an important work, or a critical biography.” Lowell’s poem “The Present Crisis,” an early work that addressed the national crisis over slavery leading up to the Civil War, has had an impact in the modern civil rights movement. The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People named its newsletter The Crisis after the poem, and Martin Luther King, Jr. frequently quoted the poem in his speeches and sermons. The poem was also the source of the hymn Once to Every Man and Nation. List of selected works Poetry collections * A Year’s Life (1841) * Miscellaneous Poems (1843) * The Biglow Papers (1848) * A Fable for Critics (1848) * Poems (1848) * The Vision of Sir Launfal (1848) * Under the Willows (1869) * The Cathedral (1870) * Heartsease and Rue (1888) Essay collections * Conversations on the Old Poets (1844) * Fireside Travels (1864) * Among My Books (1870) * My Study Windows (1871) * Among My Books (second collection, 1876) * Democracy and Other Addresses (1886) * Political Essays (1888) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Russell_Lowell


John Newton (24 July 1725– 21 December 1807) was an English sailor, in the Royal Navy for a period, and later a captain of slave ships. He became ordained as an evangelical Anglican cleric, served Olney, Buckinghamshire for two decades, and also wrote hymns, known for “Amazing Grace” and “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken”. Newton started his career at sea at a young age, and worked on slave ships in the slave trade for several years. After experiencing a period of Christian conversion Newton eventually renounced his trade and became a prominent supporter of abolitionism, living to see Britain’s abolition of the African slave trade in 1807. Early life John Newton was born in Wapping, London, in 1725, the son of Elizabeth (née Scatliff) and John Newton Sr., a shipmaster in the Mediterranean service. Elizabeth was the only daughter of Simon Scatliff, an instrument maker from London (the marriage register records her maiden name as Seatcliffe). Elizabeth was brought up as a Nonconformist. She died of tuberculosis (then called consumption) in July 1732, about two weeks before John’s seventh birthday. Newton spent two years at boarding school before going to live in Aveley in Essex, the home of his father’s new wife. At age eleven he first went to sea with his father. Newton sailed six voyages before his father retired in 1742. At that time, Newton’s father made plans for him to work at a sugarcane plantation in Jamaica. Instead, Newton signed on with a merchant ship sailing to the Mediterranean Sea. Impressment into naval service In 1743, while going to visit friends, Newton was captured and pressed into the naval service by the Royal Navy. He became a midshipman aboard HMS Harwich. At one point Newton tried to desert and was punished in front of the crew of 350. Stripped to the waist and tied to the grating, he received a flogging of eight dozen lashes and was reduced to the rank of a common seaman. Following that disgrace and humiliation, Newton initially contemplated murdering the captain and committing suicide by throwing himself overboard. He recovered, both physically and mentally. Later, while Harwich was en route to India, he transferred to Pegasus, a slave ship bound for West Africa. The ship carried goods to Africa and traded them for slaves to be shipped to the colonies in the Caribbean and North America. Enslavement and rescue Newton did not get along with the crew of Pegasus. They left him in West Africa with Amos Clowe, a slave dealer. Clowe took Newton to the coast and gave him to his wife, Princess Peye of the Sherbro people. She abused and mistreated Newton equally as much as she did her other slaves. Newton later recounted this period as the time he was “once an infidel and libertine, a servant of slaves in West Africa.” Early in 1748 he was rescued by a sea captain who had been asked by Newton’s father to search for him, and returned to England on the merchant ship Greyhound, which was carrying beeswax and dyer’s wood, now referred to as camwood. Spiritual conversion During his 1748 voyage to England after his rescue, Newton had a spiritual conversion. The ship encountered a severe storm off the coast of County Donegal in Ulster, Ireland, and almost sank. Newton awoke in the middle of the night and, as the ship filled with water, called out to God. The cargo shifted and stopped up the hole, and the ship drifted to safety. Newton marked this experience as the beginning of his conversion to evangelical Christianity. He began to read the Bible and other religious literature. By the time he reached Britain, he had accepted the doctrines of evangelical Christianity. The date was 10 March 1748, an anniversary he marked for the rest of his life. From that point on, he avoided profanity, gambling, and drinking. Although he continued to work in the slave trade, he had gained sympathy for the slaves during his time in Africa. He later said that his true conversion did not happen until some time later: “I cannot consider myself to have been a believer in the full sense of the word, until a considerable time afterwards.” Slave trading Newton returned in 1748 to Liverpool, England, a major port for the Triangle Trade. Partly due to the influence of his father’s friend Joseph Manesty, he obtained a position as first mate aboard the slave ship Brownlow, bound for the West Indies via the coast of Guinea. While in west Africa (1748–49), Newton acknowledged the inadequacy of his spiritual life. He became ill with a fever and professed his full belief in Christ, asking God to take control of his destiny. He later said that this was the first time he felt totally at peace with God. Newton did not however immediately renounce working in the slave trade. After his return to England in 1750, he made three voyages as captain of the slave ships Duke of Argyle (1750) and African (1752–53 and 1753–54). After suffering a severe stroke in 1754, he gave up seafaring and slave-trading activities. But he continued to invest in Manesty’s slaving operations. Marriage and family In 1750 Newton married his childhood sweetheart, Mary Catlett, in St. Margaret’s Church, Rochester. Newton adopted his two orphaned nieces, Elizabeth and Eliza Catlett, children of one of his brothers-in-law and his wife. Newton’s niece Alys Newton later married Mehul, a prince from India. Anglican priest In 1755 Newton was appointed as tide surveyor (a tax collector) of the Port of Liverpool, again through the influence of Manesty. In his spare time, he studied Greek, Hebrew, and Syriac, preparing for serious religious study. He became well known as an evangelical lay minister. In 1757, he applied to be ordained as a priest in the Church of England, but it was more than seven years before he was eventually accepted. During this period, he also applied to the Methodists, Independents and Presbyterians. He mailed applications directly to the Bishops of Chester and Lincoln and the Archbishops of Canterbury and York. Eventually, in 1764, he was introduced by Thomas Haweis to William Legge, 2nd Earl of Dartmouth, who was influential in recommending Newton to William Markham, Bishop of Chester. Haweis suggested Newton for the living of Olney, Buckinghamshire. On 29 April 1764 Newton received deacon’s orders, and finally was ordained as a priest on 17 June. As curate of Olney, Newton was partly sponsored by John Thornton, a wealthy merchant and evangelical philanthropist. He supplemented Newton’s stipend of £60 a year with £200 a year “for hospitality and to help the poor”. Newton soon became well known for his pastoral care, as much as for his beliefs. His friendship with Dissenters and evangelical clergy led to his being respected by Anglicans and Nonconformists alike. He spent sixteen years at Olney. His preaching was so popular that the congregation added a gallery to the church to accommodate the many persons who flocked to hear him. Some five years later, in 1772, Thomas Scott took up the curacy of the neighbouring parishes of Stoke Goldington and Weston Underwood. Newton was instrumental in converting Scott from a cynical ‘career priest’ to a true believer, a conversion which Scott related in his spiritual autobiography The Force Of Truth (1779). Later Scott became a biblical commentator and co-founder of the Church Missionary Society, In 1779 Newton was invited by John Thornton to become Rector of St Mary Woolnoth, Lombard Street, London, where he officiated until his death. The church had been built by Nicholas Hawksmoor in 1727 in the fashionable Baroque style. Newton was one of only two evangelical Anglican priests in the capital, and he soon found himself gaining in popularity amongst the growing evangelical party. He was a strong supporter of evangelicalism in the Church of England. He remained a friend of Dissenters (such as Methodists and Baptists) as well as Anglicans. Young churchmen and people struggling with faith sought his advice, including such well-known social figures as the writer and philanthropist Hannah More, and the young William Wilberforce, a Member of Parliament who had recently suffered a crisis of conscience and religious conversion while contemplating leaving politics. The younger man consulted with Newton, who encouraged Wilberforce to stay in Parliament and “serve God where he was”. In 1792, Newton was presented with the degree of Doctor of Divinity by the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University). Abolitionist In 1788, 34 years after he had retired from the slave trade, Newton broke a long silence on the subject with the publication of a forceful pamphlet Thoughts Upon the Slave Trade, in which he described the horrific conditions of the slave ships during the Middle Passage. He apologized for “a confession, which... comes too late... It will always be a subject of humiliating reflection to me, that I was once an active instrument in a business at which my heart now shudders.” He had copies sent to every MP, and the pamphlet sold so well that it swiftly required reprinting. Newton became an ally of William Wilberforce, leader of the Parliamentary campaign to abolish the African slave trade. He lived to see the British passage of the Slave Trade Act 1807, which enacted this event. Some modern writers have criticised Newton for continuing to participate in the slave trade after his religious conversion, but Christianity did not deter thousands of slaveholders in the colonies from owning other men, nor many others from profiting by the slave trade. Newton came to believe that during the first five of his nine years as a slave trader he had not been a Christian in the full sense of the term. In 1763 he wrote: “I was greatly deficient in many respects... I cannot consider myself to have been a believer in the full sense of the word, until a considerable time afterwards.” Writer and hymnist In 1767 William Cowper, the poet, moved to Olney. He worshipped in Newton’s church, and collaborated with the priest on a volume of hymns; it was published as Olney Hymns in 1779. This work had a great influence on English hymnology. The volume included Newton’s well-known hymns: “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken,” “How Sweet the Name of Jesus Sounds!,” “Let Us Love, and Sing, and Wonder,” “Come, My Soul, Thy Suit Prepare,” “Approach, My Soul, the Mercy-seat”, and “Faith’s Review and Expectation,” which has come to be known by its opening phrase, “Amazing Grace”. Many of Newton’s (as well as Cowper’s) hymns are preserved in the Sacred Harp, a hymnal used in the American South during the Second Great Awakening. Hymns were scored according to the tonal scale for shape note singing. Easily learned and incorporating singers into four-part harmony, shape note music was widely used by evangelical preachers to reach new congregants. Newton also contributed to the Cheap Repository Tracts. He wrote an autobiography entitled An Authentic Narrative of Some Remarkable And Interesting Particulars in the Life of———Communicated, in a Series of Letters, to the Reverend T. Haweiss, which he published anonymously. It was later described as 'written in an easy style, distinguished by great natural shrewdness, and sanctified by the Lord God and prayer’. Final years Newton’s wife Mary Catlett died in 1790, after which he published Letters to a Wife (1793), in which he expressed his grief. Plagued by ill health and failing eyesight, Newton died on 21 December 1807 in London. He was buried beside his wife in St. Mary Woolnoth in London. Both were reinterred at the Church of St. Peter and Paul in Olney in 1893. Commemoration Newton is memorialized with his self-penned epitaph on his gravestone at Olney. When he was initially interred in London, a memorial plaque to Newton, containing his self-penned epitaph, was installed on the wall of St Mary Woolnoth. At the bottom of the plaque are the words: "The above Epitaph was written by the Deceased who directed it to be inscribed on a plain Marble Tablet. He died on December the 21st December 1807. Aged 82 Years, and his Mortal Remains are deposited in the Vault beneath the Church.” The town of Newton, Sierra Leone is named after him. To this day his former town of Olney provides philanthropy for the African town. In 1982, Newton was recognized for his influential hymns by the Gospel Music Association when he was inducted into the Gospel Music Hall of Fame. Portrayals in media Film The film Amazing Grace (2006) highlights Newton’s influence on William Wilberforce. Albert Finney portrays Newton, Ioan Gruffudd is Wilberforce, and the film was directed by Michael Apted. The film portrays Newton as a penitent haunted by the ghosts of 20,000 slaves. The Nigerian film The Amazing Grace (2006), the creation of Nigerian director/writer/producer Jeta Amata, provides an African perspective on the slave trade. Nigerian actors Joke Silva, Mbong Odungide, and Fred Amata (brother of the director) portray Africans who are captured and taken away from their homeland by slave traders. Newton is played by Nick Moran. The 2014 film Freedom tells the story of an American slave (Samuel Woodward, played by Cuba Gooding, Jr.) escaping to freedom via the Underground Railroad. A parallel earlier story depicts John Newton (played by Bernhard Forcher) as the captain of a slave ship bound for America carrying Samuel’s grandfather. Newton’s conversion is explored as well. Stage productions African Snow (2007), a play by Murray Watts, takes place in the mind of John Newton. It was first produced at the York Theatre Royal as a co-production with Riding Lights Theatre Company, transferring to the Trafalgar Studios in London’s West End and a National Tour. Newton was played by Roger Alborough and Olaudah Equiano by Israel Oyelumade. The musical Amazing Grace is a dramatisation of Newton’s life. The 2014 pre-Broadway and 2015 Broadway productions starred Josh Young as Newton. Television Newton is portrayed by actor John Castle in the British television miniseries, The Fight Against Slavery (1975). Novels Caryl Phillips’ novel, Crossing the River (1993), includes nearly verbatim excerpts of Newton’s logs from his Journal of a Slave Trader. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Newton


Clive Staples Lewis (29 November 1898 – 22 November 1963), commonly called C. S. Lewis and known to his friends and family as “Jack”, was a novelist, poet, academic, medievalist, literary critic, essayist, lay theologian, and Christian apologist. Born in Belfast, Ireland, he held academic positions at both Oxford University (Magdalen College), 1925–1954, and Cambridge University (Magdalene College), 1954–1963. He is best known both for his fictional work, especially The Screwtape Letters, The Chronicles of Narnia, and The Space Trilogy, and for his non-fiction Christian apologetics, such as Mere Christianity, Miracles, and The Problem of Pain. Lewis and fellow novelist J. R. R. Tolkien were close friends. Both authors served on the English faculty at Oxford University, and both were active in the informal Oxford literary group known as the “Inklings”. According to his memoir Surprised by Joy, Lewis had been baptized in the Church of Ireland (part of the Anglican Communion) at birth, but fell away from his faith during his adolescence. Owing to the influence of Tolkien and other friends, at the age of 32 Lewis returned to the Anglican Communion, becoming “a very ordinary layman of the Church of England”. His faith had a profound effect on his work, and his wartime radio broadcasts on the subject of Christianity brought him wide acclaim.


Thomas Hood (23 May 1799– 3 May 1845) was an English poet, author and humourist, best known for poems such as “The Bridge of Sighs” and “The Song of the Shirt”. Hood wrote regularly for The London Magazine, the Athenaeum, and Punch. He later published a magazine largely consisting of his own works. Hood, never robust, lapsed into invalidism by the age of 41 and died at the age of 45. William Michael Rossetti in 1903 called him “the finest English poet” between the generations of Shelley and Tennyson. Hood was the father of playwright and humourist Tom Hood (1835–1874).


Erica Jong (née Mann; born March 26, 1942) is an American novelist and poet, known particularly for her 1973 novel Fear of Flying. The book became famously controversial for its attitudes towards female sexuality and figured prominently in the development of second-wave feminism. According to Washington Post, it has sold more than 20 million copies worldwide. Born in New York, she was the second of three daughters of Seymore Mann and Eda Mirsky. Attended New York’s Public High School of Music and Art in the 1950’s where she developed her passion for art and writing. As a student at Barnard College, she edited the Barnard Literary Magazine and created poetry programs for the Columbia University campus radio station.


Walter John de la Mare (25 April 1873– 22 June 1956) was an English poet, short story writer and novelist. He is probably best remembered for his works for children, for his poem “The Listeners”, and for subtle psychological horror stories, amongst them “Seaton’s Aunt” and “Out of the Deep”. His 1921 novel Memoirs of a Midget won the James Tait Black Memorial Prize for fiction, and his post-war Collected Stories for Children won the 1947 Carnegie Medal for British children’s books.


Herman Melville (August 1, 1819– September 28, 1891) was an American novelist, short story writer, and poet of the American Renaissance period best known for Typee (1846), a romantic account of his experiences in Polynesian life, and his whaling novel Moby-Dick (1851). His work was almost forgotten during his last thirty years. His writing draws on his experience at sea as a common sailor, exploration of literature and philosophy, and engagement in the contradictions of American society in a period of rapid change. He developed a complex, baroque style: the vocabulary is rich and original, a strong sense of rhythm infuses the elaborate sentences, the imagery is often mystical or ironic, and the abundance of allusion extends to Scripture, myth, philosophy, literature, and the visual arts.


Edgar Allan Poe (born Edgar Poe, January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American author, poet, editor and literary critic, considered part of the American Romantic Movement. Best known for his tales of mystery and the macabre, Poe was one of the earliest American practitioners of the short story and is considered the inventor of the detective fiction genre. He is further credited with contributing to the emerging genre of science fiction. He was the first well-known American writer to try to earn a living through writing alone, resulting in a financially difficult life and career. He was born as Edgar Poe in Boston, Massachusetts; he was orphaned young when his mother died shortly after his father abandoned the family. Poe was taken in by John and Frances Allan, of Richmond, Virginia, but they never formally adopted him. He attended the University of Virginia for one semester but left due to lack of money. After enlisting in the Army and later failing as an officer's cadet at West Point, Poe parted ways with the Allans. His publishing career began humbly, with an anonymous collection of poems, Tamerlane and Other Poems (1827), credited only to “a Bostonian”.


James McIntyre (baptised 25 May 1828– 31 March 1906), called The Cheese Poet, was a Canadian poet. McIntyre was born in Forres, Scotland and came to Canada in 1841 at the age of 14. He worked as a hired hand to begin with, performing pioneer chores that formed the basis of a number of his works. Later, he settled in St. Catharines, Ontario, where he dealt in furniture. There he married and had a daughter and son. He later moved to Ingersoll, Ontario, then a town of 5,000 on the banks of the Thames in Oxford County, the heart of Canadian dairy country at the time. He opened a furniture factory on the river as well as a store which sold furniture, along with such items as pianos and coffins. He was well loved in the community, from which he often received aid in hard times, due in part to his poesy and oratorical skills—he was called on to speak at every kind of social gathering in Ingersoll. The region seems to have inspired him, and it was in celebration of the proud history of Canada, the natural beauty and industry of the region, and especially (as noted above) its cheese, that the majority of his oeuvre was written. The ancient poets ne’er did dream That Canada was land of cream, They ne’er imagined it could flow In this cold land of ice and snow, Where everything did solid freeze They ne’er hoped or looked for cheese. from “Oxford Cheese Ode” [1] McIntyre was uninhibited by minor shortcomings—such as his lack of literary skills. The Toronto Globe ran his pieces as comic relief, and the New York Tribune expressed amusement, but their mockery did not dampen his enthusiasm. He is assumed to have continued writing until his death, in 1906. He published two volumes of poetry: Musings on the Canadian Thames (1884); Poems of James McIntyre (1889). McIntyre was forgotten after his death for a number of years, until his work was rediscovered and reprinted by William Arthur Deacon—literary editor of the Toronto Mail and Empire and its successor the Globe and Mail—in his book The Four Jameses (1927). In recent years a volume of his work, Oh! Queen of Cheese: Selections from James McIntyre, the Cheese Poet (ed. Roy A Abramson; Toronto: Cherry Tree, 1979) collected his poems together with a variety of cheese recipes and anecdotes. However, the greatest boost to his fame probably came from a number of his poems being anthologized in the collection Very Bad Poetry, edited by Ross and Kathryn Petras (Vintage, 1997). This included his masterpiece and possibly best-known poem, "Ode on the Mammoth Cheese Weighing Over 7,000 Pounds," written about an actual cheese produced in Ingersoll in 1866 and sent to exhibitions in Toronto, New York, and Britain: We have seen thee, Queen of Cheese, Lying quietly at your ease, Gently fanned by evening breeze; Thy fair form no flies dare seize. All gaily dressed, soon you’ll go To the provincial show, To be admired by many a beau In the city of Toronto. from “Ode on the Mammoth Cheese” [2] An annual poetry contest is held in Ingersoll, Ontario, to honour McIntyre. The contest is sponsored by The Ingersoll Times and the Corporation of the Town of Ingersoll, and includes a cheese-themed poetry competition. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_McIntyre_(poet)


Rupert Chawner Brooke (middle name sometimes given as "Chaucer"; 3 August 1887 – 23 April 1915) was an English poet known for his idealistic war sonnets written during the First World War, especially "The Soldier". He was also known for his boyish good looks, which were said to have prompted the Irish poet W. B. Yeats to describe him as "the handsomest young man in England”. Brooke belonged to another literary group known as the Georgian Poets and was one of the most important of the Dymock poets, associated with the Gloucestershire village of Dymock where he spent some time before the war. He also lived in the Old Vicarage, Grantchester. While travelling in Europe he prepared a thesis, entitled "John Webster and the Elizabethan Drama", which won him a scholarship to King's College, Cambridge, where he became a member of the Cambridge Apostles, was elected as President of the Cambridge University Fabian Society, helped found the Marlowe Society drama club and acted in plays including the Cambridge Greek Play. To Rupert Brooke (by Eden Phillpotts, from ‘Plain Song, 1914-1916’) Though we, a happy few, Indubitably knew That from the purple came This poet of pure flame, The world first saw his light Flash on an evil night, And heard his song from far Above the drone of war. Out of the primal dark He leapt, like lyric lark, Singing his aubade strain; Then fell to earth again. We garner all he gave, And on his hero grave, For love and honour strew, Rosemary, myrtle, rue. Son of the Morning, we Had kept you thankfully; But yours the asphodel: Hail, singer, and farewell!


