
Info


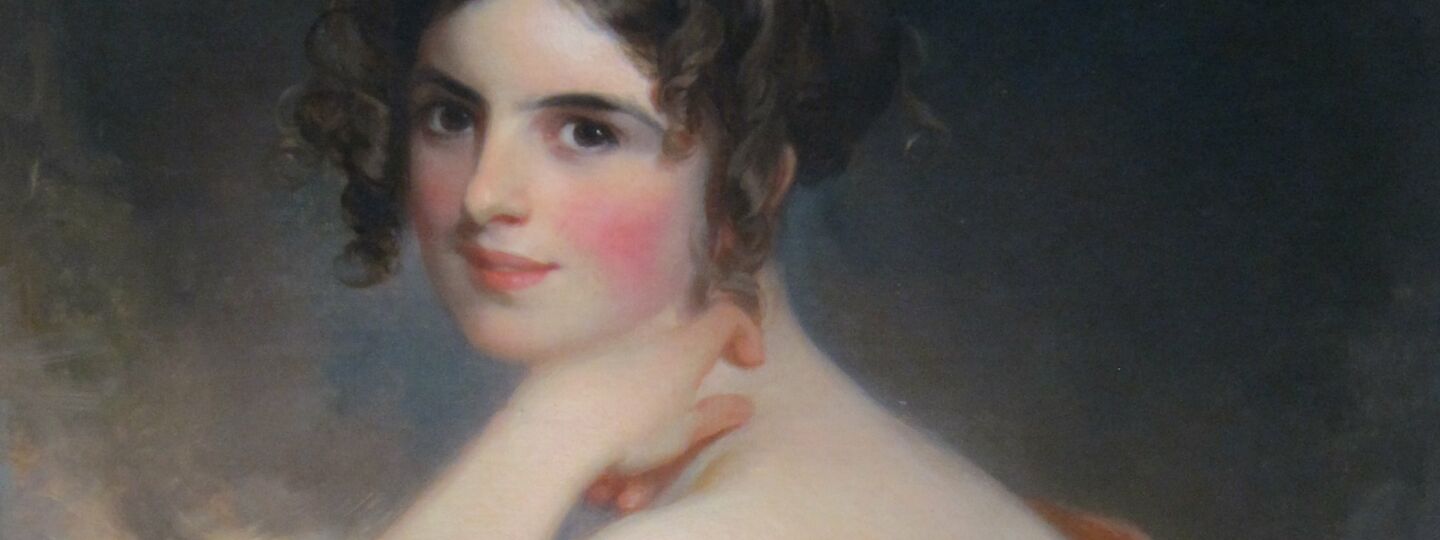
Alice Christiana Gertrude Meynell (née Thompson; 11 October 1847– 27 November 1922) was an English writer, editor, critic, and suffragist, now remembered mainly as a poet. Biography Alice Christiana Gertrude Thompson was born in Barnes, London, to Thomas James and Christiana (née Weller) Thompson. The family moved around England, Switzerland, and France, but she was brought up mostly in Italy, where a daughter of Thomas from his first marriage had settled. Her father was a friend of Charles Dickens. Preludes (1875) was her first poetry collection, illustrated by her elder sister Elizabeth (the artist Lady Elizabeth Butler, 1846–1933, whose husband was Sir William Francis Butler). The work was warmly praised by Ruskin, although it received little public notice. Ruskin especially singled out the sonnet “Renunciation” for its beauty and delicacy. After Alice, the entire Thompson family converted to the Catholic Church (1868 to 1880), and her writings migrated to subjects of religious matters. This eventually led her to the Catholic newspaper publisher and editor Wilfrid Meynell (1852–1948) in 1876. A year later (in 1877) she married Meynell, and they settled in Kensington. They became the proprietors and editors of such magazines as The Pen, the Weekly Register, and Merry England, among others. Alice and Wilfrid Meynell had eight children, Sebastian, Monica, Everard, Madeleine, Viola, Vivian (who died at three months), Olivia, and Francis. Viola Meynell (1885–1956) became an author in her own right, and the youngest child Francis Meynell (1891–1975) was a poet and printer, co-founding the Nonesuch Press. She was much involved in editorial work on publications with her husband, and in her own writing, poetry and prose. She wrote regularly for The World, The Spectator, The Magazine of Art, the Scots Observer (which became the National Observer, both edited by W. E. Henley), The Tablet, The Art Journal, the Pall Mall Gazette, and The Saturday Review. The poet Francis Thompson, down and out in London and trying to recover from his opium addiction, sent the couple a manuscript. His poems were first published in Wilfrid’s Merry England, and the Meynells became a supporter of Thompson. His 1893 book Poems was a Meynell production and initiative. Another supporter of Thompson was the poet Coventry Patmore. Alice had a deep friendship with Patmore, lasting several years, which led to his becoming obsessed with her, forcing her to break with him. At the end of the 19th century, in conjunction with uprisings against the British (among them the Indians’, the Zulus’, the Boxer Rebellion, and the Muslim revolt led by Muhammad Ahmed in the Sudan), many European scholars, writers, and artists, began to question Europe’s colonial imperialism. This led the Meynells and others in their circle to speak out for the oppressed. Alice Meynell was a vice-president of the Women Writers’ Suffrage League, founded by Cicely Hamilton and active 1908–19. Death and legacy After a series of illnesses, including migraine and depression, she died 27 November 1922. She is buried at Kensal Green Catholic Cemetery, London, England. There is a London Borough Council commemorative blue plaque on the front wall of the property at 47 Palace Court, Bayswater, London, W2, where she and her husband once lived.


Charles Sangster (July 16, 1822– December 9, 1893) was a Canadian poet whose 1856 volume, The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, “was received with unanimous acclaim as the best and most important book of poetry produced in Canada until that time.” He was “the first poet who made appreciative use of Canadian subjects in his poetical work.” The Dictionary of Canadian Biography calls him “the best of the pre-confederation poets.” Life Sangster was born at the Navy Yard on Point Frederick (now the site of Royal Military College of Canada), near Kingston, Ontario, the son of Ann Ross and James Sangster. A twin sister died in infancy. His father, a “joiner” or shipbuilder who worked for the British Navy around the Great Lakes, died at Penetanguishene just before Charles turned 2. His mother raised Charles and his 4 siblings on her own. Sangster was an indifferent student, finding “the school curriculum irrelevant and his masters stern and uninspiring.” At 15 years old, he left school to help provide for the family. He took a job in the naval lab making cartridges at Fort Henry and two years later was transferred to the Ordnance office at the fort. About this time (1839) Sangster wrote his first serious poem, a 700-line narrative in rhyming couplets called “The Rebel.” The poem “contains an extensive vocabulary and rich and imaginative historical and geographical allusions,... beyond what might be expected of a boy... who had so little formal education.... the content and form suggest considerable previous writing.” During the 12 years he worked at the Ordinance office Sangster began doing part-time work for a Kingston newspaper, the British Whig. He also continued writing poetry and submitting it, anonymously or pseudonymously, to the local papers. Writing career and success In 1849 Sangster quit his job at Fort Henry and moved to Amherstburg, Ontario, where he became editor of the Amherstburg Courier. When James Reeves, owner of the Courier, died the same year, Sangster returned to Kingston, to work as a proofreader and bookkeeper for the British Whig. Sangster first gained national attention as a poet in 1850, when his poetry began appearing in Canada’s Literary Garland magazine. Soon his work appeared in other magazines, such as Anglo-American Magazine. In 1853 Sangster took a steamship excursion down the St. Lawrence River and up the Saguenay River in Quebec, which he wrote about for the Whig in a series of travel letters called “Etchings by the Way”—material he would also use in his long poem, “The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay”. Sangster published his first book of poetry, The St Lawrence and the Saguenay, and Other Poems, in 1856. The book was widely praised by reviewers and readers. Susanna Moodie wrote to Sangster; "If a native of Canada, [one] may well be proud of her Bard, who has sung in such lofty strains the natural beauties of his native land." The National Magazine of London echoed the same sentiment: “Well may the Canadians be proud of such contributions to their infant literature.... In some sort, and according to his degree, Mr. Sangster may be regarded as the Wordsworth of Canada.” Charles Sangster "married 21-year-old Mary Kilborn of Kingston on Sept. 16, 1856, and the newlyweds moved into a brick house at 144 Barrie Street across from the grassy park. (An historical plaque directly across the street honours the Sangster home.)" Mary was to die of pneumonia just 16 months later. In 1859, Sangster wrote the poem “Brock”, commissioned for the inauguration of the monument to General Isaac Brock at Queenston Heights. Sangster’s second book of poetry, Hesperus and Other Poems and Lyrics, appeared in 1860, published in Kingston and Montreal. “A rousing success, Hesperus... received even more approval than his first book.” “Hesperus was well received, and many critics considered it superior to The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, as did Sangster himself.” The same year, Sangster remarried, to Henrietta Charlotte Mary Meagher, who was only 17 years of age (to his 38). In 1864, Sangster became a reporter for the Kingston Daily News, and 16 of his poems appeared in the first-ever anthology of Canadian poetry, Selections from Canadian Poets. The same year, the Sangsters celebrated the birth of their first child, Charlotte Mary. Post office and retirement By 1867, Sangster “was in a poor financial situation and suffered increasingly from ill health, depression, and a nervous disorder that would cause him deep mental pain the rest of his life.” To help him out his neighbor, the new Postmaster-General Alexander Campbell arranged a job for Sangster with Canada’s new Post Office Department. Accordingly, in 1868, at 46, Sangster “accepted a position in the Post-Office Department at Ottawa, where his poetic energy and ambition succumbed, apparently, to the incessant drudgery and to the hampering cares of ill-paid employment.”, “With his appointment... Sangster’s life became characterized by overwork, ill health and scant literary output.” He remained with the Post Office until his retirement in 1886. Sangster was also kept busy by a growing family. Sadly, Charlotte died in 1868, shortly after the move to Ottawa. The same year, though, Mrs. Sangster gave birth to a second daughter, Florence. Two years later, in 1870, their third daughter, Gertrude was born, followed in 1879 by a son, Roderick. Sangster published 16 poems in magazines between 1868 and 1878, most of which he had written before moving to Ottawa. He wrote virtually nothing for the 18 years he worked at the Post Office. As he later wrote: "When I went down to Ottawa... I took a pile of M.S. of a third volume with me, as I thought 'ready for the press’, but in all the 18 years I remained there I did little more than correct.... When they get a man into the Civil Service, their first duty is to crush him flat, and if he is a fool of a Poet, or dares to think of any nonsense of that kind, draw him through a Knot or a gimlet hole a few times, pile with agony of toil, toil, toil until his nerves are flattened out, all the rebound knocked out of him, and then– superannuate him... and tell him he should be thankful.” Sangster had a nervous breakdown in 1875, and developed a chronic nervous system condition during the 1880s. To make matters worse, Henrietta died sometime between 1883 and 1886, leaving him to raise his new family alone. After another breakdown in March 1886, he took a six-month leave of absence, and also resigned from the Royal Society of Canada (which had elected him in 1882). Finally, that September he retired and moved back to Kingston. For the first years of retirement, Sangster did little but convalesce. In July 1888, he received a letter from W.D. Lighthall, inquiring about new poems for an upcoming anthology (most likely Lighthall’s 1889 Songs of the Great Dominion. Sangster replied the next day, and the two men struck up a friendship by mail. Revitalized, Sangster began revising his poetry. He doubled the size of “The Saint Lawrence and the Saguenay” to over 200 stanzas, and sent the manuscript to his cousin Amos Sangster to illustrate. When Amos died, the manuscript and the new poem was lost. However, 40 of the new stanzas survived thanks to being published in various magazines. Charles Sangster also cut many of the “other” poems in the first volume, and made over 2,000 changes to the ones he kept. Hesperus got off easier, but Sangster still made more than 200 revisions to the work. As well, Sangster prepared two more volumes for publication, mostly from poems he’d written before moving to Ottawa: Norland Echoes & Other Strains, and The Angel Guest & Other Poems. By the summer of 1871, all four manuscripts were complete, and Sangster sent them off to Lighthall (who had become his literary executor). However, before any of them could be published, Sangster died. None of them were published until the 1970s. Charles Sangster died in Kingston in 1893, and is buried in the city’s Cataraqui Cemetery. Writing The Canadian Encyclopedia says that “Sangster’s poetry distinguishes him as a lover and keen observer of the natural world. He displays overwhelming passion in some poems and equally extreme melancholy in others. Whatever his mood he is consistently and intensely serious and deeply religious.” Sangster’s inspiration was drawn from three themes he was passionate about: love, nature and religion. He wrote many poems about his experiences and was commended for his ability to express the beauty of Canada’s landscapes. Sangster was often called the “father of Canadian poetry” because of this. Many of the love poems from his first book were directed towards his first wife; the nature poems were of his travels. For a man with limited educational training, Charles Sangster had a vast vocabulary and an extraordinary knowledge of history, classics, mythology and authors. His poems include an extensive knowledge of classic, historic, and mythological works, as well as British and American authors, including Shakespeare, Milton, Burns, Wordsworth, P.J. Bailey, and Longfellow. Recognition Sangster was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1892. Publications * The St. Lawrence and the Saguenay, and Other Poems. Kingston, ON: J. Creighton & J. Duff, 1856. New York: Miller, Orton & Mulligan, 1856. * Hesperus, and Other Poems and Lyrics. Kingston: J. Creighton, 1860. Montreal: J. Lovell, 1860. London, UK: Trubner, 1860. * Our Norland. Toronto: Copp Clark, [1890]. * The St Lawrence and the Saguenay and other poems; Hesperus and other poems and lyrics, intro. Gordon Johnston (Toronto: University of Toronto Press and Buffalo, N.Y., 1972. ISBN 0-8020-1935-8 * Norland echoes and other strains and lyrics,. Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1976. ISBN 0-919662-59-5 * The angel guest and other poems and lyrics. Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1977. ISBN 0-919662-63-3 * Hesperus and other poems and lyrics(rev. ed.). Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1979. ISBN 0-919662-72-2 * St. Lawrence and the Saguenay and other poems (rev. ed.). Frank M. Tierney ed. Ottawa: Tecumseh, 1984. ISBN 0-919662-95-1, ISBN 0-919662-96-X * Except where noted, bibliographic information courtesy Dictionary of Canadian Biography. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Sangster

James Laughlin (October 30, 1914 – November 12, 1997) was an American poet and literary book publisher who founded New Directions Publishing. He was born in Pittsburgh, the son of Henry Hughart and Marjory Rea Laughlin. Laughlin's family had made its fortune with the Jones and Laughlin Steel Company, founded three generations earlier by his great grandfather, James H. Laughlin, and this wealth would partially fund Laughlin's future endeavors in publishing. As Laughlin once wrote, "none of this would have been possible without the industry of my ancestors, the canny Irishmen who immigrated in 1824 from County Down to Pittsburgh, where they built up what became the fourth largest steel company in the country. I bless them with every breath." Laughlin's boyhood home is now part of the campus of Chatham University. At The Choate School (now Choate Rosemary Hall) in Wallingford, Connecticut, Laughlin showed an early interest in literature. An important influence on Laughlin at the time was the Choate teacher and translator Dudley Fitts, who later provided Laughlin with introductions to prominent writers such as Gertrude Stein and Ezra Pound. Harvard University, where Laughlin matriculated in 1933, had a more conservative literary bent, embodied in the poet and professor Robert Hillyer, who directed the writing program. According to Laughlin, Hillyer would leave the room when either Pound or Eliot was mentioned. In 1934, Laughlin traveled to France, where he met Gertrude Stein and Alice B. Toklas. Laughlin accompanied the two on a motoring tour of southern France and wrote press releases for Stein's upcoming visit to the U.S. He proceeded to Italy to meet and study with Ezra Pound, who famously told him, "You're never going to be any good as a poet. Why don't you take up something useful?" Pound suggested publishing. Later, Laughlin took a leave of absence from Harvard and stayed with Pound in Rapallo for several months. When Laughlin returned to Harvard, he used money from his father to found New Directions, which he ran first from his dorm room and later from a barn on his Aunt Leila Laughlin Carlisle's estate in Norfolk, Connecticut. (The firm opened offices in New York soon after, first at 333 Sixth Avenue and later at 80 Eighth Avenue, where it remains today.) With funds from his graduation gift, Laughlin endowed New Directions with more money, ensuring that the company could stay afloat even though it did not turn a profit until 1946. The first publication of the new press, in 1936, was New Directions in Prose & Poetry, an anthology of poetry and writings by authors such as William Carlos Williams, Ezra Pound, Elizabeth Bishop, Henry Miller, Marianne Moore, Wallace Stevens, and E. E. Cummings, a roster that heralded the fledgling company's future as a preeminent publisher of modernist literature. The volume also included a poem by "Tasilo Ribischka," a pseudonym for Laughlin himself. New Directions in Prose and Poetry became an annual publication, issuing its final number in 1991. Within just a few years New Directions had become an important publisher of modernist literature. Initially, it emphasized contemporary American writers with whom Laughlin had personal connections, such as William Carlos Williams and Pound. A born cosmopolitan, though, Laughlin also sought out cutting-edge European and Latin American authors and introduced their work to the American market. One important example of this was Hermann Hesse's novel Siddhartha, which New Directions initially published in 1951. Laughlin often remarked that the popularity of Siddhartha subsidized the publication of many other money-losing books of greater importance. Although of draft age, Laughlin avoided service in World War II due to a 4-F classification. Laughlin, like several of his male ancestors and like his son Robert, suffered from depression. Robert committed suicide in 1986 by stabbing himself multiple times in the bathtub. Laughlin later wrote a poem about this, called Experience of Blood, in which he expresses his shock at the amount of blood in the human body. Despite the horrific mess left as a result, Laughlin reasons that he cannot ask anyone else to clean it up, "because after all, it was my blood too." A natural athlete and an avid skier, Laughlin traveled the world skiing and hiking. With money from his graduation gift, he founded the Alta Ski Area in Utah and was part-owner of the resort there for many years. Laughlin also spearheaded the surveying of the Albion-Sugarloaf ski area, along with Alta notables Chic Morton, Alf Engen, and fellow Ski Enthusiast and Painter Ruth Rogers-Altmann. At times Laughlin's skiing got in the way of his business. After publishing William Carlos Williams' novel White Mule in 1937, Laughlin left for an extended ski trip. When reviewers sought additional copies of the novel, Laughlin was not available to give the book the push it could have used, and as a result Williams nursed a grudge against the young publisher for years. Laughlin's outdoor activities helped other literary friendships, though; for many years he and Kenneth Rexroth took an annual camping trip together in the Sierra Nevada mountains of California. In the 1960s, Laughlin published Rexroth's friend, the poet and essayist Gary Snyder, also an avid outdoorsman. In the early 1950s, Laughlin took part in what has come to be known as the Cultural Cold War against the Soviet Union. With funding from the Ford Foundation and with the assistance of poet and editor Hayden Carruth, Laughlin founded a nonprofit called "Intercultural Publications" that sought to publish a quarterly journal of American arts and letters, PERSPECTIVES USA, in Europe. Sixteen issues of the journal eventually appeared. Although Laughlin wished to continue the journal, the Ford Foundation cut off funding, asserting that PERSPECTIVES had limited impact and that its money would be better spent on the more effective Congress for Cultural Freedom. Following the dissolution of Intercultural Publications, Laughlin became deeply involved in the activities of the Asia Society. Pound's advice to Laughlin to give up poetry didn't stick. He published his first book of poetry, SOME NATURAL THINGS, in 1945, and continued to write verse until his death. Although he never enjoyed the acclaim that the writers he published received, Laughlin's verse (which is plainspoken and focused on everyday experience, reminiscent of Williams or even the Roman poet Catullus) was well-respected by other poets, and in the 1990s the NEW YORKER published six of his poems. Among his books are IN ANOTHER COUNTRY, THE COUNTRY ROAD, and the posthumous autobiographical poem BYWAYS. Laughlin won the 1992 Distinguished Contribution to American Letters Award from the National Book Awards Program. The Academy of American Poets' James Laughlin award, for a poet's second book, is named in his honor. He died of complications related to a stroke in Norfolk, Connecticut, at age 83. Works Laughlin's works include: * In Another Country (1979) * Selected Poems (1986) * The House of Light (1986) * Tabellae (1986) * The Owl of Minerva (Copper Canyon Press, 1987) * Collemata and Pound As Wuz (1988) * The Bird of Endless Time (Copper Canyon Press, 1989) * Collected Poems of James Laughlin (1992) * Angelica (1992) * The Man in the Wall (1993) * The Country Road (1995) * The Secret Room (1997) * A Commonplace Book of Pentastichs (1998) * Byways: A Memoir (2005) * The Way It Wasn't: From the Files of James Laughlin (2006) * Laughlin's correspondence with William Carlos Williams, Henry Miller, Thomas Merton, Delmore Schwartz, Ezra Pound, and others has been published in a series of volumes issued by Norton. References Wikipedia—http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/James_Laughlin


Francis Edward Ledwidge (19 August 1887– 31 July 1917) was an Irish war poet from County Meath. Sometimes known as the “poet of the blackbirds”, he was killed in action at the Battle of Passchendaele during World War I. Early life Ledwidge was born at Janeville, Slane, in Ireland, the eighth of nine children in a poverty-stricken family. His parents, Patrick Ledwidge (the Ledwidge family, from Shropshire, was granted land in Meath after the Norman invasion) and wife Anne Lynch (1853–1926), believed in giving their children the best education they could afford. But when Francis was only five his father Patrick died prematurely, which forced his wife and the children out to work at an early age. Francis left the local national school aged thirteen, and while he continued to educate himself, he worked at what work he could find, as farm hand, road mender and supervisor of roads, as copper miner (sacked for organising a strike for better mining conditions, three years before the general 1913 strike, and was a trade union activist since 1906) and shop assistant. Appointed secretary of the Slane branch of the Meath Labour Union (1913–14) he had aspirations of permanent white-collar work. He was known for his connections with Sinn Féin. Young poet Strongly built, with striking brown eyes and a sensuous face, Ledwidge was a keen poet, writing where ever he could– sometimes even on gates or fence posts. From the age of fourteen his works were published in his local newspaper, the Drogheda Independent reflecting his passion for the Boyne Valley. While working as a road labourer he won the patronage of the writer Lord Dunsany after writing to him in 1912, enclosing copybooks of his early work. Dunsany, a man of letters already well known in Dublin and London literary and dramatic circles, and whose own start in publishing had been with a few poems, promoted him in Dublin and introduced him to W.B. Yeats with whom he became acquainted. Dunsany supported Ledwidge with money and literary advice for some years, providing him with access to and a workspace in Dunsany Castle’s Library where he met the Irish writer Katharine Tynan, corresponding with her regularly. Dunsany later prepared his first collection of poetry Songs of the Fields, which successfully appealed to the expectations of the Irish Literary Revival and its social taste for rural poetry. Home Rule and World War I Ledwidge was a keen patriot and nationalist. His efforts to found a branch of the Gaelic League in Slane were thwarted by members of the local council. The area organiser encouraged him to continue his struggle, but Francis gave up. He did manage to act as a founding member with his brother Joseph of the Slane Branch of the Irish Volunteers (1914), a nationalist force created in response to the arming of the Ulster Volunteers who swore to resist the introduction of Home Rule for Ireland by force, if need be. The Irish Volunteers were set up to prevent their belligerence and to ensure democracy would prevail. On the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, and on account of Ireland’s involvement in the war, the Irish Volunteers split into two factions, the National Volunteers who supported John Redmond’s appeal to join Irish regiments in support of the Allied war cause and those who did not. Francis was originally of the latter party. Nevertheless, having defended this position strongly at a local council meeting, he enlisted (24 October 1914) in Lord Dunsany’s regiment, joining 5th battalion Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers, part of the 10th (Irish) Division. This was against the urgings of Dunsany who opposed his enlistment and had offered him a stipend to support him if he stayed away from the war. Some have speculated that he went to war because his sweetheart Ellie Vaughey had found a new lover, John O’Neill, whom she later married, but Ledwidge himself wrote, and forcefully, that he could not stand aside while others sought to defend Ireland’s freedom. Poetry and war Ledwidge seems to have fitted into Army life well, and rapidly achieved promotion to lance corporal. In 1915, he saw action at Suvla Bay in the Dardanelles, where he suffered severe rheumatism. Having survived huge losses sustained by his company in the Battle of Gallipoli, he became ill after a back injury on a tough mountain journey in Serbia (December 1915), a locale which inspired a number of poems. Ledwidge was dismayed by the news of the Easter Rising, and was court-martialled and demoted for overstaying his home leave and being drunk in uniform (May 1916). He gained and lost stripes over a period in Derry (he was a corporal when the introduction to his first book was written), and then, returned to the front, received back his lance corporal’s stripe one last time in January 1917 when posted to the Western Front, joining 1st Battalion, Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers, part of 29th Division. Ledwidge continued to write when feasible throughout the war years, though he lost much work, for example, in atrocious weather in Serbia. He sent much of his output to Lord Dunsany, himself moving on war assignments, as well as to readers among family, friends and literary contacts. On 31 July 1917, a group from Ledwidge’s battalion of the Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers were road-laying in preparation for an assault during the Third Battle of Ypres, near the village of Boezinge, northwest of Ieper (Ypres). While Ledwidge was drinking tea in a mud hole with his comrades, a shell exploded alongside, killing the poet and five others. A chaplain who knew him, Father Devas, arrived soon after, and recorded “Ledwidge killed, blown to bits.” The poems Ledwidge wrote on active service revealed his pride at being a soldier, as he believed, in the service of Ireland. He wondered whether he would find a soldier’s death. The dead were buried at Carrefour de Rose, and later re-interred in the nearby Artillery Wood Military Cemetery, Boezinge, (where the Welsh poet Hedd Wyn, killed on the same day, is also buried). A stone tablet commemorates him in the Island of Ireland Peace Park, Messines, Belgium. His work as “peasant poet” and “soldier poet”, once a standard part of the Irish school curriculum, faded from view for many decades of the 20th century. Its intensity, coupled with a revived interest in his period, has restored it to life. Publications and reception Much of Ledwidge’s work was published in newspapers and journals in Ireland and the UK. The only work published in book form during Ledwidge’s lifetime was the original Songs of the Fields (1915), which was very well received. The critic Edward Marsh printed three of the poems in the Georgian Poetry series, and remained a correspondent for the remainder of Ledwidge’s life. A second volume, Songs of Peace was in preparation when Ledwidge died; patron and friend Lord Dunsany wrote the introduction while both were in Derry in September 1916. Following the war, Dunsany arranged for more of Ledwidge’s work to be published, first in a third and final new volume, Last Songs, and then later in an anthology in 1919; he commented on the work with words such as: “[I was] astonished by the brilliance of that eye and that had looked at the fields of Meath and seen there all the simple birds and flowers, with a vividness which made those pages like a magnifying glass, through which one looked at familiar things for the first time.” Some of Ledwidge’s poetry was put to music by the British Composer and song-writer Michael Head, most notably in the very well received song cycle published in 1920, “Over the rim of the moon”. This includes the well-known song, “The Ships of Arcady”. Later collections: Alice Curtayne: ‘’The complete poems of Francis Ledwidge’’ (1974) who also wrote a comprehensive biography of the poet, including some previously unpublished work Liam O’Meara: ‘’The poems of Francis Ledwidge’’ (1997), (ISBN 1 870 49147 5), including some previously unpublished work Ulick O’Connor (introduction by): ‘’The best of Francis Ledwidge’’, The Inchicore Ledwidge Society, Risposte Books (2004), ISBN 1-901596-10-9 Hubert Dunn:‘’The Minstrel Boy’’, (2006) some more poems released in a commemorative volume Dermot Bolger: In 1992 long-time Ledwidge admirer, Dublin poet Dermot Bolger, published a Selected Poems of Francis Ledwidge. This was re-issued by New Island Books in 2007 under the title “A Ledwidge Treasury”, with an introduction by Seamus Heaney and an afterword by Dermot Bolger. In 2007 Bolger’s play about the life of Ledwidge, “Walking the Road”, (New Island Books, 2007) was staged in Dublin and in the Town Hall Theatre, Ieper, close where Ledwidge died. It was commissioned to mark the 90th anniversary of his death. In 1998 Bolger and the poet’s nephew, Joseph Ledwidge, were invited by the 'In Flanders Fields Museum’ to unveil a monument on the spot where Ledwidge was killed. Politics His politics are described by the Oxford Dictionary of National Biography as nationalist as well as left-wing. However far from simply being an Irish Nationalist, his poems “O’Connell Street” and "Lament for the Poets of 1916" clearly describe his sense of loss and an expression of holding the same “dreams” as the Easter Rising’s Irish Republicans who fought and died for the Irish Republic in and around O’Connell Street in 1916. Works * Songs of the Fields (1915) Full text at Internet Archive * Songs of Peace (1917) Full text at Internet Archive * Last Songs (1918) Full text at Internet Archive * The complete poems of Francis Ledwidge; with introductions by Lord Dunsany (1919) Full text at Internet Archive Quotes * Oh what a pleasant world 'twould be, * How easy we’d step thro’ it, * If all the fools who meant no harm, * Could manage not to do it! *– From a personal letter. * He shall not hear the bittern cry * in the wild sky, where he is lain, * Nor voices of the sweeter birds * Above the wailing of the rain * * Nor shall he know when the loud March blows * Thro’ slanting snows her fanfare shrill, * Blowing to flame the golden cup * Of many an upset daffodil. * * But when the dark cow leaves the moor * And pastures poor with greedy weeds * Perhaps he’ll hear her low at morn * Lifting her horn in pleasant meads. *– Lament for Thomas MacDonagh Documentary film * Ledwidge was the subject of an RTÉ documentary entitled Behind the Closed Eye, first broadcast on 18 January 1973. It won awards for Best Story and Best Implementation Documentary at the Golden Prague International Television Festival. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Francis_Ledwidge

George Oppen (April 24, 1908 – July 7, 1984) was an American poet, best known as one of the members of the Objectivist group of poets. He abandoned poetry in the 1930s for political activism and later moved to Mexico to avoid the attentions of the House Un-American Activities Committee. He returned to poetry—and to the United States—in 1958, and received the Pulitzer Prize in 1969. Early life Oppen was born in New Rochelle, New York, into a Jewish family. His father, a successful diamond merchant, was George August Oppenheimer (b. Apr. 13, 1881), his mother Elsie Rothfeld. His father changed the family name to Oppen in 1927. Oppen’s childhood was one of considerable affluence; the family was well-tended to by servants and maids and Oppen enjoyed all the benefits of a wealthy upbringing: horse riding, expensive automobiles, frequent trips to Europe. But his mother committed suicide when he was four, his father remarried three years later and the boy and his stepmother, Seville Shainwald, apparently could not get along. Oppen developed a skill for sailing at a young age and the seascapes around his childhood home left a mark on his later poetry. He was taught carpentry by the family butler; Oppen, as an adult, found work as a carpenter and cabinetmaker. In 1917, the family moved to San Francisco where Oppen attended Warren Military Academy. It is speculated that during this time Oppen’s early traumas led to fighting and drinking, so that, while reaching maturity, Oppen was also experiencing a personal crisis. By 1925, this period of personal and psychic transition culminated in a serious car wreck in which George was driver and a young passenger was killed. Ultimately, Oppen was expelled from high school just before he graduated. After this period, he traveled to England and Scotland by himself, visiting his stepmother’s relative, and attending lectures by C.A. Mace, professor in philosophy at St. Andrews. In 1926, Oppen started attending Oregon State Agricultural College (what is now Oregon State University). Here he met Mary Colby, a fiercely independent young woman from Grants Pass, Oregon. On their first date, the couple stayed out all night with the result that she was expelled and he suspended. They left Oregon, married, and started hitch-hiking across the country working at odd jobs along the way. Mary documents these events in her memoir, Meaning A Life: An Autobiography (1978). Early writing While living on the road, Oppen began writing poems and publishing in local magazines. In 1929 and 1930 he and Mary spent some time in New York, where they met Louis Zukofsky, Charles Reznikoff, musician Tibor Serly, and designer Russel Wright, among others. In 1929, George came into a small inheritance and relative financial independence. In 1930 George and Mary moved to California and then to France, where, thanks to their financial input, they were able to establish To Publishers and act as printer/publishers with Zukofsky as editor. The short-lived publishing venture managed to launch works by William Carlos Williams and Ezra Pound. Oppen had begun working on poems for what was to be his first book, Discrete Series, a seminal work in early Objectivist history. Some of these appeared in the February 1931 Objectivist issue of Poetry and the subsequent An “Objectivist’s” Anthology published in 1932. Oppen the Objectivist In 1933, the Oppens returned to New York. George Oppen, William Carlos Williams, Louis Zukofsky and Charles Reznikoff set up the Objectivist Press. The press published books by Reznikoff and Williams, as well as Oppen’s first book Discrete Series, which included a preface by Ezra Pound. Politics and war Faced with the effects of the depression and the rise of fascism, the Oppens were becoming increasingly involved in political action. Unable to bring himself to write verse propaganda, Oppen abandoned poetry and joined the Communist Party USA, serving as election campaign manager for Brooklyn in 1936, and helping organize the Utica New York Milk Strike. He and Mary were engaged and active in the cause of worker’s rights, and Oppen was tried and acquitted on a charge of felonious assault on the police. By 1942, Oppen was deferred from military service while working in the defense industry. Disillusioned by the CPUSA and willing to assist in the fight against fascism, Oppen quit his job, making himself eligible for the draft. Effectively volunteering for duty, Oppen saw active service on the Maginot Line and the Ardennes; he was seriously wounded south of the Battle of the Bulge. Shortly after Oppen was wounded, Oppen’s division helped liberate the concentration camp at Landsberg am Lech. He was awarded the Purple Heart and returned to New York in 1945. Mexico After the war, Oppen worked as a carpenter and cabinet maker. Although now less politically active, the Oppens were aware that their pasts were certain to attract the attention of Joseph McCarthy’s Senate committee and decided to move to Mexico. During these admittedly bitter years in Mexico, George ran a small furniture making business and was involved in an expatriate intellectual community. They were also kept under surveillance by the Mexican authorities in association with the Federal Bureau of Investigation. They were able to re-enter the United States in 1958 when the United States government again allowed them to obtain passports which had been revoked since 1950. Return to poetry In 1958, the Oppens considered becoming involved in Mexican real estate if their expatriate status was to continue. But they were contemplating a move back to the United States, which caused both of them considerable anxiety, prompting Mary to see a therapist. During one of her visits, George told the therapist about a dream he was having (the Oppens later referred to this incident as the “rust in copper” dream). The therapist persuaded George that the dream had a hidden meaning that would convince Oppen to begin writing poetry again. But Oppen also suggested other factors led to his return to the US and to poetry, including his daughter’s well-being, because she was beginning college at Sarah Lawrence. After a brief trip in 1958 to visit their daughter at university, the Oppens moved to Brooklyn, New York, in early 1960 (although for awhile, returning to Mexico regularly for visits). Back in Brooklyn, Oppen renewed old ties with Louis Zukofksy and Charles Reznikoff and also befriended many younger poets. The poems came in a flurry; within two years Oppen had assembled enough poems for a book and began publishing the poems in Poetry, where he had first published, and in his half-sister June Oppen Degnan’s San Francisco Review. The poems of Oppen’s first book following his return to poetry, The Materials, were poems that, as he told his sister June, should have been written ten years earlier. Oppen published two more collections of poetry during the 1960s, This In Which (1965) and Of Being Numerous (1968), the latter of which garnered him the Pulitzer Prize in 1969. Last years In 1975, Oppen was able to complete and see into publication his Collected Poems, together with a new section “Myth of the Blaze.” In 1977, Mary provided the secretarial help George needed to complete his final volume of poetry Primitive. During this time, George’s final illness, Alzheimer’s disease, began to manifest itself with confusion, failing memory, and other losses. The disease was eventually to make it impossible for him to continue writing. George Oppen, age 76, died of pneumonia with complications from Alzheimer’s disease in a convalescent home in California on July 7, 1984. Selected bibliography * Discrete Series (1934), with a “Preface” by Ezra Pound * The Materials (1962) * This in Which (1965) * Of Being Numerous (1968) * Alpine (1969) * Seascape: Needle’s Eye (1972) * The Collected Poems (1975) includes Myth of the Blaze * Primitive (1978) * Poems of George Oppen (1990); selected and introduced by Charles Tomlinson * The Selected Letters of George Oppen (2000); edited with an introduction and notes by Rachel Blau DuPlessis * New Collected Poems (2001, revised edition 2008); edited with an introduction and notes by Michael Davidson, w/ a preface by Eliot Weinberger * Selected Poems (2002), edited, with an introduction by Robert Creeley * Selected Prose, Daybooks, and Papers (2008); edited with an introduction by Stephen Cope * Speaking with George Oppen: Interviews with the Poet and Mary Oppen, 1968-1987 (2012), edited with an introduction by Richard Swigg * 21 Poems (2017) Posthumous publications * For more information on Oppen’s posthumous publications, such as his Selected Letters and New Collected Poems, see Wikipedia articles on Rachel Blau DuPlessis and Michael Davidson. Further reading * Oppen, Mary, Meaning A Life: An Autobiography, Santa Barbara, Calif: Black Sparrow Press, 1978. * Hatlen, Burton, ed., George Oppen: Man and Poet (Man/Woman and Poet Series) (Man and Poet Series), National Poetry Foundation, 1981. ISBN 0-915032-53-8 * DuPlessis, Rachel Blau, ed., The Selected Letters of George Oppen, Duke University Press, 1990. * Oppen, George. Selected Prose, Daybooks, and Papers, edited and with an introduction by Stephen Cope. University of California Press, 2007; ISBN 978-0-520-23579-3, paperback: ISBN 978-0-520-25232-5'. * Heller, Michael, Speaking the Estranged: Essays on the Work of George Oppen, Cambridge UK: Salt Publishing, 2008. * Shoemaker, Steven, ed., Thinking Poetics: Essays on George Oppen, Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press, 2009. * Swigg, Richard, ed.,Speaking with George Oppen: Interviews with the Poet and Mary Oppen, 1968-1987, Jefferson, North Carolina and London, McFarland & Company, 2012. ISBN 978-0-786-46-7884 * Swigg, Richard, George Oppen: The Words in Action, Lewisburg, Bucknell University Press, 2016. ISBN 978-1-61148-749-7 References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/George_Oppen

Max Ehrmann (September 26, 1872 – September 9, 1945) was an American writer, poet, and attorney from Terre Haute, Indiana, widely known for his 1927 prose poem "Desiderata" (Latin: "things desired"). He often wrote on spiritual themes. Education Ehrmann was of German descent; both his parents emigrated from Bavaria in the 1840s. Young Ehrmann was educated at the Terre Haute Fourth District School and the German Methodist Church. He received a degree in English from DePauw University in Greencastle, Indiana, which he attended from 1890 to 1894. While there, he was a member of Delta Tau Delta's Beta Beta chapter and was editor of the school newspaper, Depauw Weekly. Ehrmann then studied philosophy and law at Harvard University, where he was editor of Delta Tau Delta's national magazine The Rainbow, circa 1896. Professional life Ehrmann returned to his hometown of Terre Haute, Indiana in 1898 to practice law. He was a deputy state's attorney in Vigo County, Indiana for two years. Subsequently, he worked in his family's meatpacking business and in the overalls manufacturing industry (Ehrmann Manufacturing Co.) At age 40, Ehrmann left the business to write. At age 54, he wrote Desiderata, which achieved fame only after his death. Legacy Ehrmann was awarded Doctor of Letters honorary degree from DePauw University in about 1937. He was also elected to the Delta Tau Delta Distinguished Service Chapter, the fraternity's highest alumni award. Ehrmann died in 1945. He is buried in Highland Lawn Cemetery in Terre Haute, Indiana. In 2010 the city honored Ehrmann with a life-size bronze statue by sculptor Bill Wolfe. He is depicted sitting on a downtown bench, pen in hand, with a notebook in his lap. "Desiderata" is engraved on a plaque that resides next to the statue and lines from the poem are embedded in the walkway. The sculpture is in the collection of Art Spaces, Inc. – Wabash Valley Outdoor Sculpture Collection. Art Spaces also holds an annual Max Ehrmann Poetry Competition. References Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Max_Ehrmann


Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American novelist. She worked mainly in the genres of fantasy and science fiction. She also authored children’s books, short stories, poetry, and essays. Her writing was first published in the 1960s and often depicted futuristic or imaginary alternative worlds in politics, the natural environment, gender, religion, sexuality, and ethnography. In 2016, The New York Times described her as “America’s greatest living science fiction writer”, although she said that she would prefer to be known as an “American novelist”. She influenced Booker Prize winners and other writers, such as Salman Rushdie and David Mitchell, and science fiction and fantasy writers including Neil Gaiman and Iain Banks. She won the Hugo Award, Nebula Award, Locus Award, and World Fantasy Award, each more than once. In 2014, she was awarded the National Book Foundation Medal for Distinguished Contribution to American Letters. In 2003, she was made a Grandmaster of Science Fiction, one of a few women writers to take the top honor in the genre. Life Birth and family Ursula Kroeber was the daughter of anthropologist Alfred Louis Kroeber of the University of California, Berkeley, and writer Theodora Kracaw. Childhood and education Ursula and her three older brothers, Clifton, Theodore, and Karl Kroeber, were encouraged to read and were exposed to their parents’ dynamic friend group, which included Native Americans and Robert Oppenheimer, who was later to become in part a model for her hero in The Dispossessed. Le Guin stated that, in retrospect, she was grateful for the ease and happiness of her upbringing. The encouraging environment fostered Le Guin’s interest in literature; her first fantasy story was written at age 9, her first science fiction story submitted for publication in the magazine Astounding Science Fiction at age 11. The family spent the academic year in Berkeley, retreating in the summers to “Kishamish” in Napa Valley, "an old, tumble-down ranch... [and] a gathering place for scientists, writers, students, and California Indians. Even though I didn’t pay much attention, I heard a lot of interesting, grown-up conversation." She was interested in biology and poetry, but found math difficult. Le Guin attended Berkeley High School. She received her B.A. (Phi Beta Kappa) in Renaissance French and Italian literature from Radcliffe College in 1951, and M.A. in French and Italian literature from Columbia University in 1952. Soon after, Le Guin began her Ph.D. work and won a Fulbright grant to continue her studies in France from 1953 to 1954. Marriage and family In 1953, while traveling to France aboard the Queen Mary, Le Guin met her future husband, historian Charles Le Guin. They married later that year in Paris. After marrying, Le Guin chose not to continue her doctoral studies of the poet Jean Lemaire de Belges. The couple returned to the United States so that he could pursue his Ph.D. at Emory University. During this time, she worked as a secretary and taught French at the university level. Their first child, Elisabeth (1957), was born in Moscow, Idaho, where Charles taught. In 1958 the Le Guins moved to Portland, Oregon, where their daughter Caroline (1959) was born, and where they lived thereafter. Charles is Emeritus Professor of History at Portland State University. During this time, she continued to make time for writing in addition to maintaining her family life. In 1964, her third child, Theodore, was born. Death Le Guin died on January 22, 2018, at her home in Portland, Oregon; her son stated that she had been in poor health for several months. Her New York Times obituary called her “the immensely popular author who brought literary depth and a tough-minded feminist sensibility to science fiction and fantasy with books like The Left Hand of Darkness and the Earthsea series”. Writing career Le Guin became interested in literature quite early. At age 11, she submitted her first story to the magazine Astounding Science Fiction. Despite being rejected, she continued writing but did not attempt to publish for the next ten years. From 1951 to 1961 she wrote five novels, which publishers rejected, because they seemed inaccessible. She also wrote poetry during this time, including Wild Angels (1975). Her earliest writings, some of which she adapted in Orsinian Tales and Malafrena, were non-fantastic stories set in the imaginary country of Orsinia. Searching for a way to express her interests, she returned to her early interest in science fiction; in the early 1960s her work began to be published regularly. One Orsinian Tale was published in the Summer 1961 issue of The Western Humanities Review and three of her stories appeared in 1962 and 1963 numbers of Fantastic Stories of Imagination, a monthly edited by Cele Goldsmith. Goldsmith also edited Amazing Stories, which ran two of Le Guin’s stories in 1964, including the first “Hainish” story. In 1964 the short story “The Word of Unbinding” was published. This was the first of the Earthsea fantasy series, which includes six books and eight short stories. The three linked young adult novels beginning with A Wizard of Earthsea (1968), The Tombs of Atuan (1970), and The Farthest Shore (1972), sometimes referred to as The Earthsea Trilogy, in later years would be joined by the books Tehanu, Tales from Earthsea and The Other Wind. Le Guin received wide recognition for her novel The Left Hand of Darkness, which won the Hugo and Nebula awards in 1970. Her subsequent novel The Dispossessed made her the first person to win both the Hugo and Nebula Awards for Best Novel twice for the same two books. In later years, Le Guin worked in film and audio. She contributed to The Lathe of Heaven, a 1979 PBS film based on her novel of the same name. In 1985 she collaborated with avant-garde composer David Bedford on the libretto of Rigel 9, a space opera. In May 1983 she delivered a well-received commencement address entitled “A Left-Handed Commencement Address” at Mills College, Oakland, California. “A Left-Handed Commencement Address” is included in her nonfiction collection Dancing at the Edge of the World. In 1984, Le Guin was part of a group along with Ken Kesey, Brian Booth, and William Stafford that founded the Oregon Institute of Literary Arts, which is now known as Literary Arts in Portland. In December 2009, Le Guin resigned from the Authors Guild in protest over its endorsement of Google Books, Google’s book digitization project. “You decided to deal with the devil”, she wrote in her resignation letter. “There are principles involved, above all the whole concept of copyright; and these you have seen fit to abandon to a corporation, on their terms, without a struggle.” (See Authors Guild, Inc. v. Google, Inc..) Influences Le Guin was influenced by fantasy writers, including J. R. R. Tolkien, by science fiction writers, including Philip K. Dick (who was in her high school class, though they did not know each other), by central figures of Western literature such as Leo Tolstoy, Virgil and the Brontë sisters, by feminist writers such as Virginia Woolf, by children’s literature such as Alice in Wonderland, The Wind in the Willows, The Jungle Book, by Norse mythology, and by books from the Eastern tradition such as the Tao Te Ching. When asked about her influences, she replied: Once I learned to read, I read everything. I read all the famous fantasies – Alice in Wonderland, and Wind in the Willows, and Kipling. I adored Kipling’s Jungle Book. And then when I got older I found Lord Dunsany. He opened up a whole new world – the world of pure fantasy. And... Worm Ouroboros. Again, pure fantasy. Very, very fattening. And then my brother and I blundered into science fiction when I was 11 or 12. Early Asimov, things like that. But that didn’t have too much effect on me. It wasn’t until I came back to science fiction and discovered Sturgeon – but particularly Cordwainer Smith.... I read the story “Alpha Ralpha Boulevard”, and it just made me go, “Wow! This stuff is so beautiful, and so strange, and I want to do something like that.” In the mid-1950s, she read J. R. R. Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings, which had an enormous impact on her. But rather than making her want to follow in Tolkien’s footsteps, it simply showed her what was possible with the fantasy genre. Themes Le Guin exploits the creative flexibility of the science fiction and fantasy genres to undertake thorough explorations of dimensions of both social and psychological identity and of broader cultural and social structures. In doing so, she draws on sociology, anthropology, and psychology, leading some critics to categorize her work as soft science fiction. She objected to this classification of her writing, arguing the term is divisive and implies a narrow view of what constitutes valid science fiction. Underlying ideas of anarchism and environmentalism also make repeated appearances throughout Le Guin’s work. In 2014 Le Guin said about the appeal of contemplating possible futures in science fiction: anything at all can be said to happen [in the future] without fear of contradiction from a native. The future is a safe, sterile laboratory for trying out ideas in, a means of thinking about reality, a method. Sociology, anthropology and psychology Being so thoroughly informed by social science perspectives on identity and society, Le Guin treats race and gender quite deliberately. The majority of her main characters are people of color, a choice made to reflect the non-white majority of humans, and one to which she attributes the frequent lack of character illustrations on her book covers. Her writing often makes use of alien (i.e., human but non-Terran) cultures to examine structural characteristics of human culture and society and their impact on the individual. This prominent theme of cultural interaction is most likely rooted in the fact that Le Guin grew up in a household of anthropologists where she was surrounded by the remarkable case of Ishi – a Native American acclaimed in his time as the “last wild Indian” – and his interaction with the white man’s world. Le Guin’s father was director of the University of California Museum of Anthropology, where Ishi was studied and worked as a research assistant. Her mother wrote the bestseller Ishi in Two Worlds. Similar elements are echoed through many of Le Guin’s stories – from Planet of Exile and City of Illusions to The Word for World Is Forest and The Dispossessed. Le Guin’s writing notably employs the ordinary actions and transactions of everyday life, clarifying how these daily activities embed individuals in a context of relation to the physical world and to one another. For example, the engagement of the main characters with the everyday business of looking after animals, tending gardens and doing domestic chores is central to the novel Tehanu. Themes of Jungian psychology also are prominent in her writing. For example Le Guin’s Hainish Cycle, a series of novels encompassing a loose collection of societies, of various related human species, that exist largely in isolation from one another, providing the setting for her explorations of intercultural encounter. The Left Hand of Darkness, The Dispossessed and The Telling all consider the consequences of contact between different worlds and cultures. Unlike those in much mainstream science fiction, Hainish Cycle civilization does not possess reliable human faster-than-light travel, but does have technology for instantaneous communication. The social and cultural impact of the arrival of Ekumen envoys (known as “mobiles”) on remote planets, and the culture shock that the envoys experience, constitute major themes of The Left Hand of Darkness. Le Guin’s concept has been borrowed explicitly by several other well-known authors, to the extent of using the name of the communication device (the “ansible”). The Left Hand of Darkness is particularly noted for the way she explores social, cultural, and personal consequences of sexual identity through a novel involving a human’s encounter with an intermittently androgynous race. In addition to androgyny, Le Guin’s focus on sexuality breaks down normative gender roles. “Solitude”, one of the stories in The Birthday of the World: and Other Stories follows a young girl, more adventurous and daring than her older brother, into a world dominated by strong, territorial women. In Paradises Lost, the people of a spaceship several generations into the voyage to a new colony-world are saved by a female interstellar navigator, an archetypal role typically reserved for men. Environmentalism Elizabeth McDowell states in her 1992 master’s thesis that Le Guin "identif[ies] the present dominant socio-political American system as problematic and destructive to the health and life of the natural world, humanity, and their interrelations". This idea recurs in several of Le Guin’s works, most notably The Left Hand of Darkness (1969), The Word for World Is Forest (1972), The Dispossessed (1974), The Eye of the Heron (1978), Always Coming Home (1985), and “Buffalo Gals, Won’t You Come Out Tonight” (1987). All of these works center on ideas regarding socio-political organization and value-system experiments in both utopias and dystopias. As McDowell explains, “Although many of Le Guin’s works are exercises in the fantastic imagination, they are equally exercises of the political imagination.” In addition to her fiction, Le Guin’s book Out Here: Poems and Images from Steens Mountain Country, a collaboration with artist Roger Dorband, is a clear environmental testament to the natural beauty of that area of Eastern Oregon. Le Guin also wrote several works of poetry and nonfiction on Mount St. Helens following the 1980 eruption. These works explore local stories and discussions surrounding the eruption event in conjunction with Le Guin’s own perspective as it relates to viewing the eruption and mountain from her home in Portland, as well as her various visits into the blast zone. Anarchism and Taoism Le Guin’s feelings towards anarchism were closely tied to her Taoist beliefs and both ideas appear in her work. “Taoism and Anarchism fit together in some very interesting ways and I’ve been a Taoist ever since I learned what it was.” She participated in numerous peace marches and although she did not call herself an anarchist, since she did not live the lifestyle, she did feel that “Democracy is good but it isn’t the only way to achieve justice and a fair share.” Le Guin said: “The Dispossessed is an Anarchist utopian novel. Its ideas come from the Pacifist Anarchist tradition – Kropotkin etc. So did some of the ideas of the so-called counterculture of the sixties and seventies.” She also said that anarchism “is a necessary ideal at the very least. It is an ideal without which we couldn’t go on. If you are asking me is anarchism at this point a practical movement, well, then you get in the question of where you try to do it and who’s living on your boundary?” Le Guin has been credited with helping to popularize anarchism as her work "rescues anarchism from the cultural ghetto to which it has been consigned [and] introduces the anarchist vision... into the mainstream of intellectual discourse". Indeed her works were influential in developing a new anarchist way of thinking; a postmodern way that is more adaptable and looks at/addresses a broader range of concerns. Adaptations of her work Few of Le Guin’s major works have been adapted for film or television. Her 1971 novel The Lathe of Heaven has been adapted twice: The first adaptation was made in 1979 by WNET Channel 13 in New York, with her own participation, and the second adaptation was made in 2002 by the A&E Network. In a 2008 interview, she said she considers the 1979 adaptation as “the only good adaptation to film” of her work to date. In the early 1980s animator and director Hayao Miyazaki asked permission to create an animated adaptation of Earthsea. However, Le Guin, who was unfamiliar with his work and anime in general, turned down the offer. Years later, after seeing My Neighbor Totoro, she reconsidered her refusal, believing that if anyone should be allowed to direct an Earthsea film, it should be Hayao Miyazaki. The third and fourth Earthsea books were used as the basis of the 2006 animated film Tales from Earthsea (ゲド戦記, Gedo Senki). The film, however, was directed by Miyazaki’s son, Gorō, rather than Hayao Miyazaki himself, which disappointed Le Guin. While she was positive about the aesthetic of the film, writing that “much of it was beautiful”, she took great issue with its re-imagining of the moral sense of the books and greater focus on physical violence. "[E]vil has been comfortably externalized in a villain", Le Guin writes, "the wizard Kumo/Cob, who can simply be killed, thus solving all problems. In modern fantasy (literary or governmental), killing people is the usual solution to the so-called war between good and evil. My books are not conceived in terms of such a war, and offer no simple answers to simplistic questions.” In 1987, the CBC Radio anthology program Vanishing Point adapted The Dispossessed into a series of six 30-minute episodes, and at an unspecified date The Word for World Is Forest as a series of three 30-minute episodes. In 1995, Chicago’s Lifeline Theatre presented its adaptation of The Left Hand of Darkness. Reviewer Jack Helbig at the Chicago Reader wrote that the “adaptation is intelligent and well crafted but ultimately unsatisfying”, in large measure because it is extremely difficult to compress a complex 300-page novel into a two-hour stage presentation. In 2004 the Sci Fi Channel adapted the first two books of the Earthsea trilogy as the miniseries Legend of Earthsea. Le Guin was highly critical of the adaptation, calling it a “far cry from the Earthsea I envisioned”, objecting both to the use of white actors for her red, brown, or black-skinned characters, and to the way she was “cut out of the process”. Her novella, Paradises Lost, published in The Birthday of the World: and Other Stories, was adapted into an opera by the American composer Stephen Andrew Taylor and Canadian librettist Marcia Johnson. The opera premiered April 26, 2012 at the Krannert Center for the Performing Arts on the campus of the University of Illinois. In 2013, the Portland Playhouse and Hand2Mouth Theatre produced a stage adaptation of The Left Hand of Darkness, directed and adapted by Jonathan Walters, with text adapted by John Schmor. The play opened May 2, 2013, and ran until June 16, 2013, in Portland, Oregon. In 2015, the BBC commissioned radio adaptations of The Left Hand of Darkness and the first three Earthsea novels. The Left Hand of Darkness was aired as two hour-long episodes, and Earthsea as six half-hour episodes. In early 2017 Le Guin’s award winning novel The Left Hand of Darkness was picked up by Critical Content, a production company formerly known as Relativity Television, to be produced as a television limited series. Le Guin was to serve as a consulting producer on the project.


Sir Kingsley William Amis, CBE (16 April 1922– 22 October 1995) was an English novelist, poet, critic, and teacher. He wrote more than 20 novels, six volumes of poetry, a memoir, various short stories, radio and television scripts, along with works of social and literary criticism. According to his biographer, Zachary Leader, Amis was “the finest English comic novelist of the second half of the twentieth century.” He is the father of British novelist Martin Amis. In 2008, The Times ranked Kingsley Amis thirteenth on their list of the 50 greatest British writers since 1945. Life and career Kingsley Amis was born in Clapham, south London, the son of William Robert Amis, a mustard manufacturer’s clerk in the City of London and his wife, Rosa Annie (née Lucas). He was raised in Norbury– in his later estimation "not really a place, it’s an expression on a map [-] really I should say I came from Norbury station". He was educated at the City of London School on a scholarship, after his first year, and in April 1941 was admitted to St. John’s College, Oxford, also on a scholarship, where he read English. It was there that he met Philip Larkin, with whom he formed the most important friendship of his life. While at Oxford, in June 1941, Amis joined the Communist Party of Great Britain (but later broke with communism in 1956, after Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev denounced former Soviet premier Joseph Stalin in his speech On the Cult of Personality and Its Consequences). After only a year, in July 1942, he was called up for national service. After serving in the Royal Corps of Signals in the Second World War, Amis returned to Oxford in October 1945 to complete his degree. Although he worked hard and earned in 1947 a first in English, he had by then decided to give much of his time to writing. In 1946 he met Hilary Bardwell; they married in 1948 after she became pregnant with their first child, Philip. Amis initially arranged for her to have a back-street abortion, but changed his mind, fearing for her safety. He became a lecturer in English at the University of Wales, Swansea (1949–1961). Two other children followed: Martin in August 1949 and Sally in January 1954. Days after Sally’s birth, Amis’s first novel Lucky Jim was published to great acclaim; critics saw it as having caught the flavour of Britain in the 1950s, ushering in a new style of fiction. By 1972, in addition to impressive sales in Britain, one and a quarter million paperback copies had been sold in the United States, and it was eventually translated into twenty languages, including Polish, Hebrew, Korean, and Serbo-Croat. The novel won the Somerset Maugham Award for fiction and Amis was associated with the writers labelled the Angry Young Men. Lucky Jim was one of the first British campus novels, setting a precedent for later generations of writers such as Malcolm Bradbury, David Lodge, Tom Sharpe and Howard Jacobson. As a poet, Amis was associated with The Movement. During 1958–1959 he made the first of two visits to the United States, where he was Visiting Fellow in Creative Writing at Princeton University and a visiting lecturer in other northeastern universities. On returning to Britain, he fell into a rut, and he began looking for another post; after thirteen years at Swansea, Amis became a fellow of Peterhouse, Cambridge (1961–1963). He regretted the move within a year, finding Cambridge an academic and social disappointment and resigned in 1963, intent on moving to Majorca; he went no farther than London. In 1963, Hilary discovered Amis’s love affair with novelist Elizabeth Jane Howard. Hilary and Amis separated in August, and he went to live with Howard. He divorced Hilary in 1965 and married Howard the same year. In 1968 he moved with Howard to Lemmons, a house in Barnet, north London. She and Amis divorced in 1983. In his last years, Amis shared a house with his first wife Hilary and her third husband, Alastair Boyd, 7th Baron Kilmarnock. Martin wrote the memoir Experience about the life, charm, and decline of his father. Amis was knighted in 1990. In August 1995 he fell, suffering a suspected stroke. After apparently recovering, he worsened, was re-admitted to hospital, and died on 22 October 1995 at St Pancras Hospital, London. He was cremated; his ashes are at Golders Green Crematorium. Literary work Amis is chiefly known as a comedic novelist of mid– to late-20th-century British life, but his literary work extended into many genres—poetry, essays and criticism, short stories, food and drink writing, anthologies, and a number of novels in genres such as science fiction and mystery. His career initially developed in a pattern which was the inverse of that followed by his close friend Philip Larkin. Before becoming known as a poet, Larkin had published two novels; Amis, on the other hand, originally wished to be a poet, and turned to writing novels only after publishing several volumes of verse. He continued throughout his career to write poetry which is known for its typically straightforward and accessible style, yet which often masks a nuance of thought, for example, in “Bookshop Idyll” or “Against Romanticism”, just as it does in his novels. Amis’s first novel, Lucky Jim (1954), is perhaps his most famous, satirizing the high-brow academic set of an unnamed university, seen through the eyes of its protagonist, Jim Dixon, as he tries to make his way as a young lecturer of history. The novel was perceived by many as part of the Angry Young Men movement of the 1950s which reacted against the stultification of conventional British life, though Amis never encouraged this interpretation. Amis’s other novels of the 1950s and early 1960s similarly depict situations from contemporary British life, often drawn from Amis’s own experiences. That Uncertain Feeling (1955) centres on a young provincial librarian (again perhaps with reference to Larkin, librarian at Hull) and his temptation towards adultery; I Like It Here (1958) presents Amis’s contemptuous view of “abroad” and followed upon his own travels on the Continent with a young family; Take a Girl Like You (1960) steps away from the immediately autobiographical, but remains grounded in the concerns of sex and love in ordinary modern life, tracing the courtship and ultimate seduction of the heroine Jenny Bunn by a young schoolmaster, Patrick Standish. With The Anti-Death League (1966), Amis begins to show some of the experimentation– with content, if not with style– which would mark much of his work in the 1960s and 70s. Amis’s departure from the strict realism of his early comedic novels is not so abrupt as might first appear. He had avidly read science fiction since a boy, and had developed that interest into the Christian Gauss Lectures of 1958, while visiting Princeton University. The lectures were published in that year as New Maps of Hell: A Survey of Science Fiction, a serious but light-handed treatment of what the genre had to say about man and society. Amis was particularly enthusiastic about the dystopian works of Frederik Pohl and C. M. Kornbluth, and in New Maps of Hell coined the term “comic inferno” to describe a type of humorous dystopia, particularly as exemplified in the works of Robert Sheckley. Amis further displayed his devotion to the genre in editing, with the Sovietologist Robert Conquest, the science fiction anthology series Spectrum I–V, which drew heavily upon 1950s numbers of the magazine Astounding Science Fiction. Though not explicitly science fiction, The Anti-Death League takes liberties with reality not found in Amis’s earlier novels, and introduces a speculative bent into his fiction, one which would continue to develop in other of his genre novels, such as The Green Man (1969) (mystery/horror) and The Alteration (1976) (alternative history). Much of this speculation was about the improbable existence of any benevolent deity involved in human affairs. In The Anti-Death League, The Green Man, The Alteration and elsewhere, including poems such as “The Huge Artifice: an interim assessment” and “New Approach Needed”, Amis showed frustration with a God who could lace the world with such cruelty and injustice, and championed the preservation of ordinary human happiness– in family, in friendships, in physical pleasure– against the demands of any cosmological scheme. The matter of Amis’s religious views is perhaps ultimately summed up in his response, reported in his Memoirs, to the Russian poet Yevgeny Yevtushenko’s question, in his broken English: “You atheist?” Amis replied, “It’s more that I hate Him.” During this time, Amis had not turned completely away from the comedic realism of Lucky Jim and Take a Girl Like You. I Want It Now (1968) and Girl, 20 (1971) both depict the “swinging” atmosphere of London in the late '60s, in which Amis certainly participated, though neither book is strictly autobiographical. Girl, 20, for instance, is framed in the world of classical (and pop) music, of which Amis was not a part—the book’s relatively impressive command of musical terminology and opinion shows both Amis’s amateur devotion to music and the almost journalistic capacity of his intelligence to take hold of a subject which interested him. That intelligence is similarly on display in, for instance, the presentation of ecclesiastical matters in The Alteration, when Amis was neither a Roman Catholic nor, for that matter, a devotee of any Church. Throughout the 1950s, '60s, and '70s, Amis was regularly producing essays and criticism, principally for journalistic publication. Some of these pieces were collected in 1968's What Became of Jane Austen? and Other Essays, in which Amis’s wit and literary and social opinions were on display ranging over books such as Colin Wilson’s The Outsider (panned), Iris Murdoch’s debut novel Under the Net (praised), or William Empson’s Milton’s God (inclined to agree with). Amis’s opinions on books and people tended to appear (and often, be) conservative, and yet, as the title essay of the collection shows, he was not merely reverent of “the classics” and of traditional morals, but was more disposed to exercise his own rather independent judgment in all things. Amis became associated with Ian Fleming’s James Bond novels, which he greatly admired, in the late 1960s, when he began composing critical works connected with the fictional spy, either under a pseudonym or uncredited. In 1965, he wrote the popular The James Bond Dossier under his own name. That same year, he wrote The Book of Bond, or, Every Man His Own 007, a tongue-in-cheek how-to manual about being a sophisticated spy, under the pseudonym “Lt Col. William ('Bill’) Tanner”, Tanner being M’s Chief of Staff in many of Fleming’s Bond novels. In 1968 Amis wrote Colonel Sun, which was published under the pseudonym “Robert Markham”. Amis’s literary style and tone changed significantly after 1970, with the possible exception of The Old Devils, a Booker Prize winner. Several critics accused him of being old fashioned and misogynistic. His Stanley and the Women, an exploration of social sanity, could be said to instance these traits. Others said that his output lacked the humanity, wit, and compassion of earlier efforts. This period also saw Amis the anthologist, a role in which his wide knowledge of all kinds of English poetry was on display. The New Oxford Book of Light Verse (1978), which he edited, was a revision of the original volume done by W. H. Auden. Amis took the anthology in a markedly new direction: Auden had interpreted light verse to include “low” verse of working-class or lower-class origin, regardless of subject matter, while Amis defined light verse as essentially light in tone, though not necessarily simple in composition. The Amis Anthology (1988), a personal selection of his favourite poems, grew out of his work for a London newspaper, in which he selected a poem daily and presented it with a brief introduction. Amis was shortlisted for the Booker Prize three times in his writing career for Ending Up (1974), Jake’s Thing (1978), and finally winning the prize for The Old Devils in 1986. In 2008, The Times ranked Kingsley Amis thirteenth on their list of the 50 greatest British writers since 1945. Personal life and political views As a young man at Oxford, Amis briefly joined the Communist Party. He left in 1956. He later described this stage of his political life as “the callow Marxist phase that seemed almost compulsory in Oxford”. Amis remained nominally on the Left for some time after the war, declaring in the 1950s that he would always vote for the Labour Party. But he eventually moved further right, a development he discussed in the essay “Why Lucky Jim Turned Right” (1967); his conservatism and anti-communism can be seen in such later works of his as the dystopian novel Russian Hide and Seek (1980). In 1967, Amis, Robert Conquest, John Braine and several other right-wing authors signed a controversial letter to The Times entitled “Backing for U.S. Policies in Vietnam”, supporting the US government in the Vietnam War. He spoke at the Adam Smith Institute, arguing against government subsidy to the arts. Amis was by his own admission and as revealed by his biographers a serial adulterer for much of his life. This was one of the main contributory factors in the breakdown of his first marriage. A famous photograph of a sleeping Amis on a Yugoslav beach shows the slogan (written by wife Hilly) on his back "1 Fat Englishman– I fuck anything". In one of his memoirs, Amis wrote: “Now and then I become conscious of having the reputation of being one of the great drinkers, if not one of the great drunks, of our time”. He suggests that this is the result of a naïve tendency on the part of his readers to apply the behaviour of his characters to himself. This was disingenuous; the fact was that he enjoyed drink, and spent a good deal of his time in pubs. Hilary Rubinstein, who accepted Lucky Jim for publication at Victor Gollancz, commented: “I doubted whether Jim Dixon would have gone to the pub and drunk ten pints of beer... I didn’t know Kingsley very well, you see.” Clive James comments: “All on his own, he had the weekly drinks bill of a whole table at the Garrick Club even before he was elected. After he was, he would get so tight there that he could barely make it to the taxi.” Amis was, however, adamant in his belief that inspiration did not come from a bottle: “Whatever part drink may play in the writer’s life, it must play none in his or her work.” That this was certainly the case is attested to by Amis’s highly disciplined approach to writing. For 'many years’, Amis imposed a rigorous daily schedule upon himself in which writing and drinking were strictly segregated. Mornings were devoted to writing with a minimum daily output of 500 words. The drinking would only begin around lunchtime when this output had been achieved. Amis’s prodigious output would not have been possible without this kind of self-discipline. Nevertheless, according to Clive James, Amis reached a turning point when his drinking ceased to be social, and became a way of dulling his remorse and regret at his behaviour toward Hilly. “Amis had turned against himself deliberately... it seems fair to guess that the troubled grandee came to disapprove of his own conduct.” His friend Christopher Hitchens said: “The booze got to him in the end, and robbed him of his wit and charm as well as of his health.” Amis had a somewhat complex relationship with anti-Semitism, which he sometimes expressed but also disliked and opposed. He occasionally speculated on the historically received, and commonly accepted, stereotypes attributed to Jewish character. Anti-semitism was sometimes present in his conversations and letters written to friends and associates: “The great Jewish vice is glibness, fluency... also possibly just bullshit, as in Marx, Freud, Marcuse.” Or, “Chaplin is a horse’s arse. He’s a Jeeeew you see, like the Marx Brothers, like Danny Kaye.” It is a minor theme in his novel about a paranoid schizophrenic, Stanley and the Women. As for the cultural complexion of America, Amis had this to say: “I’ve finally worked out why I don’t like Americans... Because everyone there is either a Jew or a hick.” Amis himself described his anti-Semitism as being “Very mild ...” Family Amis’s first marriage, of fifteen years, was to Hilary Bardwell, daughter of a civil servant, by whom he had two sons and one daughter: Philip Amis, a graphics designer; Martin Amis, a novelist; and Sally Amis, who died in 2000. Amis was married a second time, to the novelist Elizabeth Jane Howard from 1965 to 1983, with whom he had no children. At the end of his second marriage, he went to live with his ex-wife Hilary and her third husband, in a deal brokered by their two sons Philip and Martin, so that he could be cared for until his death. Partial bibliography Poetry * 1947 Bright November * 1953 A Frame of Mind * 1954 Poems: Fantasy Portraits * 1956 A Case of Samples: Poems 1946–1956 * 1962 The Evans County * 1968 A Look Round the Estate: Poems, 1957–1967 * 1979 Collected Poems 1944–78 Fiction Novels * c.1948 The Legacy (unpublished) * 1954 Lucky Jim * 1955 That Uncertain Feeling * 1958 I Like It Here * 1960 Take a Girl Like You * 1963 One Fat Englishman * 1965 The Egyptologists (with Robert Conquest) * 1966 The Anti-Death League * 1968 Colonel Sun: a James Bond Adventure (pseud. Robert Markham) * 1968 I Want It Now * 1969 The Green Man * 1971 Girl, 20 * 1973 The Riverside Villas Murder * 1974 Ending Up * 1975 The Crime of the Century * 1976 The Alteration * 1978 Jake’s Thing * 1980 Russian Hide-and-Seek * 1984 Stanley and the Women * 1986 The Old Devils * 1988 Difficulties with Girls * 1990 The Folks That Live on the Hill * 1991 We Are All Guilty * 1992 The Russian Girl * 1994 You Can’t Do Both * 1995 The Biographer’s Moustache * c.1995 Black and White (unfinished) Short fiction collections * 1962 My Enemy’s Enemy * 1980 Collected Short Stories * 1991 Mr Barrett’s Secret and Other Stories Other short fiction 1960 “Hemingway in Space” (short story), Punch December 1960 Non-fiction * 1957 Socialism and the Intellectuals, a Fabian Society pamphlet * 1960 New Maps of Hell: A Survey of Science Fiction * 1965 The James Bond Dossier * 1965 The Book of Bond, or Every Man His Own 007 (pseud. Lt.-Col William ('Bill’) Tanner) * 1970 What Became of Jane Austen?, and Other Questions * 1972 On Drink * 1974 Rudyard Kipling and His World * 1983 Everyday Drinking * 1984 How’s Your Glass? * 1990 The Amis Collection * 1991 Memoirs * 1997 The King’s English: A Guide to Modern Usage (name in part a pun as he was sometimes called “Kingers” or “The King” by friends and family, as told by his son Martin in his memoir Experience) * 2001 The Letters of Kingsley Amis, Edited by Zachary Leader * 2008 Everyday Drinking: The Distilled Kingsley Amis, Introduction by Christopher Hitchens (an omnibus edition of On Drink, Everyday Drinking and How’s Your Glass?) Editor * 1967 Spectrum V: a fifth science fiction anthology (ed. with Robert Conquest) * 1978 The New Oxford Book of Light Verse (ed.) Poets in The Amis Anthology: A Personal Choice of English Verse (1988) Richard Aldington– Kenneth Allott– Matthew Arnold– Kenneth Ashley– W. H. Auden– William Barnes– Oliver Bayley– Hilaire Belloc– John Betjeman– Laurence Binyon– William Blake– Edmund Blunden– Rupert Brooke– Robert Browning– Robert Burns– Thomas Campbell– Thomas Campion– G. K. Chesterton– Hartley Coleridge– Robert Conquest– W. J. Cory– John Davidson– Donald Davie– C. Day Lewis– Walter de la Mare– Ernest Dowson– Michael Drayton– Lawrence Durrell– Jean Elliot– George Farewell– James Elroy Flecker– Thomas Ford– Roy Fuller– Robert Graves– Thomas Gray– Fulke Greville– Heath– Reginald Heber– Felicia Dorothea Hemans– W. E. Henley– George Herbert– Ralph Hodgson– Thomas Hood– Teresa Hooley– Gerard Manley Hopkins– A. E. Housman– Henry Howard, Earl of Surrey– T. E. Hulme– Leigh Hunt– Elizabeth Jennings– Samuel Johnson– John Keats– Henry King– Charles Kingsley– Rudyard Kipling– Philip Larkin– Henry Wadsworth Longfellow– John Lydgate– H. F. Lyte– Louis MacNeice– Andrew Marvell– John Masefield– Alice Meynell– Harold Monro– William Morris– Edwin Muir– Henry Newbolt– Alfred Noyes– Wilfred Owen– Thomas Love Peacock– George Peele– Alexander Pope– Frederic Prokosch– Walter Ralegh– John Crowe Ransom– Christina Rossetti– Siegfried Sassoon– John Skelton– Robert Southey– Edmund Spenser– Sir John Squire– Robert Louis Stevenson– John Suckling– Algernon Charles Swinburne– George Szirtes– Alfred, Lord Tennyson– Dylan Thomas– Edward Thomas– R. S. Thomas– Francis Thompson– Anthony Thwaite– Chidiock Tichborne– Aurelian Townsend– W. J. Turner– Oscar Wilde– John Wilmot, Lord Rochester– Roger Woddis– Charles Wolfe– William Wordsworth– William Butler Yeats– Andrew Young References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kingsley_Amis

Helen Joy Davidman (18 April 1915 – 13 July 1960) was an American poet and writer. Often referred to as a child prodigy, she earned a master's degree from Columbia University in English literature at age twenty in 1935. For her book of poems, Letter to a Comrade, she won the Yale Series of Younger Poets Competition in 1938 and the Russell Loines Award for Poetry in 1939. She was the author of several books, including two novels.


Tess Gallagher (born July 21, 1943 in Port Angeles, Washington) is an American poet, essayist, and short story writer. She attended the University of Washington, where she studied creative writing with Theodore Roethke and later Nelson Bentley as well as David Wagoner and Mark Strand. Her honors include a fellowship from the Guggenheim Foundation, two National Endowment for the Arts awards, the The Maxine Cushing Gray Endowed Libraries Visiting Writers Fellowship (University of Washington), and the Elliston Award for “best book of poetry published by a small press” for the collection Instructions to the Double (1976). Her late husband, Raymond Carver, encouraged her to write short stories, some of which were collected in The Lover of Horses (1987) and At the Owl Woman Saloon (1996). Her book Moon Crossing Bridge is a collection of love poems written for Carver after his death from cancer in 1988. “Moon Crossing Bridge” was followed in 2002 by the collection “Dear Ghosts.” Gallagher has taught at many colleges, most recently at Bucknell University and Whitman College. In December 2006, she published an essay in The Sun Magazine, titled “Instead of Dying”, about alcoholism and Raymond Carver’s having maintained his sobriety. The essay is an adaptation of a talk she initially delivered at the Welsh Academy’s Academi Intoxication Conference in 2006. The first lines read: “Instead of dying from alcohol, Raymond Carver chose to live. I would meet him five months after this choice, so I never knew the Ray who drank, except by report and through the characters and actions of his stories and poems.” Distant Rain, published in 2006, is a conversation between Tess and Jakuchō Setouchi, a Buddhist nun from Kyoto, which took place after Carver’s death.


Nicholas Breton (also Britton or Brittaine) (1545–1626), English poet and novelist, belonged to an old family settled at Layer Breton, Essex. Life His father, William Breton, a London merchant who had made a considerable fortune, died in 1559, and the widow (née Elizabeth Bacon) married the poet George Gascoigne before her sons had attained their majority. Nicholas Breton was probably born at the “capitall mansion house” in Red Cross Street, in the parish of St Giles without Cripplegate, mentioned in his father’s will. There is no official record of his residence at the university, but the diary of the Rev. Richard Madox tells us that he was at Antwerp in 1583 and was “once of Oriel College.” He married Ann Sutton in 1593, and had a family. He is supposed to have died shortly after the publication of his last work, Fantastickes (1626). Breton found a patron in Mary, countess of Pembroke, and wrote much in her honour until 1601, when she seems to have withdrawn her favour. It is probably safe to supplement the meagre record of his life by accepting as autobiographical some of the letters signed N.B. in A Poste with a Packet of Mad Letters (1603, enlarged 1637); the 19th letter of the second part contains a general complaint of many griefs, and proceeds as follows: “Hath another been wounded in the warres, fared hard, lain in a cold bed many a bitter storme, and beene at many a hard banquet? all these have I; another imprisoned? so have I; another long been sicke? so have I; another plagued with an unquiet life? so have I; another indebted to his hearts griefe, and fame would pay and cannot? so am I.” Works * Breton was a prolific author of considerable versatility and gift, popular with his contemporaries, and forgotten by the next generation. His work consists of religious and pastoral poems, satires, and a number of miscellaneous prose tracts. His religious poems are sometimes wearisome by their excess of fluency and sweetness, but they are evidently the expression of a devout and earnest mind. His lyrics are pure and fresh, and his romances, though full of conceits, are pleasant reading, remarkably free from grossness. His praise of the Virgin and his references to Mary Magdalene have suggested that he was a Roman Catholic, but his prose writings abundantly prove that he was an ardent Anglican. * Breton had little gift for satire, and his best work is to be found in his pastoral poetry. His Passionate Shepheard (1604) is full of sunshine and fresh air, and of unaffected gaiety. The third pastoral in this book—"Who can live in heart so glad As the merrie country lad"—is well known; with some other of Breton’s daintiest poems, among them the lullaby, “Come little babe, come silly soule,” (This poem, however, comes from The Arbor of Amorous Devises, which is only in part Breton’s work.)—it is incorporated in A. H. Bullen’s Lyrics from Elizabethan Romances (1890). His keen observation of country life appears also in his prose idyll, Wits Trenckrnour, “a conference betwixt a scholler and an angler,” and in his Fantastickes, a series of short prose pictures of the months, the Christian festivals and the hours, which throw much light on the customs of the times. Most of Breton’s books are very rare and have great bibliographical value. His works, with the exception of some belonging to private owners, were collected by Dr AB Grosart in the Chertsey Worthies Library in 1879, with an elaborate introduction quoting the documents for the poet’s history. * Breton’s poetical works, the titles of which are here somewhat abbreviated, include: * The Workes of a Young Wit (1577) * A Floorish upon Fancie (1577) * The Pilgrimage to Paradise (1592), with a prefatory letter by John Case * The Countess of Penbrook’s Passion (manuscript), first printed by JO Halliwell-Phillipps in 1853 [1] * Pasquil’s Fooles cappe (entered at Stationers’ Hall in 1600) * Pasquil’s Mistresse (1600) * Pasquil’s Passe and Passeth Not (1600) * Melancholike Humours (1600) - reprinted by Scholartis Press London. 1929. * Marie Magdalen’s Love: a Solemne Passion of the Soules Love (1595), the first part of which, a prose treatise, is probably by another hand; the second part, a poem in six-lined stanza, is certainly by Breton * A Divine Poem, including “The Ravisht Soul” and “The Blessed Weeper” (1601) * An Excellent Poem, upon the Longing of a Blessed heart (1601) * The Soules Heavenly Exercise (1601) * The Soules Harmony (1602) * Olde Madcappe newe Gaily mawfrey (1602) * The Mother’s Blessing (1602) * A True Description of Unthankfulnesse (1602) * The Passionate Shepheard (1604) * The Souies Immortail Crowne (1605) * The Honour of Valour (1605) * An Invective against Treason; I would and I would not (1614) * Bryton’s Bowre of Delights (1591), edited by Dr Grosart in 1893, an unauthorized publication which contained some poems disclaimed by Breton * The Arbor of Amorous Devises (entered at Stationers’ Hall, 1594), only in part Breton’s * contributions to England’s Helicon and other miscellanies of verse. * Of his twenty-two prose tracts may be mentioned Wit’s Trenchmour (1597), The Wil of Wit (1599), A Poste with a Packet of Mad Letters (1602-6). Sir Philip Sidney’s Ourania by N. B. (1606), A Mad World, my Masters, Adventures of Two Excellent Princes, Grimello’s Fortunes (1603), Strange News out of Divers Countries (1622), etc.; Mary Magdalen’s Lamentations (1604), and The Passion of a Discontented Mind (1601), are sometimes, but erroneously, ascribed to Breton. Footnotes References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicholas_Breton

Dorothy Mae Ann Wordsworth (25 December 1771 – 25 January 1855) was an English author, poet and diarist. She was the sister of the Romantic poet William Wordsworth, and the two were close all their lives. Wordsworth had no ambitions to be an author, and her writings consist only of series of letters, diary entries, poems and short stories. Life She was born on Christmas Day in Cockermouth, Cumberland in 1771. Despite the early deaths of both her parents, Dorothy, William and their three siblings had a happy childhood. When in 1783, their father died and the children were sent to live with various relatives. Wordsworth was sent alone to live with her aunt, Elizabeth Threlkeld, in Halifax, West Yorkshire. After she was able to reunite with William firstly at Racedown Lodge in Dorset in 1795 and afterwards (1797/98) at Alfoxden House in Somerset, they became inseparable companions. The pair lived in poverty at first; and would often beg for cast-off clothes from their friends. William wrote of her in his famous Tintern Abbey poem: Of this fair river; thou my dearest Friend, My dear, dear Friend; and in thy voice I catch The language of my former heart, and read My former pleasures in the shooting lights Of thy wild eyes [...] My dear, dear Sister! Wordsworth was a diarist and somewhat amateur poet with little interest in becoming an established writer. "I should detest the idea of setting myself up as an author," she once wrote, "give Wm. the Pleasure of it." She almost published her travel account with William to Scotland in 1803 Recollections of a Tour Made in Scotland, but a publisher was not found and it would not be published until 1874. She wrote a very early account of an ascent of Scafell Pike in 1818 (perhaps predated only by Samuel Taylor Coleridge's of 1802), climbing the mountain in the company of her friend Mary Barker, Miss Barker's maid, and two local people to act as guide and porter. Dorothy's work was used in 1822 by her brother William, unattributed, in his popular guide book to the Lake District - and this was then copied by Harriet Martineau in her equally successful guide[5] (in its fourth edition by 1876), but with attribution, if only to William Wordsworth. Consequently this story was very widely read by the many visitors to the Lake District over more than half of the 19th century. She never married, and after William married Mary Hutchinson in 1802, continued to live with them. She was by now 31, and thought of herself as too old for marriage. In 1829 she fell seriously ill and was to remain an invalid for the remainder of her life. She died at eighty-three in 1855, having spent the past twenty years in, according to the biographer Richard Cavendish, "a deepening haze of senility". Her Grasmere Journal was published in 1897, edited by William Angus Knight. The journal eloquently described her day-to-day life in the Lake District, long walks she and her brother took through the countryside, and detailed portraits of literary lights of the early 19th century, including Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Sir Walter Scott, Charles Lamb and Robert Southey, a close friend who popularised the fairytale Goldilocks and the Three Bears. Dorothy's works came to light just as literary critics were beginning to re-examine women's role in literature. The success of the Grasmere Journal led to a renewed interest in Wordsworth, and several other journals and collections of her letters have since been published. The Grasmere Journal and Wordsworth's other works revealed how vital she was to her brother's success. William relied on her detailed accounts of nature scenes and borrowed freely from her journals. For example Dorothy wrote in her journal of 5 April 1802 "... I never saw daffodils so beautiful they grew among the mossy stones about & about them, some rested their heads upon these stones as on a pillow for weariness & the rest tossed & reeled & danced & seemed as if they verily laughed with the wind that blew upon them over the Lake,...". This passage is clearly brought to mind when reading William's "Daffodils", where her brother, in this poem of two years later, describes what appears to be the shared experience in the journal as his own solitary observation. References Wikipeda - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dorothy_Wordsworth


Robert Bly (born December 23, 1926) is an American poet, author, activist and leader of the mythopoetic men’s movement. His most commercially successful book to date was Iron John: A Book About Men (1990), a key text of the mythopoetic men’s movement, which spent 62 weeks on The New York Times Best Seller list. He won the 1968 National Book Award for Poetry for his book The Light Around the Body. Life Bly was born in Lac qui Parle County, Minnesota, to Jacob and Alice Bly, who were of Norwegian ancestry. Following graduation from high school in 1944, he enlisted in the United States Navy, serving two years. After one year at St. Olaf College in Minnesota, he transferred to Harvard University, joining the later famous group of writers who were undergraduates at that time, including Donald Hall, Will Morgan, Adrienne Rich, Kenneth Koch, Frank O’Hara, John Ashbery, Harold Brodkey, George Plimpton and John Hawkes. He graduated in 1950 and spent the next few years in New York. Beginning in 1954, Bly spent two years at the University of Iowa at the Iowa Writers Workshop, completing a master’s degree in fine arts, along with W. D. Snodgrass, Donald Justice, and others. In 1956, he received a Fulbright Grant to travel to Norway and translate Norwegian poetry into English. While there, he found not only his relatives, but became acquainted with the work of a number of major poets whose work was barely known in the United States, among them Pablo Neruda, Cesar Vallejo, Antonio Machado, Gunnar Ekelof, Georg Trakl, Rumi, Hafez, Kabir, Mirabai, and Harry Martinson. Bly determined then to start a literary magazine for poetry translation in the United States. The Fifties, The Sixties, and The Seventies introduced many of these poets to the writers of his generation. He also published essays on American poets. During this time, Bly lived on a farm in Minnesota, with his wife and children. His first marriage was to award-winning short story novelist Carol Bly. They had four children, including Mary Bly—a best-selling novelist and Literature Professor at Fordham University as of 2011—and they divorced in 1979. Since 1980 Bly has been married to the former Ruth Counsell; by that marriage he had a stepdaughter and stepson, although the stepson died in a pedestrian–train incident. Career Bly’s early collection of poems, Silence in the Snowy Fields, was published in 1962, and its plain, imagistic style had considerable influence on American verse of the next two decades. The following year, he published “A Wrong Turning in American Poetry”, an essay in which he argued that the vast majority of American poetry from 1917 to 1963 was lacking in soul and “inwardness” as a result of a focus on impersonality and an objectifying, intellectual view of the world that Bly believed was instigated by the Modernists and formed the aesthetic of most post-World War II American poetry. He criticized the influence of American-born Modernists like Eliot, Pound, Marianne Moore, and William Carlos Williams and argued that American poetry needed to model itself on the more inward-looking work of European and South American poets like Pablo Neruda, César Vallejo, Juan Ramón Jiménez, Antonio Machado, and Rainer Maria Rilke. In 1966, Bly co-founded American Writers Against the Vietnam War and went on to lead much of the opposition to that war among writers. In 1968, he signed the “Writers and Editors War Tax Protest” pledge, vowing to refuse tax payments in protest against the war. In his speech accepting the National Book Award for The Light Around the Body, he announced that he would be contributing the $1000 prize to draft resistance organizations. During the sixties he was of great help to the Bengali Hungryalist poets who faced anti-establishment trial at Kolkata, India. Bly became one of the most important of American protest poets during the Vietnam War; his 1970 poem “The Teeth Mother Naked At Last,” later collected in his collection Sleepers Joining Hands (1973) is a major contribution to this poetry. During the 1970s, he published eleven books of poetry, essays, and translations, celebrating the power of myth, Indian ecstatic poetry, meditation, and storytelling. During the 1980s he published Loving a Woman in Two Worlds, The Wingéd Life: Selected Poems and Prose of Thoreau, The Man in the Black Coat Turns, and A Little Book on the Human Shadow. In 1975, he organized the first annual Great Mother Conference. Throughout the ten-day event, poetry, music, and dance were utilized to examine human consciousness. The conference has been held annually through 2015 in Nobleboro Maine. In the beginning one of its major themes was the goddess or “Great Mother” as she has been known throughout human history. Much of Bly’s 1973 book of poems “Sleepers Joining Hands” is concerned with this theme. In the context of the Vietnam War, a focus on the divine feminine was seen as urgent and necessary. Since that time, the Conference has expanded to consider a wide variety of poetic, mythological, and fairy tale traditions. In the ’80s and ’90s there was much discussion among the conference community about the changes contemporary men were (and are) going through; “the New Father” was then added to the Conference title, in recognition of this and in order to keep the Conference as inclusive as possible. Perhaps his most famous work is Iron John: A Book About Men (1990), an international bestseller which has been translated into many languages and is credited with starting the Mythopoetic men’s movement in the United States. Bly frequently conducts workshops for men with James Hillman, Michael J. Meade, and others, as well as workshops for men and women with Marion Woodman. He maintains a friendly correspondence with Clarissa Pinkola Estés, author of Women Who Run With the Wolves. Bly wrote The Maiden King: The Reunion of Masculine and Feminine with Marion Woodman. Bly was the University of Minnesota Library’s 2002 Distinguished Writer. He received the McKnight Foundation’s Distinguished Artist Award in 2000, and the Maurice English Poetry Award in 2002. He has published more than 40 collections of poetry, edited many others, and published translations of poetry and prose from such languages as Swedish, Norwegian, German, Spanish, Persian and Urdu. His book The Night Abraham Called to the Stars was nominated for a Minnesota Book Award. He also edited the prestigious Best American Poetry 1999 (Scribners). In 2006 the University of Minnesota purchased Bly’s archive, which contained more than 80,000 pages of handwritten manuscripts; a journal spanning nearly 50 years; notebooks of his “morning poems”; drafts of translations; hundreds of audio and videotapes, and correspondence with many writers such as James Wright, Donald Hall and James Dickey. The archive is housed at Elmer L. Andersen Library on the University of Minnesota campus. The university paid $775,000 from school funds and private donors. In February 2008, Bly was named Minnesota’s first poet laureate. In that year he also contributed a poem and an Afterword to From the Other World: Poems in Memory of James Wright. In February 2013, he was awarded the Robert Frost Medal, a lifetime achievement recognition given by the Poetry Society of America. Thought and the Men’s Movement Much of Bly’s writing focuses on what he saw as the particularly troubled situation in which many males find themselves today. He understood this to be a result of, among other things, the decline of traditional fathering which left young boys unguided through the stages of life leading to maturity. He claimed that in contrast with women who are better informed by their bodies (notably by the beginning and end of their menstrual cycle), men need to be actively guided out of boyhood and into manhood by their elders. Pre-modern cultures had elaborate myths, often enacted as rites of passage, as well as “men’s societies” where older men would teach young boys about these gender-specific issues. As modern fathers have become increasingly absent, this knowledge is no longer being passed down the generations, resulting in what he referred to as a Sibling Society. The “Absence of the Father” is a recurrent theme in Bly’s work and many of the phenomena of depression, juvenile delinquency and lack of leadership in business and politics are linked to it. Bly therefore sees today’s men as half-adults, trapped between boyhood and maturity, in a state where they find it hard to become responsible in their work as well as leaders in their communities. Eventually they might become weak or absent fathers themselves which will lead this behaviour to be passed down to their children. In his book The Sibling Society (1997), Bly argues that a society formed of such men is inherently problematic as it lacks creativity and a deep sense of empathy. The image of half-adults is further reinforced by popular culture which often portrays fathers as naive, overweight and almost always emotionally co-dependent. Historically this represents a recent shift from a traditional patriarchal model and Bly believes that women rushed to fill the gap that was formed through the various youth movements during the 1960s, enhancing men’s emotional capacities and helping them to connect with women’s age-old pain of repression. It has however also led to the creation of “soft males” which lacked the outwardly directed strength to revitalize the community with assertiveness and a certain warrior strength. In Bly’s view, a potential solution lies in the rediscovery of the meanings hidden in traditional myths and fairytales as well as works of poetry. He researched and collected myths that concern male maturity, often originating from the Grimms’ Fairy Tales and published them in various books, Iron John being the best known example. In contrast to the continual pursuit of higher achievements, that is constantly taught to young men today, the theme of spiritual descent (often being referred to by its Greek term κατάβασις) which is to be found in many of these myths, is presented as a necessary step for coming in contact with the deeper aspects of the masculine self and achieving its full potential. This is often presented as hero, often during the middle of his quest, going underground to pass a period of solitude and sorrow in semi-bestial mode. Bly notices that a cultural space existed in most traditional societies for such a period in a man’s life, in the absence of which, many men today go into a depression and alcoholism as they subconsciously try to emulate this innate ritual. Bly was influenced by the Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung who developed the theory of archetypes, as the discrete structures of the Psyche which emerge as images in both art and myths. The Powerful King, the Evil Witch and the Beautiful Maiden are, according to Jung, imprints of the collective unconscious and Bly wrote extensively about their meaning and relations to modern life. As an example and in accordance with Jung, he considered the Witch to be that part of the male psyche upon which the negative and destructive side of a woman is imprinted and which first developed during infancy to store the imperfections of one’s own mother’s. As a consequence, the Witch’s symbols are essentially inverted motherly symbols, where the loving act of cooking is transformed into the brewing of evil potions and knitting clothes takes the form of spider’s web. The feeding process is also reversed, with the child now in danger of being eaten to feed the body of the Witch rather than being fed by the mother’s own body. In that respect, the Witch is a mark of arrested development on the part of the man as it guards against feminine realities that the his psyche is not yet able to incorporate fully. Fairy tales according to this interpretation mostly describe internal battles laid out in externally, where the hero saves his future bride by killing a witch, as in “The Drummer” (Grimms tale 193). This particular concept is expanded in Bly’s 1989 talk “The Human Shadow” and the book it presented. Works References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_Bly


Alan Dugan (February 12, 1923– September 3, 2003) was an American poet. His first volume Poems published in 1961 was a chosen by the Yale Series of Younger Poets and went on to win the National Book Award for Poetry and the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry. His last volume, entitled Poems Seven: New and Complete Poetry, was published in 2001 by Seven Stories Press in New York and won Dugan a second National Book Award. Since his death in 2003, a complete volume of collected poetry has yet to appear.


Zora Bernice May Cross (18 May 1890– 22 January 1964) was an Australian poet, novelist and journalist. She was born on May 18, 1890 on Eagle Farm, Brisbane to Earnest William Cross and Mary Louisa Eliza Ann. Her father was a Sydney born accountant. Cross inherited her love for literature from both her parents, poetry from her mother and Celtic knowledge from her father, who was also the son of an Irish printer. and was educated at Ipswich Girls’ Grammar School and then Sydney Teachers’ College from 1909 to 1910. She taught for three years and then worked as a journalist, for the Boomerang and then as a freelance writer. On March 11, 1911, she married Stuart Smith but later refused to live with him. This led to her marriage being dissolved on September 10, 1922. Later on in her life, Cross had a “de facto” husband, David McKee Wright, who she had two daughters with.


Charles Churchill (February, 1732– 4 November 1764), was an English poet and satirist. Early life Churchill was born in Vine Street, Westminster. His father, rector of Rainham, Essex, held the curacy and lectureship of St Johns, Westminster, from 1733, and Charles was educated at Westminster School, where he became a good classical scholar, and formed a close and lasting friendship with Robert Lloyd. He was admitted to St John’s College, Cambridge on 8 July 1748. Churchill contracted a marriage within the rules of the Fleet in his eighteenth year, and never lived at Cambridge; the young couple lived in his father’s house, and Churchill was afterwards sent to the north of England to prepare for holy orders. He became curate of South Cadbury, Somerset, and, on receiving priest’s orders (1756), began to act as his father’s curate at Rainham. Two years later the elder Churchill died, and the son was elected to succeed him in his curacy and lectureship. His emoluments amounted to less than £100 a year, and he increased his income by teaching in a girls’ school. His marriage proved unhappy, and he began to spend much of his time in dissipation in the society of Robert Lloyd. He was separated from his wife in 1761, and would have been imprisoned for debt but for the timely help of Lloyd’s father, who had been an usher and was now a master at Westminster. Career as Satirist Churchill had already done some work for the booksellers, and his friend Lloyd had had some success with a didactic poem, The Actor. Churchill’s knowledge of the theatre was now made use of in the Rosciad, which appeared in March 1761. This reckless and amusing satire described with the most disconcerting accuracy the faults of the various actors and actresses on the London stage; in a competition judged by Shakespeare and Jonson, Garrick is named the greatest English actor. Its immediate popularity was no doubt largely due to its personal character, but its vigour and raciness make it worth reading even now when the objects of Churchill’s wit are forgotten. The first impression was published anonymously, and in the Critical Review, conducted by Tobias Smollett, it was confidently asserted that the poem was the joint production of George Colman the Elder, Bonnell Thornton and Robert Lloyd. Churchill immediately published an Apology addressed to the Critical Reviewers, which, after developing the subject that it is only authors who prey on their own kind, repeats the fierce attack on the stage. Incidentally it contains an enthusiastic tribute to John Dryden, of whom Churchill was a devotee. In the Rosciad he had praised Mrs Pritchard, Mrs Cibber and Mrs Clive, but no leading London actor, with the exception of David Garrick, had escaped censure, and in the Apology Garrick was clearly threatened. He deprecated criticism by showing every possible civility to Churchill, who became a terror to the actors. Thomas Davies wrote to Garrick attributing his blundering in the part of Cymbeline “to my accidentally seeing Mr Churchill in the pit, it rendering me confused and unmindful of my business.” Churchill’s satire made him many enemies, and brought reprisals. In Night, an Epistle to Robert Lloyd (1761), he answered the attacks made on him, offering by way of defense the argument that any faults were better than hypocrisy. His scandalous conduct brought down the censure of the dean of Westminster, and in 1763 the protests of his parishioners led him to resign his offices, and he was free to wear his blue coat with metal buttons and much gold lace without remonstrance from the dean. The Rosciad had been refused by several publishers, and was finally published at Churchill’s own expense. He received a considerable sum from the sale, and paid his old creditors in full, besides making an allowance to his wife. Friendship with Wilkes He now became a close ally of John Wilkes, whom he regularly assisted with The North Briton weekly newspaper. His next poem, The Prophecy of Famine: A Scots Pastoral (1763), was founded on a paper written originally for that newspaper. This violent satire on Scottish influence fell in with the current hatred of Lord Bute, and the Scottish place-hunters were as much alarmed as the actors had been. When Wilkes was arrested he gave Churchill a timely hint to retire to the country for a time, the publisher, Kearsley, having stated that he received part of the profits from the paper. His Epistle to William Hogarth (1763) was in answer to the caricature of Wilkes made during the trial, in it Hogarth’s vanity and envy were attacked in an invective which Garrick quoted as shocking and barbarous. Hogarth retaliated by a caricature of Churchill as a bear in torn clerical bands hugging a pot of porter and a club made of lies and North Britons. The Duellist (1763) is a virulent satire on the most active opponents of Wilkes in the House of Lords, especially on Bishop Warburton. He attacked Dr Johnson among others in The Ghost as “Pomposo, insolent and loud, Vain idol of a scribbling crowd”. Other poems are The Conference (1763); The Author (1763), highly praised by Churchill’s contemporaries; Gotham (1764), a poem on the duties of a king, didactic rather than satiric in tone; The Candidate (1764), a satire on John Montagu, fourth earl of Sandwich, one of Wilkes’s bitterest enemies, whom he had already denounced for his treachery in The Duellist (Bk. iii.) as too infamous to have a friend; The Farewell (1764); The Times (1764); Independence, and an unfinished Journey. Death and Legacy In October 1764 he went to Boulogne to join Wilkes. There he was attacked by a fever of which he died on 4 November. He left his property to his two sons, and made Wilkes his literary executor with full powers. Wilkes did little. He wrote an epitaph for his friend and about half a dozen notes on his poems, and Andrew Kippis acknowledges some slight assistance from him in preparing his life of Churchill for the Biographia (1780). There is more than one instance of Churchill’s generosity to his friends. In 1763 he found his friend Robert Lloyd in prison for debt. He paid a guinea a week for his better maintenance in the Fleet, and raised a subscription to set him free. Lloyd fell ill on receipt of the news of Churchill’s death, and died shortly afterwards. Churchill’s sister Patty, who was engaged to Lloyd, did not long survive them. William Cowper was his schoolfellow, and left many kindly references to him. A partial collection of Churchill’s poems appeared in 1763. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Churchill_(satirist)

Elizabeth Daryush (8 December 1887 – 7 April 1977) was an English poet. Life Daryush was the daughter of Robert Bridges; her maternal grandfather was Alfred Waterhouse. She married Ali Akbar Daryush, whom she had met when he was studying at the University of Oxford, and thereafter spent some time in Persia; most of her life was spent in Boars Hill, outside Oxford, where the Elizabeth Daryush Memorial Garden is named for her. Writings Poetry Daryush, daughter of English poet laureate Robert Bridges (some of her early work was published as 'Elizabeth Bridges’), followed her father’s lead not only in choosing poetry as her life’s work but also in the traditional style of poetry she chose to write. The themes of her work are often critical of the upper classes and the social injustice their privilege levied upon others. This characteristic was not present in her early work, including her first two books of poems, published under the name Elizabeth Bridges, which appeared while she was still in her twenties. According to John Finlay, writing in the Dictionary of Literary Biography, Daryush’s “early poetry is preoccupied with rather conventional subject matter and owes a great deal to the Edwardians.” Syllabic style Daryush took her father’s experiment in syllabic verse a step farther by making it less experimental; whereas Bridges’ syllable count excluded elidable syllables, producing some variation in the total number of pronounced syllables per line, Daryush’s was strictly aural, counting all syllables actually sounded when the poem was read aloud. It is for her successful experiments with syllabic meter that Daryush is best known to contemporary readers, as exampled in her poem Accentedal in the quaternion form. Yvor Winters, the poet and critic, considered Daryush more successful in writing syllabics than was her father, noting that her poem Still-Life was her finest syllabic experiment, and also a companion-piece to Children of Wealth. Winters considered the social context of Still Life, which is nowhere mentioned, yet from which the poem draws its power. Characteristics Beyond its social content, Daryush’s work is also recognized for a consistent and well-defined personal vision. As Finlay noted, "For her. . .poetry always dealt with the `stubborn fact’ of life as it is, and the only consolations it offered were those of understanding and a kind of half-Christian, half-stoical acceptance of the inevitable." However, he also argued that Daryush’s best poems transcend such fatalism, “dealing with the moral resources found in one’s own being. . .and a recognition of the beauties in the immediate, ordinary world around us.” In many of her terse short poems, there is formal and intellectual mastery; her last, longest and most amibitious poem, ‘Air and Variations,’ was a formal tribute to Gerard Manly Hopkins Daryush has been described as a pioneer technical innovator, a poet of the highest dedication and seriousness whose poetry grapples with life’s intensest issues.


Francis Bacon, 1st Viscount St Alban, PC KC (/ˈbeɪkən/; 22 January 1561– 9 April 1626) was an English philosopher, statesman, scientist, jurist, orator, and author. He served both as Attorney General and as Lord Chancellor of England. After his death, he remained extremely influential through his works, especially as philosophical advocate and practitioner of the scientific method during the scientific revolution. Bacon has been called the father of empiricism. His works argued for the possibility of scientific knowledge based only upon inductive and careful observation of events in nature. Most importantly, he argued this could be achieved by use of a skeptical and methodical approach whereby scientists aim to avoid misleading themselves. While his own practical ideas about such a method, the Baconian method, did not have a long lasting influence, the general idea of the importance and possibility of a skeptical methodology makes Bacon the father of scientific method. This marked a new turn in the rhetorical and theoretical framework for science, the practical details of which are still central in debates about science and methodology today. Bacon was generally neglected at court by Queen Elizabeth, but after the accession of King James I in 1603, Bacon was knighted. He was later created Baron Verulam in 1618 and Viscount St. Alban in 1621. Because he had no heirs, both titles became extinct upon his death in 1626, at 65 years of age. Bacon died of pneumonia, with one account by John Aubrey stating that he had contracted the condition while studying the effects of freezing on the preservation of meat. Biography Early life Francis Bacon was born on 22 January 1561 at York House near the Strand in London, the son of Sir Nicholas Bacon by his second wife, Anne (Cooke) Bacon, the daughter of the noted humanist Anthony Cooke. His mother’s sister was married to William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley, making Burghley Bacon’s uncle. Biographers believe that Bacon was educated at home in his early years owing to poor health, which would plague him throughout his life. He received tuition from John Walsall, a graduate of Oxford with a strong leaning toward Puritanism. He entered Trinity College, Cambridge, on 5 April 1573 at the age of 12, living for three years there, together with his older brother Anthony Bacon under the personal tutelage of Dr John Whitgift, future Archbishop of Canterbury. Bacon’s education was conducted largely in Latin and followed the medieval curriculum. He was also educated at the University of Poitiers. It was at Cambridge that he first met Queen Elizabeth, who was impressed by his precocious intellect, and was accustomed to calling him “The young lord keeper”. His studies brought him to the belief that the methods and results of science as then practised were erroneous. His reverence for Aristotle conflicted with his rejection of Aristotelian philosophy, which seemed to him barren, disputatious and wrong in its objectives. On 27 June 1576, he and Anthony entered de societate magistrorum at Gray’s Inn. A few months later, Francis went abroad with Sir Amias Paulet, the English ambassador at Paris, while Anthony continued his studies at home. The state of government and society in France under Henry III afforded him valuable political instruction. For the next three years he visited Blois, Poitiers, Tours, Italy, and Spain. During his travels, Bacon studied language, statecraft, and civil law while performing routine diplomatic tasks. On at least one occasion he delivered diplomatic letters to England for Walsingham, Burghley, and Leicester, as well as for the queen. The sudden death of his father in February 1579 prompted Bacon to return to England. Sir Nicholas had laid up a considerable sum of money to purchase an estate for his youngest son, but he died before doing so, and Francis was left with only a fifth of that money. Having borrowed money, Bacon got into debt. To support himself, he took up his residence in law at Gray’s Inn in 1579, his income being supplemented by a grant from his mother Lady Anne of the manor of Marks near Romford in Essex, which generated a rent of £46. Parliamentarian Bacon stated that he had three goals: to uncover truth, to serve his country, and to serve his church. He sought to further these ends by seeking a prestigious post. In 1580, through his uncle, Lord Burghley, he applied for a post at court that might enable him to pursue a life of learning, but his application failed. For two years he worked quietly at Gray’s Inn, until he was admitted as an outer barrister in 1582. His parliamentary career began when he was elected MP for Bossiney, Cornwall, in a by-election (similar to a special election in the US) in 1581. In 1584 he took his seat in parliament for Melcombe in Dorset, and in 1586 for Taunton. At this time, he began to write on the condition of parties in the church, as well as on the topic of philosophical reform in the lost tract Temporis Partus Maximus. Yet he failed to gain a position that he thought would lead him to success. He showed signs of sympathy to Puritanism, attending the sermons of the Puritan chaplain of Gray’s Inn and accompanying his mother to the Temple Church to hear Walter Travers. This led to the publication of his earliest surviving tract, which criticised the English church’s suppression of the Puritan clergy. In the Parliament of 1586, he openly urged execution for the Catholic Mary, Queen of Scots. About this time, he again approached his powerful uncle for help; this move was followed by his rapid progress at the bar. He became a bencher in 1586 and was elected a Reader in 1587, delivering his first set of lectures in Lent the following year. In 1589, he received the valuable appointment of reversion to the Clerkship of the Star Chamber, although he did not formally take office until 1608; the post was worth £1,600 a year. In 1588 he became MP for Liverpool and then for Middlesex in 1593. He later sat three times for Ipswich (1597, 1601, 1604) and once for Cambridge University (1614). He became known as a liberal-minded reformer, eager to amend and simplify the law. Though a friend of the crown, he opposed feudal privileges and dictatorial powers. He spoke against religious persecution. He struck at the House of Lords in its usurpation of the Money Bills. He advocated for the union of England and Scotland, which made him a significant influence toward the consolidation of the United Kingdom; and he later would advocate for the integration of Ireland into the Union. Closer constitutional ties, he believed, would bring greater peace and strength to these countries. Attorney General Bacon soon became acquainted with Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, Queen Elizabeth’s favourite. By 1591 he acted as the earl’s confidential adviser. In 1592 he was commissioned to write a tract in response to the Jesuit Robert Parson’s anti-government polemic, which he titled Certain observations made upon a libel, identifying England with the ideals of democratic Athens against the belligerence of Spain. Bacon took his third parliamentary seat for Middlesex when in February 1593 Elizabeth summoned Parliament to investigate a Roman Catholic plot against her. Bacon’s opposition to a bill that would levy triple subsidies in half the usual time offended the Queen: opponents accused him of seeking popularity, and for a time the Court excluded him from favour. When the office of Attorney General fell vacant in 1594, Lord Essex’s influence was not enough to secure the position for Bacon and it was given to Sir Edward Coke. Likewise, Bacon failed to secure the lesser office of Solicitor General in 1595, the Queen pointedly snubbing him by appointing Sir Thomas Fleming instead. To console him for these disappointments, Essex presented him with a property at Twickenham, which Bacon subsequently sold for £1,800. In 1596 Bacon became Queen’s Counsel, but missed the appointment of Master of the Rolls. During the next few years, his financial situation remained embarrassing. His friends could find no public office for him, and a scheme for retrieving his position by a marriage with the wealthy and young widow Lady Elizabeth Hatton failed after she broke off their relationship upon accepting marriage to Sir Edward Coke, a further spark of enmity between the men. In 1598 Bacon was arrested for debt. Afterward, however, his standing in the Queen’s eyes improved. Gradually, Bacon earned the standing of one of the learned counsels, though he had no commission or warrant, and received no salary. His relationship with the Queen further improved when he severed ties with Essex—a shrewd move, as Essex would be executed for treason in 1601. With others, Bacon was appointed to investigate the charges against Essex. A number of Essex’s followers confessed that Essex had planned a rebellion against the Queen. Bacon was subsequently a part of the legal team headed by the Attorney General Sir Edward Coke at Essex’s treason trial. After the execution, the Queen ordered Bacon to write the official government account of the trial, which was later published as A DECLARATION of the Practices and Treasons attempted and committed by Robert late Earle of Essex and his Complices, against her Majestie and her Kingdoms... after Bacon’s first draft was heavily edited by the Queen and her ministers. According to his personal secretary and chaplain, William Rawley, as a judge Bacon was always tender-hearted, “looking upon the examples with the eye of severity, but upon the person with the eye of pity and compassion”. And also that “he was free from malice”, “no revenger of injuries”, and “no defamer of any man”. James I comes to the throne The succession of James I brought Bacon into greater favour. He was knighted in 1603. In another shrewd move, Bacon wrote his Apologies in defence of his proceedings in the case of Essex, as Essex had favoured James to succeed to the throne. The following year, during the course of the uneventful first parliament session, Bacon married Alice Barnham. In June 1607 he was at last rewarded with the office of solicitor general. The following year, he began working as the Clerkship of the Star Chamber. Despite a generous income, old debts still could not be paid. He sought further promotion and wealth by supporting King James and his arbitrary policies. In 1610 the fourth session of James’s first parliament met. Despite Bacon’s advice to him, James and the Commons found themselves at odds over royal prerogatives and the king’s embarrassing extravagance. The House was finally dissolved in February 1611. Throughout this period Bacon managed to stay in the favour of the king while retaining the confidence of the Commons. In 1613 Bacon was finally appointed attorney general, after advising the king to shuffle judicial appointments. As attorney general, Bacon, by his zealous efforts—which included torture—to obtain the conviction of Edmund Peacham for treason, raised legal controversies of high constitutional importance; and successfully prosecuted Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset, and his wife, Frances Howard, Countess of Somerset, for murder in 1616. The so-called Prince’s Parliament of April 1614 objected to Bacon’s presence in the seat for Cambridge and to the various royal plans that Bacon had supported. Although he was allowed to stay, parliament passed a law that forbade the attorney general to sit in parliament. His influence over the king had evidently inspired resentment or apprehension in many of his peers. Bacon, however, continued to receive the King’s favour, which led to his appointment in March 1617 as temporary Regent of England (for a period of a month), and in 1618 as Lord Chancellor. On 12 July 1618 the king created Bacon Baron Verulam, of Verulam, in the Peerage of England; he then became known as Francis, Lord Verulam. Bacon continued to use his influence with the king to mediate between the throne and Parliament, and in this capacity he was further elevated in the same peerage, as Viscount St Alban, on 27 January 1621. Lord Chancellor and public disgrace Bacon’s public career ended in disgrace in 1621. After he fell into debt, a parliamentary committee on the administration of the law charged him with 23 separate counts of corruption. His lifelong enemy, Sir Edward Coke, who had instigated these accusations, was one of those appointed to prepare the charges against the chancellor. To the lords, who sent a committee to enquire whether a confession was really his, he replied, “My lords, it is my act, my hand, and my heart; I beseech your lordships to be merciful to a broken reed.” He was sentenced to a fine of £40,000 and committed to the Tower of London at the king’s pleasure; the imprisonment lasted only a few days and the fine was remitted by the king. More seriously, parliament declared Bacon incapable of holding future office or sitting in parliament. He narrowly escaped undergoing degradation, which would have stripped him of his titles of nobility. Subsequently, the disgraced viscount devoted himself to study and writing. There seems little doubt that Bacon had accepted gifts from litigants, but this was an accepted custom of the time and not necessarily evidence of deeply corrupt behaviour. While acknowledging that his conduct had been lax, he countered that he had never allowed gifts to influence his judgement and, indeed, he had on occasion given a verdict against those who had paid him. He even had an interview with King James in which he assured: The law of nature teaches me to speak in my own defence: With respect to this charge of bribery I am as innocent as any man born on St. Innocents Day. I never had a bribe or reward in my eye or thought when pronouncing judgment or order... I am ready to make an oblation of myself to the King He also wrote the following to Buckingham: My mind is calm, for my fortune is not my felicity. I know I have clean hands and a clean heart, and I hope a clean house for friends or servants; but Job himself, or whoever was the justest judge, by such hunting for matters against him as hath been used against me, may for a time seem foul, especially in a time when greatness is the mark and accusation is the game. The true reason for his acknowledgement of guilt is the subject of debate, but some authors speculate that it may have been prompted by his sickness, or by a view that through his fame and the greatness of his office he would be spared harsh punishment. He may even have been blackmailed, with a threat to charge him with sodomy, into confession. The British jurist Basil Montagu wrote in Bacon’s defence, concerning the episode of his public disgrace: Bacon has been accused of servility, of dissimulation, of various base motives, and their filthy brood of base actions, all unworthy of his high birth, and incompatible with his great wisdom, and the estimation in which he was held by the noblest spirits of the age. It is true that there were men in his own time, and will be men in all times, who are better pleased to count spots in the sun than to rejoice in its glorious brightness. Such men have openly libelled him, like Dewes and Weldon, whose falsehoods were detected as soon as uttered, or have fastened upon certain ceremonious compliments and dedications, the fashion of his day, as a sample of his servility, passing over his noble letters to the Queen, his lofty contempt for the Lord Keeper Puckering, his open dealing with Sir Robert Cecil, and with others, who, powerful when he was nothing, might have blighted his opening fortunes for ever, forgetting his advocacy of the rights of the people in the face of the court, and the true and honest counsels, always given by him, in times of great difficulty, both to Elizabeth and her successor. When was a “base sycophant” loved and honoured by piety such as that of Herbert, Tennison, and Rawley, by noble spirits like Hobbes, Ben Jonson, and Selden, or followed to the grave, and beyond it, with devoted affection such as that of Sir Thomas Meautys. Personal life When he was 36, Bacon courted Elizabeth Hatton, a young widow of 20. Reportedly, she broke off their relationship upon accepting marriage to a wealthier man, Bacon’s rival, Edward Coke. Years later, Bacon still wrote of his regret that the marriage to Hatton had not taken place. At the age of 45, Bacon married Alice Barnham, the 14-year-old daughter of a well-connected London alderman and MP. Bacon wrote two sonnets proclaiming his love for Alice. The first was written during his courtship and the second on his wedding day, 10 May 1606. When Bacon was appointed lord chancellor, “by special Warrant of the King”, Lady Bacon was given precedence over all other Court ladies. Reports of increasing friction in his marriage to Alice appeared, with speculation that some of this may have been due to financial resources not being as readily available to her as she had been accustomed to. Alice was reportedly interested in fame and fortune, and when reserves of money were no longer available there were complaints about where all the money was going. Alice Chambers Bunten wrote in her Life of Alice Barnham that, upon their descent into debt, she actually went on trips to ask for financial favours and assistance from their circle of friends. Bacon disinherited her upon discovering her secret romantic relationship with Sir John Underhill. He rewrote his will, which had previously been very generous—leaving her lands, goods, and income—revoking it all. Bacon’s personal secretary and chaplain, William Rawley, however, wrote in his biography of Bacon that his marriage was one of “much conjugal love and respect”, mentioning a robe of honour that he gave to Alice and which “she wore unto her dying day, being twenty years and more after his death”. The well-connected antiquary John Aubrey noted in his Brief Lives concerning Bacon, “He was a Pederast. His Ganimeds and Favourites tooke Bribes”, biographers continue to debate Bacon’s sexual inclinations and the precise nature of his personal relationships. Some authors believe that despite his marriage, Bacon was primarily attracted to men. Forker, for example, has explored the “historically documentable sexual preferences” of both King James and Bacon, and concluded they were all oriented to “masculine love”, a contemporary term that “seems to have been used exclusively to refer to the sexual preference of men for members of their own gender.” The Jacobean antiquarian Sir Simonds D’Ewes implied there had been a question of bringing him to trial for buggery, which his brother Anthony Bacon had also been charged with. This conclusion has been disputed by others, who point to lack of consistent evidence, and consider the sources to be more open to interpretation. In his “New Atlantis”, Bacon describes his utopian island as being “the chastest nation under heaven”, in which there was no prostitution or adultery, and further saying that “as for masculine love, they have no touch of it”. Death On 9 April 1626, Bacon died of pneumonia while at Arundel mansion at Highgate outside London. An influential account of the circumstances of his death was given by John Aubrey’s Brief Lives, with Aubrey stating he contracted pneumonia while studying the effects of freezing on the preservation of meat. Aubrey has been criticised for his evident credulousness in this and other works; on the other hand, he knew Thomas Hobbes, Bacon’s fellow-philosopher and friend. Aubrey’s vivid account, which portrays Bacon as a martyr to experimental scientific method, had him journeying to Highgate through the snow with the King’s physician when he is suddenly inspired by the possibility of using the snow to preserve meat: “They were resolved they would try the experiment presently. They alighted out of the coach and went into a poor woman’s house at the bottom of Highgate hill, and bought a fowl, and made the woman exenterate it.” After stuffing the fowl with snow, Bacon contracted a fatal case of pneumonia. Some people, including Aubrey, consider these two contiguous, possibly coincidental events as related and causative of his death: "The Snow so chilled him that he immediately fell so extremely ill, that he could not return to his Lodging... but went to the Earle of Arundel’s house at Highgate, where they put him into... a damp bed that had not been layn-in... which gave him such a cold that in 2 or 3 days as I remember Mr Hobbes told me, he died of Suffocation.” Being unwittingly on his deathbed, the philosopher wrote his last letter to his absent host and friend Lord Arundel: My very good Lord,—I was likely to have had the fortune of Caius Plinius the elder, who lost his life by trying an experiment about the burning of Mount Vesuvius; for I was also desirous to try an experiment or two touching the conservation and induration of bodies. As for the experiment itself, it succeeded excellently well; but in the journey between London and Highgate, I was taken with such a fit of casting as I know not whether it were the Stone, or some surfeit or cold, or indeed a touch of them all three. But when I came to your Lordship’s House, I was not able to go back, and therefore was forced to take up my lodging here, where your housekeeper is very careful and diligent about me, which I assure myself your Lordship will not only pardon towards him, but think the better of him for it. For indeed your Lordship’s House was happy to me, and I kiss your noble hands for the welcome which I am sure you give me to it. I know how unfit it is for me to write with any other hand than mine own, but by my troth my fingers are so disjointed with sickness that I cannot steadily hold a pen. Another account appears in a biography by William Rawley, Bacon’s personal secretary and chaplain: He died on the ninth day of April in the year 1626, in the early morning of the day then celebrated for our Saviour’s resurrection, in the sixty-sixth year of his age, at the Earl of Arundel’s house in Highgate, near London, to which place he casually repaired about a week before; God so ordaining that he should die there of a gentle fever, accidentally accompanied with a great cold, whereby the defluxion of rheum fell so plentifully upon his breast, that he died by suffocation. At the news of his death, over 30 great minds collected together their eulogies of him, which were then later published in Latin. He left personal assets of about £7,000 and lands that realised £6,000 when sold. His debts amounted to more than £23,000, equivalent to more than £3m at current value. Philosophy and works Francis Bacon’s philosophy is displayed in the vast and varied writings he left, which might be divided into three great branches: Scientific works– in which his ideas for an universal reform of knowledge into scientific methodology and the improvement of mankind’s state using the Scientific method are presented. Religious and literary works– in which he presents his moral philosophy and theological meditations. Juridical works– in which his reforms in English Law are proposed. Influence Science Bacon’s seminal work Novum Organum was influential in the 1630s and 1650s among scholars, in particular Sir Thomas Browne, who in his encyclopaedia Pseudodoxia Epidemica (1646–72) frequently adheres to a Baconian approach to his scientific enquiries. During the Restoration, Bacon was commonly invoked as a guiding spirit of the Royal Society founded under Charles II in 1660. During the 18th-century French Enlightenment, Bacon’s non-metaphysical approach to science became more influential than the dualism of his French contemporary Descartes, and was associated with criticism of the ancien regime. In 1733 Voltaire introduced him to a French audience as the “father” of the scientific method, an understanding which had become widespread by the 1750s. In the 19th century his emphasis on induction was revived and developed by William Whewell, among others. He has been reputed as the “Father of Experimental Philosophy”. He also wrote a long treatise on Medicine, History of Life and Death, with natural and experimental observations for the prolongation of life. One of his biographers, the historian William Hepworth Dixon, states: “Bacon’s influence in the modern world is so great that every man who rides in a train, sends a telegram, follows a steam plough, sits in an easy chair, crosses the channel or the Atlantic, eats a good dinner, enjoys a beautiful garden, or undergoes a painless surgical operation, owes him something.” In 1902 Hugo von Hofmannsthal published a fictional letter addressed to Bacon and dated 1603, about a writer who is experiencing a crisis of language. Known as The Lord Chandos Letter, it has been proposed that Bacon was identified as its recipient as having laid the foundation for the work of scientists such as Ernst Mach, notable both for his academic distinction in the history and philosophy of the inductive sciences, and for his own contributions to physics. North America Bacon played a leading role in establishing the British colonies in North America, especially in Virginia, the Carolinas and Newfoundland in northeastern Canada. His government report on “The Virginia Colony” was submitted in 1609. In 1610 Bacon and his associates received a charter from the king to form the Tresurer and the Companye of Adventurers and planter of the Cittye of London and Bristoll for the Collonye or plantacon in Newfoundland, and sent John Guy to found a colony there. Thomas Jefferson, the third President of the United States, wrote: “Bacon, Locke and Newton. I consider them as the three greatest men that have ever lived, without any exception, and as having laid the foundation of those superstructures which have been raised in the Physical and Moral sciences”. In 1910 Newfoundland issued a postage stamp to commemorate Bacon’s role in establishing the colony. The stamp describes Bacon as "the guiding spirit in Colonization Schemes in 1610". Moreover, some scholars believe he was largely responsible for the drafting, in 1609 and 1612, of two charters of government for the Virginia Colony. William Hepworth Dixon considered that Bacon’s name could be included in the list of Founders of the United States. Law Although few of his proposals for law reform were adopted during his lifetime, his legal legacy was considered by the magazine New Scientist in 1961 as having influenced the drafting of the Napoleonic Code as well as the law reforms introduced by 19th-century British Prime Minister Sir Robert Peel. The historian William Hepworth Dixon had referred to the Napoleonic Code as “the sole embodiment of Bacon’s thought”, saying that Bacon’s legal work “has had more success abroad than it has found at home”, and that in France “it has blossomed and come into fruit”. Harvey Wheeler attributed to Bacon, in Francis Bacon’s Verulamium—the Common Law Template of The Modern in English Science and Culture, the creation of these distinguishing features of the modern common law system: using cases as repositories of evidence about the “unwritten law”; determining the relevance of precedents by exclusionary principles of evidence and logic; treating opposing legal briefs as adversarial hypotheses about the application of the “unwritten law” to a new set of facts. As late as the 18th century some juries still declared the law rather than the facts, but already before the end of the 17th century Sir Matthew Hale explained modern common law adjudication procedure and acknowledged Bacon as the inventor of the process of discovering unwritten laws from the evidences of their applications. The method combined empiricism and inductivism in a new way that was to imprint its signature on many of the distinctive features of modern English society. Paul H. Kocher writes that Bacon is considered by some jurists to be the father of modern Jurisprudence. Bacon is commemorated with a statue in Gray’s Inn, South Square in London where he received his legal training, and where he was elected Treasurer of the Inn in 1608. James McClellan, a political scientist from the University of Virginia, considered Bacon to have had “a great following” in the American colonies. More recent scholarship on Bacon’s jurisprudence has focused on his advocating torture as a legal recourse for the crown. Bacon himself was not a stranger to the torture chamber: in his various legal capacities in both Elizabeth I’s and James I’s reigns, Bacon was listed as a commissioner on five torture warrants. In 1613(?), in a letter addressed to King James I on the question of torture’s place within English law, Bacon identifies the scope of torture: a means to further the investigation of threats to the state: “In the cases of treasons, torture is used for discovery, and not for evidence.” For Bacon, torture was not a punitive measure, an intended form of state repression, but instead offered a modus operandi for the government agent tasked with uncovering acts of treason. Historical debates Bacon and Shakespeare The Baconian hypothesis of Shakespearean authorship, first proposed in the mid-19th century, contends that Francis Bacon wrote some or even all of the plays conventionally attributed to William Shakespeare. Occult hypotheses Francis Bacon often gathered with the men at Gray’s Inn to discuss politics and philosophy, and to try out various theatrical scenes that he admitted writing. Bacon’s alleged connection to the Rosicrucians and the Freemasons has been widely discussed by authors and scholars in many books. However, others, including Daphne du Maurier in her biography of Bacon, have argued that there is no substantive evidence to support claims of involvement with the Rosicrucians. Frances Yates does not make the claim that Bacon was a Rosicrucian, but presents evidence that he was nevertheless involved in some of the more closed intellectual movements of his day. She argues that Bacon’s movement for the advancement of learning was closely connected with the German Rosicrucian movement, while Bacon’s New Atlantis portrays a land ruled by Rosicrucians. He apparently saw his own movement for the advancement of learning to be in conformity with Rosicrucian ideals. The link between Bacon’s work and the Rosicrucians ideals which Yates allegedly found was the conformity of the purposes expressed by the Rosicrucian Manifestos and Bacon’s plan of a “Great Instauration”, for the two were calling for a reformation of both “divine and human understanding”, as well as both had in view the purpose of mankind’s return to the “state before the Fall”. Another major link is said to be the resemblance between Bacon’s New Atlantis and the German Rosicrucian Johann Valentin Andreae’s Description of the Republic of Christianopolis (1619). Andreae describes a utopic island in which Christian theosophy and applied science ruled, and in which the spiritual fulfillment and intellectual activity constituted the primary goals of each individual, the scientific pursuits being the highest intellectual calling—linked to the achievement of spiritual perfection. Andreae’s island also depicts a great advancement in technology, with many industries separated in different zones which supplied the population’s needs—which shows great resemblance to Bacon’s scientific methods and purposes. The Rosicrucian organisation AMORC claims that Bacon was the “Imperator” (leader) of the Rosicrucian Order in both England and the European continent, and would have directed it during his lifetime. Bacon’s influence can also be seen on a variety of religious and spiritual authors, and on groups that have utilised his writings in their own belief systems. Bibliography * Some of the more notable works by Bacon are: * Essays (1st edition 1597) * The Advancement and Proficience of Learning Divine and Human (1605) * Essays (2nd edition– 38 essays, 1612) * Novum Organum Scientiarum ('New Method’, 1620) * Essays, or Counsels Civil and Moral (3rd/final edition– 58 essays, 1625) * New Atlantis (1627) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Francis_Bacon


Henry VIII (28 June 1491– 28 January 1547) was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was the first English King of Ireland, and continued the nominal claim by English monarchs to the Kingdom of France. Henry was the second Tudor monarch, succeeding his father, Henry VII. Henry is known for his consequential role in the separation of the Church of England from the Roman Catholic Church, besides his six marriages and many extramarital affairs, as well as his effort to obtain an annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon, which led to conflict with the Pope. His disagreements with the Pope led Henry to separate the Church of England from papal authority, with himself as king and as the Supreme Head of the Church of England; the disputes also led to the Dissolution of the Monasteries. His principal dispute was with papal authority rather than with doctrinal matters, and he remained a believer in core Catholic theological teachings despite his excommunication from the Roman Catholic Church. Henry oversaw the legal union of England and Wales with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. He is also well known for a long personal rivalry with both Francis I of France and the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, with whom he frequently warred. Domestically, Henry is known for his radical changes to the English Constitution, ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings to England. Besides asserting the sovereign’s supremacy over the Church of England, thus initiating the English Reformation, he greatly expanded royal power. Charges of treason and heresy were commonly used to quash dissent, and those accused were often executed without a formal trial, by means of bills of attainder. He achieved many of his political aims through the work of his chief ministers, some of whom were banished or executed when they fell out of his favour. People such as Thomas Wolsey, Thomas More, Thomas Cromwell, Richard Rich, and Thomas Cranmer figured prominently in Henry’s administration. He was an extravagant spender and used the proceeds from the Dissolution of the Monasteries and acts of the Reformation Parliament to convert money into royal revenue that was formerly paid to Rome. Despite the influx of money from these sources, Henry was continually on the verge of financial ruin due to his personal extravagance as well as his numerous costly continental wars. His contemporaries considered Henry in his prime to be an attractive, educated, and accomplished king, and he has been described as “one of the most charismatic rulers to sit on the English throne”. Besides ruling with considerable power, he was also an author and composer. His desire to provide England with a male heir stemmed partly from personal vanity and partly from his belief that a daughter would be unable to consolidate Tudor power and maintain the fragile peace that existed following the Wars of the Roses. This led to the two things for which Henry is most remembered: his six marriages and his break with the pope (who would not allow an annulment of Henry’s first marriage). As he aged, Henry became severely obese and his health suffered, contributing to his death in 1547. He is frequently characterised in his later life as a lustful, egotistical, harsh, and insecure king. He was succeeded by his son Edward VI. Early years Born 28 June 1491 at the Palace of Placentia in Greenwich, London, Henry Tudor was the third child and second son of Henry VII and Elizabeth of York. Of the young Henry’s six siblings, only three– Arthur, Prince of Wales; Margaret; and Mary– survived infancy. He was baptised by Richard Fox, the Bishop of Exeter, at a church of the Observant Franciscans close to the palace. In 1493, at the age of two, Henry was appointed Constable of Dover Castle and Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports. He was subsequently appointed Earl Marshal of England and Lord Lieutenant of Ireland at age three, and was inducted into the Order of the Bath soon after. The day after the ceremony he was created Duke of York and a month or so later made Warden of the Scottish Marches. In May 1495, he was appointed to the Order of the Garter. Henry was given a first-rate education from leading tutors, becoming fluent in Latin and French, and learning at least some Italian. Not much is known about his early life– save for his appointments– because he was not expected to become king. In November 1501, Henry also played a considerable part in the ceremonies surrounding the marriage of his brother, Prince Arthur, to Catherine of Aragon, the youngest surviving child of King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella I of Castile. As Duke of York, Henry used the arms of his father as king, differenced by a label of three points ermine. In 1502, Arthur died at the age of 15 of sweating sickness, just 20 weeks after his marriage to Catherine. Arthur’s death thrust all his duties upon his younger brother, the 10-year-old Henry. After a little debate, Henry became the new Duke of Cornwall in October 1502, and the new Prince of Wales and Earl of Chester in February 1503. Henry VII gave the boy few tasks. Young Henry was strictly supervised and did not appear in public. As a result, the young Henry would later ascend the throne “untrained in the exacting art of kingship”. Henry VII renewed his efforts to seal a marital alliance between England and Spain, by offering his second son in marriage to Arthur’s widow Catherine. Both Isabella and Henry VII were keen on the idea, which had arisen very shortly after Arthur’s death. On 23 June 1503, a treaty was signed for their marriage, and they were betrothed two days later. A papal dispensation was only needed for the “impediment of public honesty” if the marriage had not been consummated as Catherine and her duenna claimed, but Henry VII and the Spanish ambassador set out instead to obtain a dispensation for “affinity”, which took account of the possibility of consummation. The young Henry’s age, only eleven, prevented cohabitation. Isabella’s death in 1504, and the ensuing problems of succession in Castile, complicated matters. Her father preferred her to stay in England, but Henry VII’s relations with Ferdinand had deteriorated. Catherine was therefore left in limbo for some time, culminating in Prince Henry’s rejection of the marriage as soon he was able, at the age of 14. Ferdinand’s solution was to make his daughter ambassador, allowing her to stay in England indefinitely. Devout, she began to believe that it was God’s will that she marry the prince despite his opposition. Early reign Henry VII died on 21 April 1509, and the 17-year-old Henry succeeded him as king. Soon after his father’s burial on 10 May, Henry suddenly declared that he would indeed marry Catherine, leaving unresolved several issues concerning the papal dispensation and a missing part of the marriage portion. The new king maintained that it had been his father’s dying wish that he marry Catherine. Whether or not this was true, it was certainly convenient. Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I had been attempting to marry his granddaughter (and Catherine’s niece) Eleanor to Henry; she had now been jilted. Henry’s wedding to Catherine was kept low-key and was held at the friar’s church in Greenwich on 11 June 1509. On 23 June 1509, Henry led the now 23-year-old Catherine from the Tower of London to Westminster Abbey for their coronation, which took place the following day. It was a grand affair: the king’s passage was lined with tapestries and laid with fine cloth. Following the ceremony, there was a grand banquet in Westminster Hall. As Catherine wrote to her father, “our time is spent in continuous festival”. Two days after Henry’s coronation, he arrested his father’s two most unpopular ministers, Sir Richard Empson and Edmund Dudley. They were charged with high treason and were executed in 1510. Historian Ian Crofton has maintained that such executions would become Henry’s primary tactic for dealing with those who stood in his way; the two executions were certainly not the last. Henry also returned to the public some of the money supposedly extorted by the two ministers. By contrast, Henry’s view of the House of York– potential rival claimants for the throne– was more moderate than his father’s had been. Several who had been imprisoned by his father, including the Marquess of Dorset, were pardoned. Others (most notably Edmund de la Pole) went unreconciled; de la Pole was eventually beheaded in 1513, an execution prompted by his brother Richard siding against the king. Soon after, Catherine conceived, but the child, a girl, was stillborn on 31 January 1510. About four months later, Catherine again became pregnant. On New Year’s Day 1511, the child– Henry– was born. After the grief of losing their first child, the couple were pleased to have a boy and there were festivities to celebrate, including a jousting tournament. However, the child died seven weeks later. Catherine had two stillborn sons in 1514 and 1515, but gave birth in February 1516 to a girl, Mary. Relations between Henry and Catherine had been strained, but they eased slightly after Mary’s birth. Although Henry’s marriage to Catherine has since been described as “unusually good”, it is known that Henry took mistresses. It was revealed in 1510 that Henry had been conducting an affair with one of the sisters of Edward Stafford, 3rd Duke of Buckingham, either Elizabeth or Anne Hastings, Countess of Huntingdon. The most significant mistress for about three years, starting in 1516, was Elizabeth Blount. Blount is one of only two completely undisputed mistresses, few for a virile young king. Exactly how many Henry had is disputed: David Loades believes Henry had mistresses “only to a very limited extent”, whilst Alison Weir believes there were numerous other affairs. Catherine did not protest, and in 1518 fell pregnant again with another girl, who was also stillborn. Blount gave birth in June 1519 to Henry’s illegitimate son, Henry FitzRoy. The young boy was made Duke of Richmond in June 1525 in what some thought was one step on the path to his eventual legitimisation. In 1533, FitzRoy married Mary Howard, but died childless three years later. At the time of Richmond’s death in June 1536, Parliament was enacting the Second Succession Act, which could have allowed him to become king. France and the Habsburgs In 1510, France, with a fragile alliance with the Holy Roman Empire in the League of Cambrai, was winning a war against Venice. Henry renewed his father’s friendship with Louis XII of France, an issue that divided his council. Certainly war with the combined might of the two powers would have been exceedingly difficult. Shortly thereafter, however, Henry also signed a pact with Ferdinand. After Pope Julius II created the anti-French Holy League in October 1511, Henry followed Ferdinand’s lead and brought England into the new League. An initial joint Anglo-Spanish attack was planned for the spring to recover Aquitaine for England, the start of making Henry’s dreams of ruling France a reality. The attack, however, following a formal declaration of war in April 1512, was not led by Henry personally and was a considerable failure; Ferdinand used it simply to further his own ends, and it strained the Anglo-Spanish alliance. Nevertheless, the French were pushed out of Italy soon after, and the alliance survived, with both parties keen to win further victories over the French. Henry then pulled off a diplomatic coup by convincing the Emperor to join the Holy League. Remarkably, Henry had also secured the promised title of “Most Christian King of France” from Julius and possibly coronation by the Pope himself in Paris, if only Louis could be defeated. On 30 June 1513, Henry invaded France, and his troops defeated a French army at the Battle of the Spurs– a relatively minor result, but one which was seized on by the English for propaganda purposes. Soon after, the English took Thérouanne and handed it over to Maximillian; Tournai, a more significant settlement, followed. Henry had led the army personally, complete with large entourage. His absence from the country, however, had prompted his brother-in-law, James IV of Scotland, to invade England at the behest of Louis. Nevertheless, the English army, overseen by Queen Catherine, decisively defeated the Scots at the Battle of Flodden on 9 September 1513. Among the dead was the Scottish king, thus ending Scotland’s brief involvement in the war. These campaigns had given Henry a taste of the military success he so desired. However, despite initial indications, he decided not to pursue a 1514 campaign. He had been supporting Ferdinand and Maximilian financially during the campaign but had received little in return; England’s coffers were now empty. With the replacement of Julius by Pope Leo X, who was inclined to negotiate for peace with France, Henry signed his own treaty with Louis: his sister Mary would become Louis’ wife, having previously been pledged to the younger Charles, and peace was secured for eight years, a remarkably long time. Charles V ascended the thrones of both Spain and the Holy Roman Empire following the deaths of his grandfathers, Ferdinand in 1516 and Maximilian in 1519. Francis I likewise became king of France upon the death of Louis in 1515, leaving three relatively young rulers and an opportunity for a clean slate. The careful diplomacy of Cardinal Thomas Wolsey had resulted in the Treaty of London in 1518, aimed at uniting the kingdoms of western Europe in the wake of a new Ottoman threat, and it seemed that peace might be secured. Henry met Francis I on 7 June 1520 at the Field of the Cloth of Gold near Calais for a fortnight of lavish entertainment. Both hoped for friendly relations in place of the wars of the previous decade. The strong air of competition laid to rest any hopes of a renewal of the Treaty of London, however, and conflict was inevitable. Henry had more in common with Charles, whom he met once before and once after Francis. Charles brought the Empire into war with France in 1521; Henry offered to mediate, but little was achieved and by the end of the year Henry had aligned England with Charles. He still clung to his previous aim of restoring English lands in France, but also sought to secure an alliance with Burgundy, then part of Charles’ realm, and the continued support of Charles. A small English attack in the north of France made up little ground. Charles defeated and captured Francis at Pavia and could dictate peace; but he believed he owed Henry nothing. Sensing this, Henry decided to take England out of the war before his ally, signing the Treaty of the More on 30 August 1525. Annulment from Catherine During his first marriage to Catherine of Aragon, Henry conducted an affair with Mary Boleyn, Catherine’s lady-in-waiting. There has been speculation that Mary’s two children, Henry and Catherine Carey, were fathered by Henry, but this has never been proved, and the King never acknowledged them as he did Henry FitzRoy. In 1525, as Henry grew more impatient with Catherine’s inability to produce the male heir he desired, he became enamoured of Mary Boleyn’s sister, Anne, then a charismatic young woman of 25 in the Queen’s entourage. Anne, however, resisted his attempts to seduce her, and refused to become his mistress as her sister Mary Boleyn had. It was in this context that Henry considered his three options for finding a dynastic successor and hence resolving what came to be described at court as the King’s “great matter”. These options were legitimising Henry FitzRoy, which would take the intervention of the pope and would be open to challenge; marrying off Mary as soon as possible and hoping for a grandson to inherit directly, but Mary was considered unlikely to conceive before Henry’s death; or somehow rejecting Catherine and marrying someone else of child-bearing age. Probably seeing the possibility of marrying Anne, the third was ultimately the most attractive possibility to the 34-year-old Henry, and it soon became the King’s absorbing desire to annul his marriage to the now 40-year-old Catherine. It was a decision that would lead Henry to reject papal authority and initiate the English Reformation. Henry’s precise motivations and intentions over the coming years are not widely agreed on. Henry himself, at least in the early part of his reign, was a devout and well-informed Catholic to the extent that his 1521 publication Assertio Septem Sacramentorum ("Defence of the Seven Sacraments") earned him the title of Fidei Defensor (Defender of the Faith) from Pope Leo X. The work represented a staunch defence of papal supremacy, albeit one couched in somewhat contingent terms. It is not clear exactly when Henry changed his mind on the issue as he grew more intent on a second marriage. Certainly, by 1527 he had convinced himself that in marrying Catherine, his brother’s wife, he had acted contrary to Leviticus 20:21, an impediment the Pope had never had (he now believed) the authority to dispense with. It was this argument Henry took to Pope Clement VII in 1527 in the hope of having his marriage to Catherine annulled, forgoing at least one less openly defiant line of attack. In going public, all hope of tempting Catherine to retire to a nunnery or otherwise stay quiet were lost. Henry sent his secretary, William Knight, to appeal directly to the Holy See by way of a deceptively worded draft papal bull. Knight was unsuccessful; the Pope could not be misled so easily. Other missions concentrated on arranging an ecclesiastical court to meet in England, with a representative from Clement VII. Though Clement agreed to the creation of such a court, he never had any intention of empowering his legate, Lorenzo Campeggio, to decide in Henry’s favour. This bias was perhaps the result of pressure from Charles V, Catherine’s nephew, though it is not clear how far this influenced either Campeggio or the Pope. After less than two months of hearing evidence, Clement called the case back to Rome in July 1529, from which it was clear that it would never re-emerge. With the chance for an annulment lost and England’s place in Europe forfeit, Cardinal Wolsey bore the blame. He was charged with praemunire in October 1529 and his fall from grace was “sudden and total”. Briefly reconciled with Henry (and officially pardoned) in the first half of 1530, he was charged once more in November 1530, this time for treason, but died while awaiting trial. After a short period in which Henry took government upon his own shoulders, Sir Thomas More took on the role of Lord Chancellor and chief minister. Intelligent and able, but also a devout Catholic and opponent of the annulment, More initially cooperated with the king’s new policy, denouncing Wolsey in Parliament. A year later, Catherine was banished from court, and her rooms were given to Anne. Anne was an unusually educated and intellectual woman for her time, and was keenly absorbed and engaged with the ideas of the Protestant Reformers, though the extent to which she herself was a committed Protestant is much debated. When Archbishop of Canterbury William Warham died, Anne’s influence and the need to find a trustworthy supporter of the annulment had Thomas Cranmer appointed to the vacant position. This was approved by the Pope, unaware of the King’s nascent plans for the Church. Marriage to Anne Boleyn In the winter of 1532, Henry met with Francis I at Calais and enlisted the support of the French king for his new marriage. Immediately upon returning to Dover in England, Henry, now 41, and Anne, now 32, went through a secret wedding service. She soon became pregnant, and there was a second wedding service in London on 25 January 1533. On 23 May 1533, Cranmer, sitting in judgment at a special court convened at Dunstable Priory to rule on the validity of the king’s marriage to Catherine of Aragon, declared the marriage of Henry and Catherine null and void. Five days later, on 28 May 1533, Cranmer declared the marriage of Henry and Anne to be valid. Catherine was formally stripped of her title as queen, becoming instead “princess dowager” as the widow of Arthur. In her place, Anne was crowned queen consort on 1 June 1533. The queen gave birth to a daughter slightly prematurely on 7 September 1533. The child was christened Elizabeth, in honour of Henry’s mother, Elizabeth of York. Following the marriage, there was a period of consolidation taking the form of a series of statutes of the Reformation Parliament aimed at finding solutions to any remaining issues, whilst protecting the new reforms from challenge, convincing the public of their legitimacy, and exposing and dealing with opponents. Although the canon law was dealt with at length by Cranmer and others, these acts were advanced by Thomas Cromwell, Thomas Audley and the Duke of Norfolk and indeed by Henry himself. With this process complete, in May 1532 More resigned as Lord Chancellor, leaving Cromwell as Henry’s chief minister. With the Act of Succession 1533, Catherine’s daughter, Mary, was declared illegitimate; Henry’s marriage to Anne was declared legitimate; and Anne’s issue was decided to be next in the line of succession. With the Acts of Supremacy in 1534, Parliament also recognised the King’s status as head of the church in England and, with the Act in Restraint of Appeals in 1532, abolished the right of appeal to Rome. It was only then that Pope Clement took the step of excommunicating Henry and Thomas Cranmer, although the excommunication was not made official until some time later. The king and queen were not pleased with married life. The royal couple enjoyed periods of calm and affection, but Anne refused to play the submissive role expected of her. The vivacity and opinionated intellect that had made her so attractive as an illicit lover made her too independent for the largely ceremonial role of a royal wife and it made her many enemies. For his part, Henry disliked Anne’s constant irritability and violent temper. After a false pregnancy or miscarriage in 1534, he saw her failure to give him a son as a betrayal. As early as Christmas 1534, Henry was discussing with Cranmer and Cromwell the chances of leaving Anne without having to return to Catherine. Henry is traditionally believed to have had an affair with Margaret ("Madge") Shelton in 1535, although historian Antonia Fraser argues that Henry in fact had an affair with her sister Mary Shelton. Opposition to Henry’s religious policies was quickly suppressed in England. A number of dissenting monks, including the first Carthusian Martyrs, were executed and many more pilloried. The most prominent resisters included John Fisher, Bishop of Rochester, and Sir Thomas More, both of whom refused to take the oath to the King. Neither Henry nor Cromwell sought to have the men executed; rather, they hoped that the two might change their minds and save themselves. Fisher openly rejected Henry as supreme head of the Church, but More was careful to avoid openly breaking the Treason Act, which (unlike later acts) did not forbid mere silence. Both men were subsequently convicted of high treason, however– More on the evidence of a single conversation with Richard Rich, the Solicitor General. Both were duly executed in the summer of 1535. These suppressions, as well as the Dissolution of the Lesser Monasteries Act of 1536, in turn contributed to more general resistance to Henry’s reforms, most notably in the Pilgrimage of Grace, a large uprising in northern England in October 1536. Some 20,000 to 40,000 rebels were led by Robert Aske, together with parts of the northern nobility. Henry VIII promised the rebels he would pardon them and thanked them for raising the issues. Aske told the rebels they had been successful and they could disperse and go home. Henry saw the rebels as traitors and did not feel obliged to keep his promises with them, so when further violence occurred after Henry’s offer of a pardon he was quick to break his promise of clemency. The leaders, including Aske, were arrested and executed for treason. In total, about 200 rebels were executed, and the disturbances ended. Execution of Anne Boleyn On 8 January 1536 news reached the king and the queen that Catherine of Aragon had died. Henry called for public displays of joy regarding Catherine’s death. The queen was pregnant again, and she was aware of the consequences if she failed to give birth to a son. Later that month, the King was unhorsed in a tournament and was badly injured and it seemed for a time that his life was in danger. When news of this accident reached the queen, she was sent into shock and miscarried a male child that was about 15 weeks old, on the day of Catherine’s funeral, 29 January 1536. For most observers, this personal loss was the beginning of the end of the royal marriage. Given the king’s desperate desire for a son, the sequence of Anne’s pregnancies has attracted much interest. Author Mike Ashley speculated that Anne had two stillborn children after Elizabeth’s birth and before the birth of the male child she miscarried in 1536. Most sources attest only to the birth of Elizabeth in September 1533, a possible miscarriage in the summer of 1534, and the miscarriage of a male child, of almost four months gestation, in January 1536. Although the Boleyn family still held important positions on the Privy Council, Anne had many enemies, including the Duke of Suffolk. Even her own uncle, the Duke of Norfolk, had come to resent her attitude to her power. The Boleyns preferred France over the Emperor as a potential ally, but the King’s favour had swung towards the latter (partly because of Cromwell), damaging the family’s influence. Also opposed to Anne were supporters of reconciliation with Princess Mary (among them the former supporters of Catherine), who had reached maturity. A second annulment was now a real possibility, although it is commonly believed that it was Cromwell’s anti-Boleyn influence that led opponents to look for a way of having her executed. Anne’s downfall came shortly after she had recovered from her final miscarriage. Whether it was primarily the result of allegations of conspiracy, adultery, or witchcraft remains a matter of debate among historians. Early signs of a fall from grace included the King’s new mistress, the 28-year-old Jane Seymour, being moved into new quarters, and Anne’s brother, George Boleyn, being refused the Order of the Garter, which was instead given to Nicholas Carew. Between 30 April and 2 May, five men, including Anne’s brother, were arrested on charges of treasonable adultery and accused of having sexual relationships with the queen. Anne was also arrested, accused of treasonous adultery and incest. Although the evidence against them was unconvincing, the accused were found guilty and condemned to death. George Boleyn and the other accused men were executed on 17 May 1536. At 8 am on 19 May 1536, Anne, age 36, was executed on Tower Green. Marriage to Jane Seymour; domestic and foreign affairs The day after Anne’s execution in 1536 the 45-year-old Henry became engaged to Seymour, who had been one of the Queen’s ladies-in-waiting. They were married ten days later. On 12 October 1537, Jane gave birth to a son, Prince Edward, the future Edward VI. The birth was difficult, and the queen died on 24 October 1537 from an infection and was buried in Windsor. The euphoria that had accompanied Edward’s birth became sorrow, but it was only over time that Henry came to long for his wife. At the time, Henry recovered quickly from the shock. Measures were immediately put in place to find another wife for Henry, which, at the insistence of Cromwell and the court, were focused on the European continent. With Charles V distracted by the internal politics of his many kingdoms and external threats, and Henry and Francis on relatively good terms, domestic and not foreign policy issues had been Henry’s priority in the first half of the 1530s. In 1536, for example, Henry granted his assent to the Laws in Wales Act 1535, which legally annexed Wales, uniting England and Wales into a single nation. This was followed by the Second Succession Act (the Act of Succession 1536), which declared Henry’s children by Jane to be next in the line of succession and declared both Mary and Elizabeth illegitimate, thus excluding them from the throne. The king was also granted the power to further determine the line of succession in his will, should he have no further issue. However, when Charles and Francis made peace in January 1539, Henry became increasingly paranoid, perhaps as a result of receiving a constant list of threats to the kingdom (real or imaginary, minor or serious) supplied by Cromwell in his role as spymaster. Enriched by the dissolution of the monasteries, Henry used some of his financial reserves to build a series of coastal defences and set some aside for use in the event of a Franco-German invasion. Marriage to Anne of Cleves Having considered the matter, Cromwell, now Earl of Essex, suggested Anne, the 25-year-old sister of the Duke of Cleves, who was seen as an important ally in case of a Roman Catholic attack on England, for the duke fell between Lutheranism and Catholicism. Hans Holbein the Younger was dispatched to Cleves to paint a portrait of Anne for the king. Despite speculation that Holbein painted her in an overly flattering light, it is more likely that the portrait was accurate; Holbein remained in favour at court. After seeing Holbein’s portrait, and urged on by the complimentary description of Anne given by his courtiers, the 49-year-old king agreed to wed Anne. However, it was not long before Henry wished to annul the marriage so he could marry another. Anne did not argue, and confirmed that the marriage had never been consummated. Anne’s previous betrothal to the Duke of Lorraine’s son provided further grounds for the annulment. The marriage was subsequently dissolved, and Anne received the title of “The King’s Sister”, two houses and a generous allowance. It was soon clear that Henry had fallen for the 17-year-old Catherine Howard, the Duke of Norfolk’s niece, the politics of which worried Cromwell, for Norfolk was a political opponent. Shortly after, the religious reformers (and protégés of Cromwell) Robert Barnes, William Jerome and Thomas Garret were burned as heretics. Cromwell, meanwhile, fell out of favour although it is unclear exactly why, for there is little evidence of differences of domestic or foreign policy. Despite his role, he was never formally accused of being responsible for Henry’s failed marriage. Cromwell was now surrounded by enemies at court, with Norfolk also able to draw on his niece’s position. Cromwell was charged with treason, selling export licences, granting passports, and drawing up commissions without permission, and may also have been blamed for the failure of the foreign policy that accompanied the attempted marriage to Anne. He was subsequently attainted and beheaded. Marriage to Catherine Howard On 28 July 1540 (the same day Cromwell was executed), Henry married the young Catherine Howard, a first cousin and lady-in-waiting of Anne Boleyn. He was absolutely delighted with his new queen, and awarded her the lands of Cromwell and a vast array of jewellery. Soon after the marriage, however, Queen Catherine had an affair with the courtier Thomas Culpeper. She also employed Francis Dereham, who had previously been informally engaged to her and had an affair with her prior to her marriage, as her secretary. The court was informed of her affair with Dereham whilst Henry was away; they dispatched Thomas Cranmer to investigate, who brought evidence of Queen Catherine’s previous affair with Dereham to the king’s notice. Though Henry originally refused to believe the allegations, Dereham confessed. It took another meeting of the council, however, before Henry believed the accusations against Dereham and went into a rage, blaming the council before consoling himself in hunting. When questioned, the queen could have admitted a prior contract to marry Dereham, which would have made her subsequent marriage to Henry invalid, but she instead claimed that Dereham had forced her to enter into an adulterous relationship. Dereham, meanwhile, exposed Queen Catherine’s relationship with Culpeper. Culpeper and Dereham were both executed, and Catherine too was beheaded on 13 February 1542. Shrines destroyed and monasteries dissolved In 1538, the chief minister T. Cromwell pursued an extensive campaign against what is termed “idolatry” by the followers of the old religion, culminating in September with the dismantling of the shrine of St. Thomas Becket at Canterbury. As a consequence, the king was excommunicated by the Pope Paul III on 17 December of the same year. In 1540, Henry sanctioned the complete destruction of shrines to saints. In 1542, England’s remaining monasteries were all dissolved, and their property transferred to the Crown. Abbots and priors lost their seats in the House of Lords; only archbishops and bishops remained. Consequently, the Lords Spiritual– as members of the clergy with seats in the House of Lords were known– were for the first time outnumbered by the Lords Temporal. Second invasion of France and the “Rough Wooing” of Scotland The 1539 alliance between Francis and Charles had soured, eventually degenerating into renewed war. With Catherine of Aragon and Anne Boleyn dead, relations between Charles and Henry improved considerably, and Henry concluded a secret alliance with the Emperor and decided to enter the Italian War in favour of his new ally. An invasion of France was planned for 1543. In preparation for it, Henry moved to eliminate the potential threat of Scotland under the youthful James V. Victory would continue the Reformation in Scotland, which was still Catholic, and Henry hoped to unite the crowns of England and Scotland by marriage of James’ daughter, the future Mary, Queen of Scots, to his son Edward. Henry made war on Scotland for several years in pursuit of this goal, a campaign dubbed by Victorian chroniclers as “the Rough Wooing”. The Scots were defeated at Battle of Solway Moss on 24 November 1542, and James died on 15 December. The Scottish Regent Arran agreed to the marriage in the Treaty of Greenwich on 1 July 1543. Despite the success with Scotland, Henry hesitated to invade France, annoying Charles. Henry finally went to France in June 1544 with a two-pronged attack. One force under Norfolk ineffectively besieged Montreuil. The other, under Suffolk, laid siege to Boulogne. Henry later took personal command, and Boulogne fell on 18 September 1544. However, Henry had refused Charles’ request to march against Paris. Charles’ own campaign fizzled, and he made peace with France that same day. Henry was left alone against France, unable to make peace. Francis attempted to invade England in the summer of 1545, but reached only the Isle of Wight before being repulsed. Out of money, France and England signed the Treaty of Camp on 7 June 1546. Henry secured Boulogne for eight years. The city was then to be returned to France for 2 million crowns (£750,000). Henry needed the money; the 1544 campaign had cost £650,000, and England was once again bankrupt. Meanwhile, though Henry still clung to the Treaty of Greenwich, the Scots repudiated it in December 1543. Henry launched another war on Scotland, sending an army to burn Edinburgh and lay waste to the country. The Scots would not submit, though. Defeat at Ancrum Moor prompted a second invasion force. This war was nominally ended by the Treaty of Camp, although unrest continued in Scotland, including French and English interventions, up to Henry’s death. Marriage to Catherine Parr Henry married his last wife, the wealthy widow Catherine Parr, in July 1543. A reformer at heart, she argued with Henry over religion. Ultimately, Henry remained committed to an idiosyncratic mixture of Catholicism and Protestantism; the reactionary mood which had gained ground following the fall of Cromwell had neither eliminated his Protestant streak nor been overcome by it. Parr helped reconcile Henry with his daughters Mary and Elizabeth. In 1543, an Act of Parliament put the daughters back in the line of succession after Edward, Prince of Wales. The same act allowed Henry to determine further succession to the throne in his will. Physical decline Late in life, Henry became obese, with a waist measurement of 54 inches (140 cm), and had to be moved about with the help of mechanical inventions. He was covered with painful, pus-filled boils and possibly suffered from gout. His obesity and other medical problems can be traced from the jousting accident in 1536, in which he suffered a leg wound. The accident re-opened and aggravated a previous injury he had sustained years earlier, to the extent that his doctors found it difficult to treat. The wound festered for the remainder of his life and became ulcerated, thus preventing him from maintaining the level of physical activity he had previously enjoyed. The jousting accident is also believed to have caused Henry’s mood swings, which may have had a dramatic effect on his personality and temperament. The theory that Henry suffered from syphilis has been dismissed by most historians. A more recent theory suggests that Henry’s medical symptoms are characteristic of untreated type 2 diabetes. Alternatively, his wives’ pattern of pregnancies and his mental deterioration have led some to suggest that the king may have been Kell positive and suffered from McLeod syndrome. According to another study, Henry VIII’s history and body morphology may have been the result of traumatic brain injury after his 1536 jousting accident, which in turn led to a neuroendocrine cause of his obesity. This analysis identifies growth hormone deficiency (GHD) as the source for his increased adiposity but also significant behavioural changes noted in his later years, including his multiple marriages. Death and burial Henry’s obesity hastened his death at the age of 55, which occurred on 28 January 1547 in the Palace of Whitehall, on what would have been his father’s 90th birthday. He allegedly uttered his last words: “Monks! Monks! Monks!” perhaps in reference to the monks he caused to be evicted during the Dissolution of the Monasteries. On 14 February 1547 Henry’s coffin lay overnight at Syon Monastery, en route for burial in St George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle. Twelve years before in 1535 a Franciscan friar named William Peyto (or Peto, Petow) (died 1558 or 1559), had preached before the King at Greenwich Palace “that God’s judgements were ready to fall upon his head and that dogs would lick his blood, as they had done to Ahab”, whose infamy rests upon 1 Kings 16:33: “And Ahab did more to provoke the Lord God of Israel to anger than all the kings of Israel that were before him”. The prophecy was said to have been fulfilled during this night at Syon, when some “corrupted matter of a bloody colour” fell from the coffin to the floor. Henry VIII was interred in St George’s Chapel in Windsor Castle, next to Jane Seymour. Over a hundred years later, King Charles I (1625–1649) was buried in the same vault. Succession After his death, Henry’s only legitimate son, Edward, inherited the Crown, becoming Edward VI (1547–1553). Since Edward was then only nine years old, he could not exercise actual power. Rather, Henry’s will designated 16 executors to serve on a council of regency until Edward reached the age of 18. The executors chose Edward Seymour, 1st Earl of Hertford, Jane Seymour’s elder brother, to be Lord Protector of the Realm. If Edward went childless, the throne was to pass to Mary, Henry VIII’s daughter by Catherine of Aragon, and her heirs. If Mary’s issue failed, the crown was to go to Elizabeth, Henry’s daughter by Anne Boleyn, and her heirs. Finally, if Elizabeth’s line became extinct, the crown was to be inherited by the descendants of Henry VIII’s deceased younger sister, Queen Mary of France, the Greys. The descendants of Henry’s sister Margaret– the Stuarts, rulers of Scotland– were thereby excluded from the succession. This final provision failed when James VI of Scotland became James I of England upon Elizabeth’s death. Public image Henry cultivated the image of a Renaissance man, and his court was a centre of scholarly and artistic innovation and glamorous excess, epitomised by the Field of the Cloth of Gold. He scouted the country for choirboys, taking some directly from Wolsey’s choir, and introduced Renaissance music into court. Musicians included Benedict de Opitiis, Richard Sampson, Ambrose Lupo, and Venetian organist Dionisio Memo. Henry himself kept a considerable collection of instruments; he was skilled on the lute, could play the organ, and was a talented player of the virginals. He could also sight read music and sing well. He was an accomplished musician, author, and poet; his best known piece of music is “Pastime with Good Company” ("The Kynges Ballade"). He is often reputed to have written “Greensleeves” but probably did not. He was an avid gambler and dice player, and excelled at sports, especially jousting, hunting, and real tennis. He was known for his strong defence of conventional Christian piety. The King was involved in the original construction and improvement of several significant buildings, including Nonsuch Palace, King’s College Chapel, Cambridge and Westminster Abbey in London. Many of the existing buildings Henry improved were properties confiscated from Wolsey, such as Christ Church, Oxford; Hampton Court Palace; the Palace of Whitehall; and Trinity College, Cambridge. Henry was an intellectual. The first English king with a modern humanist education, he read and wrote English, French and Latin, and was thoroughly at home in his well-stocked library. He personally annotated many books and wrote and published one of his own. To promote the public support for the reformation of the church, Henry had numerous pamphlets and lectures prepared. For example, Richard Sampson’s Oratio (1534) was an argument for absolute obedience to the monarchy and claimed that the English church had always been independent from Rome. At the popular level, theatre and minstrel troupes funded by the crown travelled around the land to promote the new religious practices: the pope and Catholic priests and monks were mocked as foreign devils, while the glorious king was hailed as a brave and heroic defender of the true faith. Henry worked hard to present an image of unchallengeable authority and irresistible power. A large well-built athlete (over 6 feet [1.8 m] tall and strong and broad in proportion), Henry excelled at jousting and hunting. More than pastimes, they were political devices that served multiple goals, from enhancing his athletic royal image to impressing foreign emissaries and rulers, to conveying Henry’s ability to suppress any rebellion. Thus he arranged a jousting tournament at Greenwich in 1517, where he wore gilded armour, gilded horse trappings, and outfits of velvet, satin and cloth of gold dripping with pearls and jewels. It suitably impressed foreign ambassadors, one of whom wrote home that, “The wealth and civilisation of the world are here, and those who call the English barbarians appear to me to render themselves such”. Henry finally retired from jousting in 1536 after a heavy fall from his horse left him unconscious for two hours, but he continued to sponsor two lavish tournaments a year. He then started adding weight and lost the trim, athletic figure that had made him so handsome; Henry’s courtiers began dressing in heavily padded clothes to emulate– and flatter– their increasingly stout monarch. Towards the end of his reign his health rapidly declined. Government The power of Tudor monarchs, including Henry, was 'whole’ and 'entire’, ruling, as they claimed, by the grace of God alone. The crown could also rely on the exclusive use of those functions that constituted the royal prerogative. These included acts of diplomacy (including royal marriages), declarations of war, management of the coinage, the issue of royal pardons and the power to summon and dissolve parliament as and when required. Nevertheless, as evident during Henry’s break with Rome, the monarch worked within established limits, whether legal or financial, that forced him to work closely with both the nobility and parliament (representing the gentry). In practice, Tudor monarchs used patronage to maintain a royal court that included formal institutions such as the Privy Council as well as more informal advisers and confidants. Both the rise and fall of court nobles could be swift: although the often-quoted figure of 72,000 executions during his reign is inflated, Henry did undoubtedly execute at will, burning or beheading two of his wives, twenty peers, four leading public servants, six close attendants and friends, one cardinal (John Fisher) and numerous abbots. Among those who were in favour at any given point in Henry’s reign, one could usually be identified as a chief minister, though one of the enduring debates in the historiography of the period has been the extent to which those chief ministers controlled Henry rather than vice versa. In particular, historian G. R. Elton has argued that one such minister, Thomas Cromwell, led a “Tudor revolution in government” quite independent of the king, whom Elton presented as an opportunistic, essentially lazy participant in the nitty-gritty of politics. Where Henry did intervene personally in the running of the country, Elton argued, he mostly did so to its detriment. The prominence and influence of faction in Henry’s court is similarly discussed in the context of at least five episodes of Henry’s reign, including the downfall of Anne Boleyn. From 1514 to 1529, Thomas Wolsey (1473–1530), a cardinal of the established Church, oversaw domestic and foreign policy for the young king from his position as Lord Chancellor. Wolsey centralised the national government and extended the jurisdiction of the conciliar courts, particularly the Star Chamber. The Star Chamber’s overall structure remained unchanged, but Wolsey used it to provide for much-needed reform of the criminal law. The power of the court itself did not outlive Wolsey, however, since no serious administrative reform was undertaken and its role was eventually devolved to the localities. Wolsey helped fill the gap left by Henry’s declining participation in government (particularly in comparison to his father) but did so mostly by imposing himself in the King’s place. His use of these courts to pursue personal grievances, and particularly to treat delinquents as if mere examples of a whole class worthy of punishment, angered the rich, who were annoyed as well by his enormous wealth and ostentatious living. Following Wolsey’s downfall, Henry took full control of his government, although at court numerous complex factions continued to try to ruin and destroy each other. Thomas Cromwell (c. 1485–1540) also came to define Henry’s government. Returning to England from the continent in 1514 or 1515, Cromwell soon entered Wolsey’s service. He turned to law, also picking up a good knowledge of the Bible, and was admitted to Gray’s Inn in 1524. He became Wolsey’s “man of all work”. Cromwell, driven in part by his religious beliefs, attempted to reform the body politic of the English government through discussion and consent, and through the vehicle of continuity and not outward change. He was seen by many people as the man they wanted to bring about their shared aims, including Thomas Audley. By 1531, Cromwell and those associated with him were already responsible for the drafting of much legislation. Cromwell’s first office was that of the master of the King’s jewels in 1532, from which he began to invigorate the government finances. By this point, Cromwell’s power as an efficient administrator in a Council full of politicians exceeded what Wolsey had achieved. Cromwell did much work through his many offices to remove the tasks of government from the Royal Household (and ideologically from the personal body of the King) and into a public state. He did so, however, in a haphazard fashion that left several remnants, not least because he needed to retain Henry’s support, his own power, and the possibility of actually achieving the plan he set out. Cromwell made the various income streams put in place by Henry VII more formal and assigned largely autonomous bodies for their administration. The role of the King’s Council was transferred to a reformed Privy Council, much smaller and more efficient than its predecessor. A difference emerged between the financial health of the king, and that of the country, although Cromwell’s fall undermined much of his bureaucracy, which required his hand to keep order among the many new bodies and prevent profligate spending that strained relations as well as finances. Cromwell’s reforms ground to a halt in 1539, the initiative lost, and he failed to secure the passage of an enabling act, the Proclamation by the Crown Act 1539. He too was executed, on 28 July 1540. Finances Henry inherited a vast fortune and a prosperous economy from his father Henry VII, who had been frugal and careful with money. This fortune was estimated to £1,250,000 (£375 million by today’s standards). By comparison, however, the reign of Henry was a near-disaster in financial terms. Although he further augmented his royal treasury through the seizure of church lands, Henry’s heavy spending and long periods of mismanagement damaged the economy. Much of this wealth was spent by Henry on maintaining his court and household, including many of the building works he undertook on royal palaces. Henry hung 2,000 tapestries in his palaces; by comparison, James V of Scotland hung just 200. Henry took pride in showing off his collection of weapons, which included exotic archery equipment, 2,250 pieces of land ordnance and 6,500 handguns. Tudor monarchs had to fund all the expenses of government out of their own income. This income came from the Crown lands that Henry owned as well as from customs duties like tonnage and poundage, granted by parliament to the king for life. During Henry’s reign the revenues of the Crown remained constant (around £100,000), but were eroded by inflation and rising prices brought about by war. Indeed, war and Henry’s dynastic ambitions in Europe exhausted the surplus he had inherited from his father by the mid-1520s. Whereas Henry VII had not involved Parliament in his affairs very much, Henry VIII had to turn to Parliament during his reign for money, in particular for grants of subsidies to fund his wars. The Dissolution of the Monasteries provided a means to replenish the treasury, and as a result the Crown took possession of monastic lands worth £120,000 (£36 million) a year. The Crown had profited a small amount in 1526 when Wolsey had put England onto a gold, rather than silver, standard, and had debased the currency slightly. Cromwell debased the currency more significantly, starting in Ireland in 1540. The English pound halved in value against the Flemish pound between 1540 and 1551 as a result. The nominal profit made was significant, helping to bring income and expenditure together, but it had a catastrophic effect on the overall economy of the country. In part, it helped to bring about a period of very high inflation from 1544 onwards. Reformation Henry is generally credited with initiating the English Reformation– the process of transforming England from a Catholic country to a Protestant one– though his progress at the elite and mass levels is disputed, and the precise narrative not widely agreed. Certainly, in 1527, Henry, until then an observant and well-informed Catholic, appealed to the Pope for an annulment of his marriage to Catherine. No annulment was immediately forthcoming, the result in part of Charles V’s control of the Papacy. The traditional narrative gives this refusal as the trigger for Henry’s rejection of papal supremacy (which he had previously defended), though as historian A. F. Pollard has argued, even if Henry had not needed an annulment, Henry may have come to reject papal control over the governance of England purely for political reasons. In any case, between 1532 and 1537, Henry instituted a number of statutes that dealt with the relationship between king and pope and hence the structure of the nascent Church of England. These included the Statute in Restraint of Appeals (passed 1533), which extended the charge of praemunire against all who introduced papal bulls into England, potentially exposing them to the death penalty if found guilty. Other acts included the Supplication against the Ordinaries and the Submission of the Clergy, which recognised Royal Supremacy over the church. The Ecclesiastical Appointments Act 1534 required the clergy to elect bishops nominated by the Sovereign. The Act of Supremacy in 1534 declared that the King was “the only Supreme Head in Earth of the Church of England” and the Treasons Act 1534 made it high treason, punishable by death, to refuse the Oath of Supremacy acknowledging the King as such. Similarly, following the passage of the Act of Succession 1533, all adults in the Kingdom were required to acknowledge the Act’s provisions (declaring Henry’s marriage to Anne legitimate and his marriage to Catherine illegitimate) by oath; those who refused were subject to imprisonment for life, and any publisher or printer of any literature alleging that the marriage to Anne was invalid subject to the death penalty. Finally, the Peter’s Pence Act was passed, and it reiterated that England had “no superior under God, but only your Grace” and that Henry’s “imperial crown” had been diminished by “the unreasonable and uncharitable usurpations and exactions” of the Pope. The King had much support from the Church under Cranmer. Henry, to Thomas Cromwell’s annoyance, insisted on parliamentary time to discuss questions of faith, which he achieved through the Duke of Norfolk. This led to the passing of the Act of Six Articles, whereby six major questions were all answered by asserting the religious orthodoxy, thus restraining the reform movement in England. It was followed by the beginnings of a reformed liturgy and of the Book of Common Prayer, which would take until 1549 to complete. The victory won by religious conservatives did not convert into much change in personnel, however, and Cranmer remained in his position. Overall, the rest of Henry’s reign saw a subtle movement away from religious orthodoxy, helped in part by the deaths of prominent figures from before the break with Rome, especially the executions of Thomas More and John Fisher in 1535 for refusing to renounce papal authority. Henry established a new political theology of obedience to the crown that was continued for the next decade. It reflected Martin Luther’s new interpretation of the fourth commandment ("Honour thy father and mother"), brought to England by William Tyndale. The founding of royal authority on the Ten Commandments was another important shift: reformers within the Church utilised the Commandments’ emphasis on faith and the word of God, while conservatives emphasised the need for dedication to God and doing good. The reformers’ efforts lay behind the publication of the Great Bible in 1539 in English. Protestant Reformers still faced persecution, particularly over objections to Henry’s annulment. Many fled abroad, including the influential Tyndale, who was eventually executed and his body burned at Henry’s behest. When taxes once payable to Rome were transferred to the Crown, Cromwell saw the need to assess the taxable value of the Church’s extensive holdings as they stood in 1535. The result was an extensive compendium, the Valor Ecclesiasticus. In September of the same year, Cromwell commissioned a more general visitation of religious institutions, to be undertaken by four appointee visitors. The visitation focussed almost exclusively on the country’s religious houses, with largely negative conclusions. In addition to reporting back to Cromwell, the visitors made the lives of the monks more difficult by enforcing strict behavioural standards. The result was to encourage self-dissolution. In any case, the evidence gathered by Cromwell led swiftly to the beginning of the state-enforced dissolution of the monasteries with all religious houses worth less than £200 vested by statute in the crown in January 1536. After a short pause, surviving religious houses were transferred one by one to the Crown and onto new owners, and the dissolution confirmed by a further statute in 1539. By January 1540 no such houses remained: some 800 had been dissolved. The process had been efficient, with minimal resistance, and brought the crown some £90,000 a year. The extent to which the dissolution of all houses was planned from the start is debated by historians; there is some evidence that major houses were originally intended only to be reformed. Cromwell’s actions transferred a fifth of England’s landed wealth to new hands. The programme was designed primarily to create a landed gentry beholden to the crown, which would use the lands much more efficiently. Although little opposition to the supremacy could be found in England’s religious houses, they had links to the international church and were an obstacle to further religious reform. Response to the reforms was mixed. The religious houses had been the only support of the impoverished, and the reforms alienated much of the population outside London, helping to provoke the great northern rising of 1536–1537, known as the Pilgrimage of Grace. Elsewhere the changes were accepted and welcomed, and those who clung to Catholic rites kept quiet or moved in secrecy. They would re-emerge during the reign of Henry’s daughter Mary (1553–1558). Military Apart from permanent garrisons at Berwick, Calais, and Carlisle, England’s standing army numbered only a few hundred men. This was increased only slightly by Henry. Henry’s invasion force of 1513, some 30,000 men, was composed of billmen and longbowmen, at a time when the other European nations were moving to hand guns and pikemen. The difference in capability was at this stage not significant, however, and Henry’s forces had new armour and weaponry. They were also supported by battlefield artillery, a relatively new invention, and several large and expensive siege guns. The invasion force of 1544 was similarly well-equipped and organised, although command on the battlefield was laid with the dukes of Suffolk and Norfolk, which in the case of the latter produced disastrous results at Montreuil. Henry is traditionally cited as one of the founders of the Royal Navy. Technologically, Henry invested in large cannon for his warships, an idea that had taken hold in other countries, to replace the smaller serpentines in use. He also flirted with designing ships personally– although his contribution to larger vessels, if any, is not known, it is believed that he influenced the design of rowbarges and similar galleys. Henry was also responsible for the creation of a permanent navy, with the supporting anchorages and dockyards. Tactically, Henry’s reign saw the Navy move away from boarding tactics to employ gunnery instead. The Navy was enlarged up to fifty ships (the Mary Rose was one of them), and Henry was responsible for the establishment of the “council for marine causes” to specifically oversee all the maintenance and operation of the Navy, becoming the basis for the later Admiralty. Henry’s break with Rome incurred the threat of a large-scale French or Spanish invasion. To guard against this, in 1538, he began to build a chain of expensive, state-of-the-art defences, along Britain’s southern and eastern coasts from Kent to Cornwall, largely built of material gained from the demolition of the monasteries. These were known as Henry VIII’s Device Forts. He also strengthened existing coastal defence fortresses such as Dover Castle and, at Dover, Moat Bulwark and Archcliffe Fort, which he personally visited for a few months to supervise. Wolsey had many years before conducted the censuses required for an overhaul of the system of militia, but no reform resulted. In 1538–39, Cromwell overhauled the shire musters, but his work mainly served to demonstrate how inadequate they were in organisation. The building works, including that at Berwick, along with the reform of the militias and musters, were eventually finished under Queen Mary. Ireland At the beginning of Henry’s reign, Ireland was effectively divided into three zones: the Pale, where English rule was unchallenged; Leinster and Munster, the so-called “obedient land” of Anglo-Irish peers; and the Gaelic Connaught and Ulster, with merely nominal English rule. Until 1513, Henry continued the policy of his father, to allow Irish lords to rule in the king’s name and accept steep divisions between the communities. However, upon the death of the 8th Earl of Kildare, governor of Ireland, fractious Irish politics combined with a more ambitious Henry to cause trouble. When Thomas Butler, 7th Earl of Ormond died, Henry recognised one successor for Ormond’s English, Welsh and Scottish lands, whilst in Ireland another took control. Kildare’s successor, the 9th Earl, was replaced as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland by Thomas Howard, Earl of Surrey in 1520. Surrey’s ambitious aims were costly, but ineffective; English rule became trapped between winning the Irish lords over with diplomacy, as favoured by Henry and Wolsey, and a sweeping military occupation as proposed by Surrey. Surrey was recalled in 1521, with Piers Butler– one of claimants to the Earldom of Ormond– appointed in his place. Butler proved unable to control opposition, including that of Kildare. Kildare was appointed chief governor in 1524, resuming his dispute with Butler, which had before been in a lull. Meanwhile, the Earl of Desmond, an Anglo-Irish peer, had turned his support to Richard de la Pole as pretender to the English throne; when in 1528 Kildare failed to take suitable actions against him, Kildare was once again removed from his post. The Desmond situation was resolved on his death in 1529, which was followed by a period of uncertainty. This was effectively ended with the appointment of Henry FitzRoy, Duke of Richmond and the king’s son, as lord lieutenant. Richmond had never before visited Ireland, his appointment a break with past policy. For a time it looked as if peace might be restored with the return of Kildare to Ireland to manage the tribes, but the effect was limited and the Irish parliament soon rendered ineffective. Ireland began to receive the attention of Cromwell, who had supporters of Ormond and Desmond promoted. Kildare, on the other hand, was summoned to London; after some hesitation, he departed for London in 1534, where he would face charges of treason. His son, Thomas, Lord Offaly was more forthright, denouncing the king and leading a “Catholic crusade” against the king, who was by this time mired in marital problems. Offaly had the Archbishop of Dublin murdered, and besieged Dublin. Offaly led a mixture of Pale gentry and Irish tribes, although he failed to secure the support of Lord Darcy, a sympathiser, or Charles V. What was effectively a civil war was ended with the intervention of 2,000 English troops– a large army by Irish standards– and the execution of Offaly (his father was already dead) and his uncles. Although the Offaly revolt was followed by a determination to rule Ireland more closely, Henry was wary of drawn-out conflict with the tribes, and a royal commission recommended that the only relationship with the tribes was to be promises of peace, their land protected from English expansion. The man to lead this effort was Sir Antony St Leger, as Lord Deputy of Ireland, who would remain into the post past Henry’s death. Until the break with Rome, it was widely believed that Ireland was a Papal possession granted as a mere fiefdom to the English king, so in 1541 Henry asserted England’s claim to the Kingdom of Ireland free from the Papal overlordship. This change did, however, also allow a policy of peaceful reconciliation and expansion: the Lords of Ireland would grant their lands to the King, before being returned as fiefdoms. The incentive to comply with Henry’s request was an accompanying barony, and thus a right to sit in the Irish House of Lords, which was to run in parallel with England’s. The Irish law of the tribes did not suit such an arrangement, because the chieftain did not have the required rights; this made progress tortuous, and the plan was abandoned in 1543, not to be replaced. Historiography The complexities and sheer scale of Henry’s legacy ensured that, in the words of Betteridge and Freeman, "throughout the centuries [since his death], Henry has been praised and reviled, but he has never been ignored". A particular focus of modern historiography has been the extent to which the events of Henry’s life (including his marriages, foreign policy and religious changes) were the result of his own initiative and, if they were, whether they were the result of opportunism or of a principled undertaking by Henry. The traditional interpretation of those events was provided by historian A.F. Pollard, who in 1902 presented his own, largely positive, view of the king, "laud[ing him] as the king and statesman who, whatever his personal failings, led England down the road to parliamentary democracy and empire". Pollard’s interpretation, which was broadly comparable to 17th century publications of Lord Herbert of Cherbury and his contemporaries, remained the dominant interpretation of Henry’s life until the publication of the doctoral thesis of G. R. Elton in 1953. That thesis, entitled “The Tudor Revolution in Government”, maintained Pollard’s positive interpretation of the Henrician period as a whole, but reinterpreted Henry himself as a follower rather than a leader. For Elton, it was Cromwell and not Henry who undertook the changes in government– Henry was shrewd, but lacked the vision to follow a complex plan through. Henry was little more, in other words, than an “ego-centric monstrosity” whose reign "owed its successes and virtues to better and greater men about him; most of its horrors and failures sprang more directly from [the king]". Although the central tenets of Elton’s thesis have now been all but abandoned, it has consistently provided the starting point for much later work, including that of J. J. Scarisbrick, his student. Scarisbrick largely kept Elton’s regard for Cromwell’s abilities, but returned agency to Henry, who Scarisbrick considered to have ultimately directed and shaped policy. For Scarisbrick, Henry was a formidable, captivating man who “wore regality with a splendid conviction”. The effect of endowing Henry with this ability, however, was largely negative in Scarisbrick’s eyes: to Scarisbrick the Henrician period was one of upheaval and destruction and those in charge worthy of blame more than praise. Even among more recent biographers, including David Loades, David Starkey and John Guy, there has ultimately been little consensus on the extent to which Henry was responsible for the changes he oversaw or the correct assessment of those he did bring about. This lack of clarity about Henry’s control over events has contributed to the variation in the qualities ascribed to him: religious conservative or dangerous radical; lover of beauty or brutal destroyer of priceless artefacts; friend and patron or betrayer of those around him; chivalry incarnate or ruthless chauvinist. One traditional approach, favoured by Starkey and others, is to divide Henry’s reign into two halves, the first Henry being dominated by positive qualities (politically inclusive, pious, athletic but also intellectual) who presided over a period of stability and calm, and the latter a “hulking tyrant” who presided over a period of dramatic, sometimes whimsical, change. Other writers have tried to merge Henry’s disparate personality into a single whole; Lacey Baldwin Smith, for example, considered him an egotistical borderline neurotic given to great fits of temper and deep and dangerous suspicions, with a mechanical and conventional, but deeply held piety, and having at best a mediocre intellect. Style and arms Many changes were made to the royal style during his reign. Henry originally used the style “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England, France and Lord of Ireland”. In 1521, pursuant to a grant from Pope Leo X rewarding Henry for his Defence of the Seven Sacraments, the royal style became “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England and France, Defender of the Faith and Lord of Ireland”. Following Henry’s excommunication, Pope Paul III rescinded the grant of the title “Defender of the Faith”, but an Act of Parliament declared that it remained valid; and it continues in royal usage to the present day. Henry’s motto was “Coeur Loyal” ("true heart"), and he had this embroidered on his clothes in the form of a heart symbol and with the word “loyal”. His emblem was the Tudor rose and the Beaufort portcullis. As king, Henry’s arms were the same as those used by his predecessors since Henry IV: Quarterly, Azure three fleurs-de-lys Or (for France) and Gules three lions passant guardant in pale Or (for England). In 1535, Henry added the “supremacy phrase” to the royal style, which became “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England and France, Defender of the Faith, Lord of Ireland and of the Church of England in Earth Supreme Head”. In 1536, the phrase “of the Church of England” changed to “of the Church of England and also of Ireland”. In 1541, Henry had the Irish Parliament change the title “Lord of Ireland” to “King of Ireland” with the Crown of Ireland Act 1542, after being advised that many Irish people regarded the Pope as the true head of their country, with the Lord acting as a mere representative. The reason the Irish regarded the Pope as their overlord was that Ireland had originally been given to King Henry II of England by Pope Adrian IV in the 12th century as a feudal territory under papal overlordship. The meeting of Irish Parliament that proclaimed Henry VIII as King of Ireland was the first meeting attended by the Gaelic Irish chieftains as well as the Anglo-Irish aristocrats. The style “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith and of the Church of England and also of Ireland in Earth Supreme Head” remained in use until the end of Henry’s reign. Ancestry Marriages and issue References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henry_VIII_of_England


Thomas Campion (sometimes Campian) (12 February 1567 – 1 March 1620) was an English composer, poet, and physician. He wrote over a hundred lute songs, masques for dancing, and an authoritative technical treatise on music. Life Campion was born in London, the son of John Campion, a clerk of the Court of Chancery, and Lucy (née Searle– daughter of Laurence Searle, one of the queen’s serjeants-at-arms). Upon the death of Campion’s father in 1576, his mother married Augustine Steward, dying soon afterwards. His stepfather assumed charge of the boy and sent him, in 1581, to study at Peterhouse, Cambridge as a “gentleman pensioner”; he left the university after four years without taking a degree. He later entered Gray’s Inn to study law in 1586. However, he left in 1595 without having been called to the bar. On 10 February 1605, he received his medical degree from the University of Caen. Campion is thought to have lived in London, practising as a physician, until his death in March 1620– possibly of the plague. He was apparently unmarried and had no children. He was buried the same day at St Dunstan-in-the-West in Fleet Street. He was implicated in the murder of Sir Thomas Overbury, but was eventually exonerated, as it was found that he had unwittingly delivered the bribe that had procured Overbury’s death. Poetry and songs The body of his works is considerable, the earliest known being a group of five anonymous poems included in the “Songs of Divers Noblemen and Gentlemen,” appended to Newman’s edition of Sir Philip Sidney’s Astrophel and Stella, which appeared in 1591. In 1595, Poemata, a collection of Latin panegyrics, elegies and epigrams was published, winning him a considerable reputation. This was followed, in 1601, by a songbook, A Booke of Ayres, with words by himself and music composed by himself and Philip Rosseter. The following year he published his Observations in the Art of English Poesie, “against the vulgar and unartificial custom of riming,” in favour of rhymeless verse on the model of classical quantitative verse. Campion’s theories on poetry were demolished by Samuel Daniel in “Defence of Rhyme” (1603). In 1607, he wrote and published a masque for the occasion of the marriage of Lord Hayes, and, in 1613, issued a volume of Songs of Mourning: Bewailing the Untimely Death of Prince Henry, set to music by John Cooper (also known as Coperario). The same year he wrote and arranged three masques: The Lords’ Masque for the marriage of Princess Elizabeth; an entertainment for the amusement of Queen Anne at Caversham House; and a third for the marriage of the Earl of Somerset to the infamous Frances Howard, Countess of Essex. If, moreover, as appears quite likely, his Two Bookes of Ayres (both words and music written by himself) belongs also to this year, it was indeed his annus mirabilis. In 1615, he published a book on counterpoint, A New Way of Making Fowre Parts in Counterpoint By a Most Familiar and Infallible Rule, a technical treatise which was for many years the standard textbook on the subject. It was included, with annotations by Christopher Sympson, in Playford’s Brief Introduction to the Skill of Musick, and two editions appear to have been published by 1660. Some time in or after 1617 appeared his Third and Fourth Booke of Ayres. In 1618 appeared the airs that were sung and played at Brougham Castle on the occasion of the King’s entertainment there, the music by George Mason and John Earsden, while the words were almost certainly by Campion. In 1619, he published his Epigrammatum Libri II. Umbra Elegiarum liber unus, a reprint of his 1595 collection with considerable omissions, additions (in the form of another book of epigrams) and corrections. Legacy Campion made a nuncupative will on 1 March 1619/20 before 'divers credible witnesses’: a memorandum was made that he did 'not longe before his death say that he did give all that he had unto Mr Phillip Rosseter, and wished that his estate had bin farre more’, and Rosseter was sworn before Dr Edmund Pope to administer as principal legatee on 3 March 1619/20. While Campion had attained a considerable reputation in his own day, in the years that followed his death his works sank into complete oblivion. No doubt this was due to the nature of the media in which he mainly worked, the masque and the song-book. The masque was an amusement at any time too costly to be popular, and during the commonwealth period it was practically extinguished. The vogue of the song-books was even more ephemeral, and, as in the case of the masque, the Puritan ascendancy, with its distaste for all secular music, effectively put an end to the madrigal. Its loss involved that of many hundreds of dainty lyrics, including those of Campion, and it was due to the work of A. H. Bullen (see bibliography), who first published a collection of the poet’s works in 1889, that his genius was recognised and his place among the foremost rank of Elizabethan lyric poets restored. Campion set little store by his English lyrics; they were to him “the superfluous blossoms of his deeper studies,” but we may thank the fates that his ideas on rhymeless versification so little affected his work. His rhymeless experiments are certainly better conceived than many others, but they lack the spontaneous grace and freshness of his other poetry, while the whole scheme was, of course, unnatural. He must have possessed a very delicate musical ear, for not one of his songs is unmusical; moreover, his ability to compose both words and music gave rise to a metrical fluidity which is one of his most characteristic features. Rarely are his rhythms uniform, while they frequently shift from line to line. His range was very great both in feeling and expression, and whether he attempts an elaborate epithalamium or a simple country ditty, the result is always full of unstudied freshness and tuneful charm. In some of his sacred pieces, he is particularly successful, combining real poetry with genuine religious fervour. Some of Campion’s works could also be quite ribald– such as “Beauty, since you so much desire”. Early dictionary writers, such as Fétis, saw Campion as a theorist. It was much later on that people began to see him as a composer. He was the writer of a poem, Cherry Ripe, which is not the later famous poem of that title but has several similarities. In popular culture Repeated reference was made to Campion in an October 2010 episode of the BBC TV series, James May’s Man Lab (BBC2), where his works are used as the inspiration for a young man trying to serenade a female colleague. This segment was referenced in the second and third series of the programme as well. Occasional mention is made of Campion ("Campian") in the comic strip 9 Chickweed Lane (i.e., 5 April 2004), referencing historical context for playing the lute. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thomas_Campion

Alfred Charles Tomlinson, CBE (born 8 January 1927) is a British poet and translator, and also an academic and artist. He was born and raised in Penkhull in the city of Stoke-on-Trent, Staffordshire. After attending Longton High School, Tomlinson read English at Queens' College, Cambridge, where he studied with Donald Davie. After leaving university he spent a year in Liguria in Italy and then taught in a primary school. He later became Emeritus Professor of English Poetry at the University of Bristol, England. He and his wife Brenda now live in a Cotswold cottage at Ozleworth, near Wotton-under-Edge.[1] They met as teenagers, and have two daughters and a granddaughter. He is also an artist, and In Black and White: The Graphics of Charles Tomlinson, with an introduction by Nobel prize-winner Octavio Paz, was published in 1976. Poetry Tomlinson's first book of poetry was published in 1951, and his Collected Poems was published by the Oxford University Press in 1985, followed by the Selected Poems: 1955-1997 in 1997. His poetry has won international recognition and has received many prizes in Europe and the United States, including the 1993 Bennett Award from Hudson Review; the New Criterion Poetry Prize, 2002; the Premio Internazionale di Poesie Ennio Flaiano, 2001; and the Premio Internazionale di Poesia Attilio Bertolucci, 2004. He is an Honorary Fellow of the American Academy of the Arts and Sciences and of the Modern Language Association. Charles Tomlinson was made a CBE in 2001 for his contribution to literature. Charles Tomlinson's Selected Poems, his collections Skywriting, Metamorphoses and The Vineyard Above the Sea, amongst others, are all published by Carcanet Press. His latest collection Cracks in the Universe was published in May 2006 in Carcanet Press' Oxford Poets series. In his book Some Americans Tomlinson acknowledges his poetic debts to modern American poetry, in particular William Carlos Williams, George Oppen, Marianne Moore, and Louis Zukofsky. In his critical study Lives of Poets, Michael Schmidt observes that 'Wallace Stevens was the guiding star [Tomlinson] initially steered by'. Schmidt goes on to define the two characteristic voices of Tomlinson: 'one is intellectual, meditative, feeling its way through ideas' whilst the other voice engages with 'landscapes and images from the natural world'. Tomlinson's poetry often circles around these themes of place and return, exploring his native landscape of Stoke and the shifting cityscape of modern Bristol. In Against Extremity Tomlinson expresses a distrust of confessional verse and rejects the 'willed extremism of poets like Sylvia Plath and Anne Sexton'. He has been active in the field of collaborative poetry, writing renshi under the guidance of Makoto Ooka with James Lasdun and Mikiro Sasaki. From 1985 to 2000 he recorded all of his published poetry for Keele University. Included are his Stoke-on-Trent poems, which are: At Stoke; The Slag Heap; Steel; Canal; Poem for My Father; John Maydew; The Hand at Callow Hill Farm; The Farmer's Wife; Black Brook; The Question; The Shaft; After a Death; Night Ride; Gladstone Street; Etruria Vale; Penkhull New Road; The Way In; The Tree; Midlands; Portrait of the Artist I; Portrait of the Artist II; The Hoard; Consolations for Double Bass; The Rich; Class; The Hawthorn in Trent Vale; Written on Water; The Marl Pits. Translations Tomlinson has excelled as an authoritative translator of poetry from the Russian, Spanish and Italian, including the work of Antonio Machado, Fyodor Tyutchev, César Vallejo and Attilio Bertolucci. He has collaborated with the Mexican writer Octavio Paz. He edited the seminal Oxford Book of Verse in English Translation and the Selected Poems of William Carlos Williams. Works * A Peopled Landscape, Oxford University Press, 1963 * Renga: A Chain of Poems, with Octavio Paz, Jacques Roubaud, and Edoardo Sanguineti. (Braziller, 1971) * Door in the Wall (Carcanet Press, 1999) * Selected Poems (Carcanet Press, 1999) * Annunciation (Carcanet Press, 1999) * The Vineyard Above the Sea (Carcanet Press, 1999) * American Essays (Carcanet Press, 2001) * Metamorphoses: Poetry and Translation (Carcanet Press, 2003) * Skywriting (Carcanet Press, 2003) * Cracks in the Universe (Carcanet Press, 2006) References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Tomlinson


Marjorie Lowry Christie Pickthall (14 September 1883, Gunnersbury, London– 19 April 1922, Vancouver), was a Canadian writer who was born in England but lived in Canada from the time she was seven. She was once “thought to be the best Canadian poet of her generation.” According to her father, she had planned her career before she was six; she would be a writer and illustrator of books. Her parents encouraged her artistic talents with lessons in drawing and music; an accomplished violinist, she continued studying violin until she was twenty.


Reginald Gibbons (born 1947) is an American poet, fiction writer, translator, literary critic, and Professor of English and Classics at Northwestern University and Director of the Center for the Writing Arts there. Gibbons has published numerous books, as well as poems, short stories, essays and reviews in journals and magazines, has held Guggenheim Foundation and NEA fellowships in poetry and a research fellowship from the Center for Hellenic Studies in Washington D.C. He has won the Anisfield-Wolf Book Award, the Carl Sandburg Prize, the Folger Shakespeare Library’s O. B. Hardison, Jr. Poetry Prize, and other honors, among them the inclusion of his work in Best American Poetry and Pushcart Prize anthologies. His book Creatures of a Day was a finalist for the 2008 National Book Award for poetry. He attended public school in Spring Branch (at that time, outside Houston, Texas; now incorporated into the city), Princeton University (BA Spanish and Portuguese), and Stanford University (MA in English and Creative Writing; PhD in Comparative Literature). Before moving to Northwestern University, he taught creative writing at Princeton and Columbia. At Northwestern, he was the editor of TriQuarterly magazine from 1981 to 1997, and co-founded TriQuarterly Books (after 1997, an imprint of Northwestern University Press). As the editor of TriQuarterly, he edited or co-edited the special issues Chicago (1984), From South Africa: New Writing, Photography and Art (1987), A Window on Poland (1983), Prose from Spain (1983), New Writing from Mexico (1992), and others, as well as many general issues of the magazine. He edited two works of William Goyen (1915-1983): the 50th Anniversary edition of The House of Breath and the Goyen’s posthumously published second novel, Half a Look of Cain (both published by Northwestern University Press). In 1989, he was one of a group of co-founders of the Guild Literary Complex (Chicago), a literary presenting organization, where he continues to volunteer, and he is a member of the large team that is creating the American Writers Museum (Chicago; opening in 2017). Career * Lecturer in creative writing, Princeton University (Princeton, NJ), 1976-1980 * Lecturer in creative writing, Columbia University School of General Studies, 1980-81 * Professor of English, Northwestern University (Evanston, IL), 1981- * Editor of TriQuarterly magazine, 1981-1997 * Core faculty member of MFA Program for Writers, Warren Wilson College (Asheville, NC), 1989-2011 * Co-founder and member of the board of directors, Guild Complex, 1989- * Member, National Advisory Council and Content Leadership Team, American Writers Museum, 2012- Poetry * Roofs Voices Roads. (Quarterly Review of Literature, 1979). * The Ruined Motel. (Houghton, 1981). * Saints. (Persea Books, 1986). * Maybe It Was So. (University of Chicago Press, 1991). ISBN 978-0-226-29056-0 * Sparrow: New and Selected Poems. (LSU Press, 1997). ISBN 978-0-8071-2232-7 * Homage to Longshot O’Leary: Poems. (Holy Cow! Press, 1999). * It’s Time: Poems. (LSU Press, 2002). ISBN 978-0-8071-2815-2 * Creatures of a Day: Poems. (LSU Press, 2008). ISBN 978-0-8071-3318-7 * Desde una barca de papel (Poemas 1981-2008). (Littera Libros (Villanueva de la Serena, SPAIN), 2009. (Bilingual edition) * Slow Trains Overhead: Chicago Poems and Stories. (University of Chicago Press, 2010). ISBN 978-0-226-29058-4 * L’abitino blue. (Gattomerlino (Rome, ITALY). (Bilingual edition) * Last Lake. (University of Chicago Press, 2016. ISBN 978-0-226-41745-5 Fiction * Sweetbitter: A Novel. (LSU Press, 2003). ISBN 978-0-8071-2871-8 * Five Pears or Peaches. (Broken Moon Press, 1991). * Orchard in the Street. (BOA Editions, Ltd, forthcoming 2017). Other Books * Sophocles, Selected Poems: Odes and Fragments (Princeton University Press, 2008.) Translated and Introduced by Reginald Gibbons. ISBN 978-0-691-13024-8 * How Poems Think (University of Chicago Press, 2015). ISBN 978-0-226-27800-1 * Sophocles, Antigone (Oxford University Press, 2007). Translated by Reginald Gibbons and Charles Segal. ISBN 978-0-19514310-2 * Goyen: Autobiographical Essays, Notesbooks, Evocations, Interviews, by William Goyen (University of Texas Press, 2007. ISBN 978-0-292-72225-5 * The Complete Sophocles, Volume I: The Theban Plays (Oxford University Press, 2011.) Antigone translated by Reginald Gibbons and Charles Segal. ISBN 978-0-19-538880-0 * The Complete Euripides, Volume IV: Bacchae and Other Plays (Oxford University Press, 2009.) Bacchae translated by Reginald Gibbons and Charles Segal. ISBN 978-0-19-537340-0 * New Writing from Mexico, edited by Reginald Gibbons. TriQuarterly Books, 1992. * Thomas McGrath: Life and the Poem, edited by Reginald Gibbons and Terrence Des Press. (University of Illinois Press, 1992. ISBN 0-252-06177-2 References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reginald_Gibbons


David McKee Wright (6 August 1869– 5 February 1928) was an Irish-born poet and journalist, active in New Zealand and Australia. Early life Wright was born at Ballynaskeagh, County Down, Ireland, the second son of Rev. William Wright, D.D. (1837-1899), a Congregational missionary working in Damascus, scholar and author, and his wife Ann (d.1877), née McKee, daughter of the Rev. David McKee, an educationist and author. David Wright was born while his parents were home on furlough and was left with a grandmother (Rebecca McKee) until he was seven years old. Wright was educated at the local Glascar School and then from 1876 in England at Mr Pope’s School and the Crystal Palace School of Engineering, London. New Zealand Wright migrated to New Zealand in 1887 and spent several years as a rabbiter on stations in Central Otago. During this time he wrote in both prose and verse for major provincial newspapers about station life. He studied for the Congregational ministry and Wright studied divinity from 1896 at the University of Otago. Wright had done a lot of private reading, but found that apart from English his education was generally below that of the other students. In 1897 Wright was awarded a Stuart prize for poetry. Wright published four volumes of ballads, Aorangi and other Verses (1896), Station Ballads and other Verses (1897), Wisps of Tussock (1900), and New Zealand Chimes (1900). As a clergyman Wright was liked, but he found the work uncongenial and gave it up for journalism in which he had considerable experience in New Zealand. Wright married Elizabeth Couper at Dunedin on 3 August 1899; a son David was born in 1900, but the marriage failed. Wright joined the New Zealand Mail as parliamentary reporter in 1907. Australia Wright moved to Sydney in 1910 and did a large amount of successful freelance work for the Sun, The Bulletin, and other papers. Wright was editor of the Red Page of The Bulletin 1916–1926 and encouraged many of the rising writers of the time, and continued to do a large amount of writing himself in both prose and verse. Much of this appeared over pen-names such as “Pat O’Maori” and “Mary McCommonwealth” and much was signed with his initials. As Wright grew older his mind turned more and more to the country of his birth, he published his most important volume, An Irish Heart (1918). In 1920 he was awarded the prize for the best poem in commemoration of the visit of the Prince of Wales, and in the same year the Rupert Brooke memorial prize for a long poem, “Gallipoli”. Neither of these poems has been published in book form. From 1912-18 Wright lived with the writer 'Margaret Fane’ (Beatrice Florence Osborne, 1887-1962) in Sydney; they had four sons. From 1918 Wright lived with Zora Cross in Greeanawn, Glenbrook, Blue Mountains. He died there on 5 February 1928. The couple had two daughters, Davidina Wright and April McKee Wright (also known as April Hersey), who went on to write at least one wartime thriller. Legacy Wright was a friend of Christopher Brennan, Randolph Bedford, Frank Morton and Henry Lawson. Though much of a Bohemian, something of the clergyman still clung to him. Zora Cross, in An Introduction to the Study of Australian Literature, gave him a high position among Australian poets. Charming though An Irish Heart may be, it is too derivative to be work of the highest kind. It is not a question of individual words or phrases, but rather of a man steeping himself in the modern Irish school of poetry, and with all the skill of his practised craftsmanship reproducing its spirit in another land. A large amount of his work, including some short plays, has never been collected. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/David_McKee_Wright


Keith Castellain Douglas (24 January 1920– 9 June 1944) was an English poet noted for his war poetry during the Second World War and his wry memoir of the Western Desert campaign, Alamein to Zem Zem. He was killed in action during the invasion of Normandy. Poetry Douglas described his poetic style as “extrospective”; that is, he focused on external impressions rather than inner emotions. The result is a poetry which, according to his detractors, can be callous in the midst of war’s atrocities. For others, Douglas’s work is powerful and unsettling because its exact descriptions eschew egotism and shift the burden of emotion from the poet to the reader. His best poetry is generally considered to rank alongside the 20th century’s finest soldier-poetry. In his poem, “Desert Flowers” (1943), Douglas mentions World War I poet Isaac Rosenberg, claiming that he is only repeating what Rosenberg has already written. Early life Douglas was born in Tunbridge Wells, Kent, the son of Capt. Keith Sholto Douglas, MC (retired) and Marie Josephine Castellain. His mother became unwell and collapsed in 1924 of encephalitis lethargica, never to fully recover. By 1926, the chicken farm set up by his father had collapsed. Douglas was sent to a preparatory school (Edgeborough School in Guildford) the same year. The family became increasingly poor, and his father had to leave home in early 1928 to seek better employment in Wales. The persistent ill-health of Marie led to the collapse of the marriage of his parents by the end of that year, and his father remarried in 1930. Douglas was deeply hurt by his father not communicating with him after 1928, and when Capt. Douglas did write at last in 1938, Keith did not agree to meet him. In one of his letters written in 1940 Douglas looked back on his childhood: “I lived alone during the most fluid and formative years of my life, and during that time I lived on my imagination, which was so powerful as to persuade me that the things I imagined would come true.” Education Marie Douglas faced extreme financial distress, so much so that only the generosity of the Edgeborough headmaster Mr. James permitted Douglas to attend school in 1930–1931, his last year there. Douglas sat in 1931 for the entrance examination to Christ’s Hospital, where education was free and there was monetary assistance to cover all other costs. He was accepted, and joined Christ’s Hospital, near Horsham, in September 1931, studying there till 1938. It was at this school that his considerable poetic talent and artistic ability were recognised. So was his cavalier attitude to authority and property, which nearly led to expulsion in 1935 over a purloined training rifle. In surprising contrast, he excelled as a member of the school’s Officers Training Corps, particularly enjoying drill, although he was philosophically opposed to militarism. University After his bruising brush with authority in 1935, Douglas settled down to a less troubled and more productive period at school, during which he excelled both at studies and games, and at the end of which he won an open exhibition to Merton College, Oxford in 1938 to read History and English. The First World War-veteran and well-known poet Edmund Blunden was his tutor at Merton, and regarded his poetic talent highly. Blunden sent his poems to T. S. Eliot, the doyen of English poetry, who found Douglas’s verses 'impressive’. Douglas became the editor of Cherwell, and one of the poets anthologised in the collection Eight Oxford Poets (1941), although by the time that volume appeared he was already in the army. He does not seem to have been acquainted with somewhat junior but contemporary Oxford poets such as Sidney Keyes, Drummond Allison, John Heath-Stubbs and Philip Larkin, who would make names for themselves. At Oxford, Douglas entered a relationship with a sophisticated Chinese student named Yingcheng, or Betty Sze, the daughter of a diplomat. Her own sentiments towards him were less intense, and she refused to marry him. Yingcheng remained the unrequited love of Douglas’s life and the source of his best romantic verse, despite his involvements with other women later, most notably Milena Guiterrez Penya. Military service Within days of the declaration of war he reported to an army recruiting centre with the intention of joining a cavalry regiment, but like many others keen to serve he had to wait, and it was not until July 1940 that he started his training. On 1 February 1941 he passed out from the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, the British Army training academy for officers, and was commissioned into the 2nd Derbyshire Yeomanry at Ripon. He was posted to the Middle East in July 1941 and transferred to the Nottinghamshire (Sherwood Rangers) Yeomanry. Posted initially at Cairo and Palestine, he found himself stuck at Headquarters twenty miles behind El Alamein as a camouflage officer as the Second Battle of El Alamein began. At dawn on 24 October 1942, the Regiment advanced, and suffered numerous casualties from enemy anti-tank guns. Chafing at inactivity, Douglas took off against orders on 27 October, drove to the Regimental HQ in a truck, and reported to the C.O., Colonel E. O. Kellett, lying that he had been instructed to go to the front (luckily this escapade did not land him in serious trouble; in a reprise of 1935, Douglas got off with an apology). Desperately needing officer replacements, the Colonel posted him to A Squadron, and gave him the opportunity to take part as a fighting tanker in the Eighth Army’s victorious sweep through North Africa vividly recounted in his memoir Alamein to Zem Zem, illustrated with his own drawings. Death Captain Douglas returned from North Africa to England in December 1943 and took part in the D-Day invasion of Normandy on 6 June 1944. He was killed by enemy mortar fire on 9 June, while his regiment was advancing from Bayeux. Captain Leslie Skinner (regimental chaplain) buried him by a hedge, close to where he had died on "forward slopes point 102". Shortly after the war his remains were reburied at Tilly-sur-Seulles War Cemetery (14 km south of Bayeux) in plot 1, row E, grave number 2. Bibliography * Selected Poems (Keith Douglas, J.C. Hall, Norman Nicholson) (1943) * Alamein to Zem Zem (1946), reprinted 1966 * Collected Poems (Editions Poetry London 1951), reprinted 1966 * Selected Poems (Faber 1964) * The Complete Poems (Faber & Faber 1978), reprinted in 1987, 1997, 2011 * Alldritt, Keith. Modernism in the Second World War ISBN 0-8204-0865-4 * The Letters of Keith Douglas edited by Desmond Graham (Carcanet Press, 2000) ISBN 978 1 857544 77 0 Biography * Keith Douglas, 1920–1944 by Desmond Graham (OUP, 1974) ISBN 0-19-211716-5 References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keith_Douglas

Cid (Sidney) Corman (June 29, 1924 – March 12, 2004) was an American poet, translator and editor, most notably of Origin, who was a key figure in the history of American poetry in the second half of the 20th century. Corman was born in Boston's Roxbury neighborhood and grew up nearby in the Dorchester neighborhood. His parents were both from the Ukraine. From an early age he was an avid reader and showed an aptitude for drawing and calligraphy. He attended Boston Latin School and in 1941 he entered Tufts University, where he achieved Phi Beta Kappa honours and wrote his first poems. He was excused from service in World War II for medical reasons and graduated in 1945. Corman studied for his Master's degree at the University of Michigan, where he won the Hopwood poetry award, but dropped out when two credits short of completion. After a brief stint at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, he spent some time travelling around the United States, returning to Boston in 1948. Here he ran poetry events in public libraries and, with the help of his high-school friend Nat Hentoff, he started the country's first poetry radio program. In 1952, Corman wrote: "I initiated my weekly broadcasts, known as This Is Poetry, from WMEX (1510 kc.) in Boston. The program has been usually a fifteen-minute reading of modern verse on Saturday evenings at seven thirty; however, I have taken some liberties and have read from Moby Dick and from stories by Dylan Thomas, Robert Creeley, and Joyce."[3] This program featured readings by Robert Creeley, Stephen Spender, Theodore Roethke and many other Boston-based and visiting poets. He also spent some time at the Yaddo artists' retreat in Saratoga Springs. It was about this time that Corman changed his name from Sydney Corman to the simpler "Cid." As Corman indicated in conversation, this name change--similar to Whitman's assumption of Walt over Walter--signaled his beginnings as a poet for the common man. During this period, Corman was writing prolifically and published in excess of 500 poems in about 100 magazines by 1954. He considered this to be a kind of apprenticeship, and none of these poems were ever published in book form. Origin and Europe In 1951, Corman began Origin in response to the failure of a magazine that Creeley had planned. The magazine typically featured one writer per issue and ran, with breaks, until the mid 1980s. Poets featured included Robert Creeley, Robert Duncan, Larry Eigner, Denise Levertov, William Bronk, Theodore Enslin, Charles Olson, Louis Zukofsky, Gary Snyder, Lorine Niedecker, Wallace Stevens, William Carlos Williams, Paul Blackburn and Frank Samperi. The magazine also led to the establishment of Origin Press, which published books by a similar range of poets as well as by Corman himself and which remains currently active. In 1954, Corman won a Fulbright Fellowship grant (with an endorsement from Marianne Moore) and moved to France, where he studied for a time at the Sorbonne. He then moved to Italy to teach English in a small town called Matera. By this time, Corman had published a number of small books, but his Italian experiences were to provide the materials for his first major work, Sun Rock Man (1962). He also experimented with oral poetry, recording improvised poems on tape. These tapes were later to influence the talk-poems of David Antin, one of the key developments in the emergence of performance poetry. At this time he produced the first English translations of Paul Celan, even though he didn't have the poet's approval. Japan In 1958, Corman got a teaching job in Kyoto through the auspices of Will Petersen or, according to one account, poet Gary Snyder. Here he continued to write and to run Origin and in 1959 he published Snyder's first book, Riprap. He remained in Japan until 1960, when he returned to the States for two years. Back in Japan he married Konishi Shizumi, a Japanese TV news editor. Corman began to translate Japanese poetry, particularly work by Bashō and Kusano Shimpei. The Cormans spent the years 1970 to 1982 in Boston, where they unsuccessfully tried to establish a number of small businesses. They returned to Kyoto, where they remained, running CC's Coffee Shop in Kyoto, "offering poetry and western-style patisserie". Later work Corman has been associated with the Beats, Black Mountain poets and Objectivists, mainly through his championing as an editor, publisher and critic. However, he remained independent of all groups and fashions throughout his career. Michael Carlson, who contributed to Origins and corresponded with Corman starting in the 1980s, described Corman's correspondence this way: "In the days before email his words came by return post, aerogrammes densely typed to take advantage of every inch of space, or postcards printed in his fine hand. They were encouraging, gossipy, and always challenging; he expected everyone to match his commitment to poetry as a way of life. But they also digressed into other shared enthusiasms: in my case his love of baseball and sumo wrestling, and often into the difficulties of making a living in expensive Japan." He was a prolific poet until his final illness, publishing more than 100 books and pamphlets. In 1990, he published the first two volumes of his selected poems, OF, running to some 1500 poems. Volume 3, with a further 750 poems appeared in 1998 and two further volumes are planned. Several collections of wide-ranging essays have been published. His translations (or co-translations) include Bashō's Back Roads to Far Towns, Things by Francis Ponge, poems by Paul Celan and collections of haiku. Cid Corman did not speak, read or write Japanese, even though his co-translation with Susumu Kamaike of Bashō's Oku No Hosomichi (see above) is considered to be one of the most accurate in tone in the English language. Corman also felt himself able to translate from classical Chinese without so much as a minimal understanding of the language. One of Corman's last appearances in the United States was at the 2003 centennial symposium and celebration in southern Wisconsin that honored his friend and fellow poet, Lorine Niedecker. At the time, Corman spoke warmly about his connection to the Fort Atkinson, Wisconsin, poet (playing the only known audio tape of Niedecker reading from her works). Niedecker had died in 1970, shortly after Corman had visited her. As he told friends and admirers during the 2003 gathering, Corman had not returned to the Black Hawk Island haunts of Niedecker since that first (and only) visit with Niedecker. He died in Kyoto, Japan on March 12, 2004 after being hospitalized for a cardiac condition since January 2004. References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cid_Corman


Karl Jay Shapiro (November 10, 1913– May 14, 2000) was an American poet. He was appointed the fifth Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress in 1946. Biography Karl Shapiro was born in Baltimore, Maryland and graduated from the Baltimore City College high school. He attended the University of Virginia before World War II, and immortalized it in a scathing poem called “University,” which noted that “to hate the Negro and avoid the Jew is the curriculum.” He did not return after his military service. Karl Shapiro, a stylish writer with a commendable regard for his craft, wrote poetry in the Pacific Theater while he served there during World War II. His collection V-Letter and Other Poems, written while Shapiro was stationed in New Guinea, was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry in 1945, while Shapiro was still in the military. Shapiro was American Poet Laureate in 1946 and 1947. (At the time this title was Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress which was changed by Congress in 1985 to Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress.) Poems from his earlier books display a mastery of formal verse with a modern sensibility that viewed such topics as automobiles, house flies, and drug stores as worthy of attention. In 1963, the poet/critic Randall Jarrell praised Shapiro’s work: Karl Shapiro’s poems are fresh and young and rash and live; their hard clear outlines, their flat bold colors create a world like that of a knowing and skillful neoprimitive painting, without any of the confusion or profundity of atmosphere, of aerial perspective, but with notable visual and satiric force. The poet early perfected a style, derived from Auden but decidedly individual, which he has not developed in later life but has temporarily replaced with the clear Rilke-like rhetoric of his Adam and Eve poems, the frankly Whitmanesque convolutions of his latest work. His best poem—poems like “The Leg,” “Waitress,” “Scyros,” “Going to School,” “Cadillac”—have a real precision, a memorable exactness of realization, yet they plainly come out of life’s raw hubbub, out of the disgraceful foundations, the exciting and disgraceful surfaces of existence. In his later work, he experimented with more open forms, beginning with The Bourgeois Poet (1964) and continuing with White-Haired Lover (1968). The influences of Walt Whitman, D. H. Lawrence, W. H. Auden and William Carlos Williams were evident in his work. Shapiro’s interest in formal verse and prosody led to his writing multiple books on the subject including the long poem Essay on Rime (1945), A Bibliography of Modern Prosody (1948), and A Prosody Handbook (with Robert Beum, 1965; reissued 2006). His Selected Poems appeared in 1968. Shapiro also published one novel, Edsel (1971) and a three-part autobiography simply titled, “Poet” (1988–1990). Shapiro edited the prestigious magazine, Poetry for several years, and he was a professor of English at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, where he edited Prairie Schooner, and at the University of California, Davis, from which he retired in the mid-1980s. His other works include Person, Place and Thing (1942), (with Ernst Lert) the libretto to Hugo Weisgall’s opera The Tenor (1950), To Abolish Children (1968), and The Old Horsefly (1993). Shapiro received the 1969 Bollingen Prize for Poetry, sharing the award that year with John Berryman. He died in New York City, aged 86, on May 14, 2000. More recent editions of his work include The Wild Card: Selected Poems Early and Late (1998) and Selected Poems (2003). Shapiro’s last work, Coda: Last Poems, (2008) was recently published in a volume organized posthumously by editor Robert Phillips. The poems, divided into three sections according to love poems to his last wife, poems concerning roses, and other various poems, were discovered in the drawers of Shapiro’s desk by his wife two years after his death. Awards * Jeanette S Davis Prize and Levinson prize, both from Poetry in 1942 * Contemporary Poetry prize, 1943 * American Academy of Arts and Letters grant, 1944 * Guggenheim Foundation fellowships, 1944, 1953 * Pulitzer Prize in poetry, 1945, for V-Letter and Other Poems * Shelley Memorial Prize, 1946 * Poetry Consultant at the Library of Congress (United States Poet Laureate), 1946–47 * Kenyon School of Letters fellowship, 1956–57 * Eunice Tietjens Memorial Prize, 1961 * Oscar Blumenthal Prize, Poetry, 1963 * Bollingen Prize, 1968 * Robert Kirsch Award, LA Times, 1989 * Charity Randall Citation, 1990 * Fellow in American Letters, Library of Congress Bibliography Poetry collections * * Adult Bookstore (1976) * Collected Poems, 1940–1978 (1978) * Essay on Rime (1945) * New and Selected Poems, 1940–1987 (1988) * Person, Place, and Thing (1942) * Place of Love (1943) * Poems (1935) * Poems 1940-1953 (1953) * Poems of a Jew (1950) * Selected Poems (Random House, 1968) * Selected Poems (Library of America, 2003), edited by John Updike. * The Bourgeois Poet (1964) * The Old Horsefly (1993) * The Place of Love (1943) * Trial of a Poet (1947) * V-Letter and Other Poems (1945) * White Haired Lover (1968) * The Wild Card: Selected Poems, Early and Late (1998) * Coda: Last Poems (2008) Autobiography * * Poet: Volume I: The Younger Son (1988) * Reports of My Death (1990) * Poet: An Autobiography in Three Parts (Chapel Hill: Algonquin Books, 1988–1990) Essay collections * * The Poetry Wreck (1975) * To Abolish children and Other Essays (1968) * A Primer for Poets (1965) * In Defense of Ignorance (1960) * Randall Jarrell (1967) * Start With the Sun: Studies in the Whitman Tradition, with James E. Miller, Jr., and Bernice Slote (1963) * Prose Keys to Modern Poetry (1962) Novels * * Edsel (1971) Secondary sources * * Lee Bartlett, Karl Shapiro: A Descriptive Bibliography 1933-1977 (New York: Garland, 1979) * Gail Gloston, Karl Shapiro, Delmore Schwartz, and Randall Jarrell: The Image of the Poet in the Late 1940s (Thesis: Reed College, 1957) * Charles F. Madden, Talks With Authors (Carbondale: Southern Illinois U. Press, 1968) * Hans Ostrom, "Karl Shapiro 1913-2000" (poem), in The Coast Starlight: Collected Poems 1976-2006 (Indianapolis, 2006) * Joseph Reino, Karl Shapiro (New York: Twayne, 1981) * Stephen Stepanchev, American Poetry Since 1945: A Critical Survey (1965) * Melvin B. Tolson, Harlem Gallery (1965), with an introduction by Karl Shapiro * Sue Walker, ed., Seriously Meeting Karl Shapiro (Mobile: Negative Capability Press, 1993) * William White, Karl Shapiro: A Bibliography, with a note by Karl Shapiro (Detroit: Wayne State U. Press, 1960) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karl_Shapiro


Aphra Behn (14 December 1640? April 1689) was an English playwright, poet, translator and fiction writer from the Restoration era. As one of the first English women to earn her living by her writing, she broke cultural barriers and served as a literary role model for later generations of women authors. Rising from obscurity, she came to the notice of Charles II, who employed her as a spy in Antwerp. Upon her return to London and a probable brief stay in debtors’ prison, she began writing for the stage. She belonged to a coterie of poets and famous libertines such as John Wilmot, Lord Rochester. She wrote under the pastoral pseudonym Astrea. During the turbulent political times of the Exclusion Crisis, she wrote an epilogue and prologue that brought her into legal trouble; she thereafter devoted most of her writing to prose genres and translations. A staunch supporter of the Stuart line, she declined an invitation from Bishop Burnet to write a welcoming poem to the new king William III. She died shortly after.She is remembered in Virginia Woolf’s A Room of One’s Own: “All women together ought to let flowers fall upon the tomb of Aphra Behn which is, most scandalously but rather appropriately, in Westminster Abbey, for it was she who earned them the right to speak their minds.” Her grave is not included in the Poets’ Corner but lies in the East Cloister near the steps to the church. Life and work Versions of her early life Information regarding Behn’s life is scant, especially regarding her early years. This may be due to intentional obscuring on Behn’s part. One version of Behn’s life tells that she was born to a barber named John Amis and his wife Amy. Another story has Behn born to a couple named Cooper. The Histories And Novels of the Late Ingenious Mrs. Behn (1696) states that Behn was born to Bartholomew Johnson, a barber, and Elizabeth Denham, a wet-nurse. Colonel Thomas Colepeper, the only person who claimed to have known her as a child, wrote in Adversaria that she was born at “Sturry or Canterbury” to a Mr Johnson and that she had a sister named Frances. Another contemporary, Anne Finch, wrote that Behn was born in Wye in Kent, the “Daughter to a Barber”. In some accounts the profile of her father fits Eaffrey Johnson.Behn was born during the buildup of the English Civil War, a child of the political tensions of the time. One version of Behn’s story has her travelling with a Bartholomew Johnson to Surinam. He was said to die on the journey, with his wife and children spending some months in the country, though there is no evidence of this. During this trip Behn said she met an African slave leader, whose story formed the basis for one of her most famous works, Oroonoko. It is possible that she acted a spy in the colony. There is little verifiable evidence to confirm any one story. In Oroonoko Behn gives herself the position of narrator and her first biographer accepted the assumption that Behn was the daughter of the lieutenant general of Surinam, as in the story. There is little evidence that this was the case, and none of her contemporaries acknowledge any aristocratic status. There is also no evidence that Oroonoko existed as an actual person or that any such slave revolt, as is featured in the story, really happened. Writer Germaine Greer has called Behn “a palimpsest; she has scratched herself out,” and biographer Janet Todd noted that Behn “has a lethal combination of obscurity, secrecy and staginess which makes her an uneasy fit for any narrative, speculative or factual. She is not so much a woman to be unmasked as an unending combination of masks”. It is notable that her name is not mentioned in tax or church records. During her lifetime she was also known as Ann Behn, Mrs Bean, agent 160 and Astrea. Career Shortly after her supposed return to England from Surinam in 1664, Behn may have married Johan Behn (also written as Johann and John Behn). He may have been a merchant of German or Dutch extraction, possibly from Hamburg. He died or the couple separated soon after 1664, however from this point the writer used “Mrs Behn” as her professional name.Behn may have had a Catholic upbringing. She once commented that she was “designed for a nun,” and the fact that she had so many Catholic connections, such as Henry Neville who was later arrested for his Catholicism, would have aroused suspicions during the anti-Catholic fervour of the 1680s. She was a monarchist, and her sympathy for the Stuarts, and particularly for the Catholic Duke of York may be demonstrated by her dedication of her play The Rover II to him after he had been exiled for the second time. Behn was dedicated to the restored King Charles II. As political parties emerged during this time, Behn became a Tory supporter.By 1666 Behn had become attached to the court, possibly through the influence of Thomas Culpeper and other associates. The Second Anglo-Dutch War had broken out between England and the Netherlands in 1665, and she was recruited as a political spy in Antwerp on behalf of King Charles II, possibly under the auspices of courtier Thomas Killigrew. This is the first well-documented account we have of her activities. Her code name is said to have been Astrea, a name under which she later published many of her writings. Her chief role was to establish an intimacy with William Scot, son of Thomas Scot, a regicide who had been executed in 1660. Scot was believed to be ready to become a spy in the English service and to report on the doings of the English exiles who were plotting against the King. Behn arrived in Bruges in July 1666, probably with two others, as London was wracked with plague and fire. Behn’s job was to turn Scot into a double agent, but there is evidence that Scot betrayed her to the Dutch.Behn’s exploits were not profitable however; the cost of living shocked her, and she was left unprepared. One month after arrival, she pawned her jewellry. King Charles was slow in paying (if he paid at all), either for her services or for her expenses whilst abroad. Money had to be borrowed so that Behn could return to London, where a year’s petitioning of Charles for payment was unsuccessful. It may be that she was never paid by the crown. A warrant was issued for her arrest, but there is no evidence it was served or that she went to prison for her debt, though apocryphally it is often given as part of her history. Forced by debt and her husband’s death, Behn began to work for the King’s Company and the Duke’s Company players as a scribe. She had, however, written poetry up until this point. While she is recorded to have written before she adopted her debt, John Palmer said in a review of her works that, “Mrs. Behn wrote for a livelihood. Playwriting was her refuge from starvation and a debtor’s prison.” The theatres that had been closed under Cromwell were now re-opening under Charles II, plays enjoying a revival. Her first play, The Forc’d Marriage, was staged in 1670, followed by The Amorous Prince (1671). After her third play, The Dutch Lover, failed, Behn falls off the public record for three years. It is speculated that she went travelling again, possibly in her capacity as a spy. She gradually moved towards comic works, which proved more commercially successful. Her most popular works included The Rover. Behn became friends with notable writers of the day, including John Dryden, Elizabeth Barry, John Hoyle, Thomas Otway and Edward Ravenscroft, and was acknowledged as a part of the circle of the Earl of Rochester. Behn often used her writings to attack the parliamentary Whigs claiming, “In public spirits call’d, good o’ th’ Commonwealth... So tho’ by different ways the fever seize... in all ’tis one and the same mad disease.” This was Behn’s reproach to parliament which had denied the king funds. Final years and death In 1688, in the year before her death, she published A Discovery of New Worlds, a translation of a French popularisation of astronomy, Entretiens sur la pluralité des mondes, by Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle, written as a novel in a form similar to her own work, but with her new, religiously oriented preface. In all she would write and stage 19 plays, contribute to more, and become one of the first prolific, high-profile female dramatists in Britain. During the 1670s and 1680s she was one of the most productive playwrights in Britain, second only to Poet Laureate John Dryden.In her last four years, Behn’s health began to fail, beset by poverty and debt, but she continued to write ferociously, though it became increasingly hard for her to hold a pen. In her final days, she wrote the translation of the final book of Abraham Cowley’s Six Books of Plants. She died on 16 April 1689, and was buried in the East Cloister Westminster Abbey. The inscription on her tombstone reads: “Here lies a Proof that Wit can never be Defence enough against Mortality.” She was quoted as stating that she had led a “life dedicated to pleasure and poetry.” Published works Behn earned a living writing, one of the earliest Englishwoman to do so. After John Dryden she was the most prolific writer of the English Restoration. Behn was not the first woman in England to publish a play. In 1613 Lady Elizabeth Cary had published The Tragedy of Miriam, in the 1650s Margaret Cavendish published two volumes of plays, and in 1663 a translation of Corneille’s Pompey by Katherine Philips was performed in Dublin and London. Women had been excluded from theatre in the Elizabethan era, but in Restoration England they made up a significant part of the audience and professional actresses played the women’s parts. This changed the nature and themes of Restoration theatre.Behn’s first play The Forc’d Marriage was a romantic tragicomedy on arranged marriages and was staged by the Duke’s Company in September 1670. The performance ran for six nights, which was regarded as a good run for an unknown author. Six months later Behn’s play The Amorous Prince was successfully staged. Again, Behn used the play to comment on the harmful effects of arranged marriages. Behn did not hide the fact that she was a woman, instead she made a point of it. When in 1673 the Dorset Garden Theatre staged The Dutch Lover, critics sabotaged the play on the grounds that the author was a woman. Behn tackled the critics head on in Epistle to the Reader. She argued that women had been held back by their unjust exclusion from education, not their lack of ability. After a three-year publication pause, Behn published four plays in close succession. In 1676 she published Abdelazar, The Town Fop and The Rover. In early 1678 Sir Patient Fancy was published. This succession of box-office successes led to frequent attacks on Behn. She was attacked for her private life, the morality of her plays was questioned and she was accused of plagiarising The Rover. Behn countered these public attacks in the prefaces of her published plays. In the preface to Sir Patient Fancy she argued that she was being singled out because she was a woman, while male playwrights were free to live the most scandalous lives and write bawdy plays.Under Charles II of England prevailing Puritan ethics was reversed in the fashionable society of London. The King associated with playwrights that poured scorn on marriage and the idea of consistency in love. Among the King’s favourite was the Earl of Rochester John Wilmot, who became famous for his cynical libertinism. Behn was a friend of Wilmot and Behn became a bold proponent of sexual freedom for both women and men. Like her contemporary male libertines, she wrote freely about sex. In the infamous poem The Disappointment she wrote a comic account of male impotence from a woman’s perspective. Critics Lisa Zeitz and Peter Thoms contend that the poem “playfully and wittily questions conventional gender roles and the structures of oppression which they support”. In The Dutch Lover Behn forthrightly acknowledged female sexual desire. Critics of Behn were provided with ammunition because of her public liaison with John Hoyle, a bisexual lawyer who scandalised his contemporaries.By the late 1670s Behn was among the leading playwrights of England. Her plays were staged frequently and attended by the King. The Rover became a favourite at the King’s court. Behn became heavily involved in the political debate about the succession. Because Charles II had no heir a prolonged political crisis ensued. Mass hysteria commenced as in 1678 the rumoured Popish Plot suggested the King should be replaced with his Roman Catholic brother James. Political parties developed, the Whigs wanted to exclude James, while the Tories did not believe succession should be altered in any way. Charles II eventually dissolved the Cavalier Parliament and James II succeeded him in 1685. Behn supported the Tory position and in the two years between 1681 and 1682 produced five plays to discredit the Whigs. The London audience, mainly Tory sympathisers, attended the plays in large numbers. But Behn was arrested on the order of King Charles II when she used one of the plays to attack James Scott, Duke of Monmouth, the illegitimate son of the King.As audience numbers declined, theatres staged mainly old works to save costs. Nevertheless, Behn published The Luckey Chance in 1686. In response to the criticism levelled at they play she articulated a long and passionate defence of women writers. Her play The Emperor of the Moon was published and staged in 1687, it became one of her longest running plays. Behn stopped writing plays and turned to prose fiction. Today she is mostly known for the novels she wrote in the later part of her life. Her first novel was the three-part Love-Letters Between a Nobleman and His Sister, published between 1682 and 1687. The novels were inspired by a contemporary scandal, which saw Lord Grey elope with his sister-in-law Lady Henrietta Berkeley. At the time of publication Love Letters was very popular and went through more than 16 editions. Today Behn’s prose work is critically acknowledged as having been important to the development of the English novel. Following Behn’s death, new female dramatists such as Delarivier Manley, Mary Pix, Susanna Centlivre and Catherine Trotter acknowledged Behn as their most vital predecessor, who opened up public space for women writers.In 1688, less than a year before her death, Behn published Oroonoko: or, The Royal Oroonoko, the story of the enslaved Oroonoko and his love Imoinda. It was based on Behn’s travel to Surinam twenty years earlier. The novel became a great success. In 1696 it was adapted for the stage by Thomas Southerne and continuously performed throughout the 18th century. In 1745 the novel was translated into French, going through seven French editions. As abolitionism gathered pace in the late 18th century the novel was celebrated as the first anti-slavery novel. Legacy and re-evaluation After her death in 1689 Behn’s literary work was marginalised and dismissed outright. Until the mid-20th century Behn was repeatedly dismissed as morally depraved minor writer. In the 18th century her literary work was scandalised as lewd by Thomas Brown, William Wycherley, Richard Steele and John Duncombe. Alexander Pope penned the famous lines “The stage how loosely does Astrea tread, Who fairly puts all characters to bed!”. In the 19th century Mary Hays, Matilda Betham, Alexander Dyce, Jane Williams and Julia Kavanagh decided that Behn’s writings were unfit to read, because they were corrupt and deplorable. Among the few critics who believed that Behn was an important writer were Leigh Hunt, William Forsyth and William Henry Hudson.The life and times of Behn were recounted by a long line of biographers, among them Dyce, Edmund Gosse, Ernest Bernbaum, Montague Summers, Vita Sackville-West, Virginia Woolf, George Woodcock, William J. Cameron and Frederick Link.Of Behn’s considerable literary output only Oroonoko was seriously considered by literary scholars. The late 18th century the novel is regarded as one of the first abolitionist and humanitarian novel published in the English language. It is credited as precursor to Jean-Jaques Rousseau’s Discourses on Inequality. Since the 1970s Behn’s literary works have been re-evaluated by feminist critics and writers. Behn was rediscovered as a significant female writer by Maureen Duffy, Angeline Goreau, Ruth Perry, Hilda Lee Smith, Moira Ferguson, Jane Spencer, Dale Spender, Elaine Hobby and Janet Todd. This led to the reprinting of her works. The Rover was republished in 1967, Oroonoko was republished in 1973, Love Letters between a Nobleman and His Sisters was published again in 1987 and The Lucky Chance was reprinted in 1988. Montague Summers, an author of scholarly works on the English drama of the 17th century, published a six-volume collection of her work, in hopes of rehabilitating her reputation. Summers was fiercely passionate about the work of Behn and found himself incredibly devoted to the appreciation of 17th century literature. Felix Schelling wrote in The Cambridge History of English Literature, that she was “a very gifted woman, compelled to write for bread in an age in which literature... catered habitually to the lowest and most depraved of human inclinations,” and that, “Her success depended upon her ability to write like a man.” Edmund Gosse remarked that she was, “...the George Sand of the Restoration”.The criticism of Behn’s poetry focuses on the themes of gender, sexuality, femininity, pleasure, and love. A feminist critique tends to focus on Behn’s inclusion of female pleasure and sexuality in her poetry, which was a radical concept at the time she was writing. One critic, Alison Conway, views Behn as instrumental to the formation of modern thought around the female gender and sexuality: "Behn wrote about these subjects before the technologies of sexuality we now associate were in place, which is, in part, why she proves so hard to situate in the trajectories most familiar to us”. Virginia Woolf wrote, in A Room of One’s Own: All women together, ought to let flowers fall upon the grave of Aphra Behn... for it was she who earned them the right to speak their minds... Behn proved that money could be made by writing at the sacrifice, perhaps, of certain agreeable qualities; and so by degrees writing became not merely a sign of folly and a distracted mind but was of practical importance. Adaptations of Behn in Literature Behn’s life has been adapted for the stage in the 2014 play Empress of the Moon: The Lives of Aphra Behn by Chris Braak, and the 2015 play [exit Mrs Behn] or, The Leo Play by Christopher VanderArk. She is one of the characters in the 2010 play Or, by Liz Duffy Adams. Behn appears as a character in Daniel O’Mahony’s Newtons Sleep, in Phillip Jose Farmer’s The Magic Labyrinth and Gods of Riverworld, in Molly Brown’s Invitation to a Funeral (1999), and in Diana Norman’s The Vizard Mask. She is referred to in Patrick O’Brian’s novel Desolation Island.


Ralph Nicholas Chubb (8 February 1892– 14 January 1960) was an English poet, printer, and artist. Heavily influenced by Whitman, Blake, and the Romantics, his work was the creation of a highly intricate personal mythology, one that was anti-materialist and sexually revolutionary. Life Ralph Chubb was born in Harpenden, Hertfordshire. His family moved to the historic town of St Albans before his first birthday. Chubb attended St Albans School and Selwyn College, Cambridge before becoming an officer in the First World War. He served with distinction but developed neurasthenia, and he was invalided out in 1918. From 1919 to 1922 Chubb studied at the Slade School of Art in London. It was there that he met Leon Underwood and other influential artists. He went on to contribute several articles and poems for Underwood’s magazine, The Island. Although his work was displayed at such venues as the Goupil Gallery and the Royal Academy of Art, his paintings did not sell. There are several in public collections in Britain. His major painting The Well (1920) is in Wakefield; Southampton has bathers with boys wrestling, and there are nudes at Leamington, all illustrated in the Public Art Foundation catalogues. He moved with his family to the village of Curridge, near Newbury in Berkshire. He began to devote his artistic talents to the printed works which would remain his chief labour in life. His books were created in several chief phases. His typeset books of the twenties were a humble offering, exhibiting Chubb’s talent for woodcutting and his quaint, visually inspired poetry. Even at this early stage, Chubb’s lifelong obsession with adolescent males was beginning to become apparent. He expands upon this theme more explicitly in An Appendix, a pederastic and spiritualist manifesto duplicated from a cursive manuscript. An Appendix was the first of his printed works to be printed in his own hand; he soon followed this with the first of his opulent lithographic books, The Sun Spirit. Throughout the nineteen-thirties, Chubb’s books became more elaborate and appealing. Water Cherubs crystallizes Chubb’s aesthetic of the youthful male form, and The Secret Country unfolds like an illuminated manuscript, recounting stories of Chubb’s family and his journeys among the Romani of the New Forest in Hampshire. Chubb’s printing press was interrupted by the war, but in 1948 he entered into the third period of career with two massive volumes: The Child Of Dawn and Flames of Sunrise. Each page of these two volumes is crowded with obscure digressions on Chubb’s mythology and drawings of symbolic significance. Briefly summarized, Chubb’s vision was a prophecy of the redemption of 'Albion’, or England, by the boy-god Ra-el-phaos, of whom Ralph claimed himself to be the prophet and herald. This echoes an earlier announcement to be found in The Heavenly Cupid: I announce a secret event as tremendous and mysterious as any that has occurred in the spiritual history of the world. I announce the inauguration of a Third Dispensation, the dispensation of the Holy Ghost on earth, and the visible advent thereof on earth in the form of a Young Boy of thirteen years old, naked perfect and unblemished. Other themes run through all of Chubb’s work. He was forever haunted by the memory of a young chorister at St Albans who disappeared from Chubb’s life just as he had summoned up the courage to speak to him. Similarly, a brief sexual relationship with another boy when Ralph was 19 seemed to serve as a template for future visions of paradise. Chubb’s books become progressively more self-involved and paranoid. Seeking to articulate his pederastic desires, he created a personal mythology which explained everything in terms only he could understand. Nonetheless, Chubb’s work is of fascinating psychological significance; each of the various angels, knights, seers, and boy-gods in his dream world represents an aspect of his introspective and persecuted self. Chubb, like many other artists of his generation, resented science for its intrusion into his imagination. He disparaged the scientists, orthodox theologians, and politicians of world, accusing them of squelching his personal thirst for liberty. In 1927 he wrote: Existence, besides being a miracle, is a symbol. Albeit here for inscrutable purposes the spirit is only to be discerned as it were in a distorting-glass. (The Book of God’s Madness) Chubb sought to persuade his readers in An Appendix of the verity of his solipsism by illustrating some examples of serendipitous events from his life. His aim is more on the mark when he excoriates the taboos and frustrations of modern life. The green green hills, the blue blue sky, blue sea, great golden SUN, yellow dandelions, the pink naked beauty of ripe boyhood, deathless free and happy, brimming with health. This I must have. Nothing less than this can ever satisfy me! GIVE ME MY HEAVEN! GIVE ME MY HEAVEN! (Water-Cherubs) Failing in health and facing continuing legal and financial difficulties, Ralph Chubb abandoned his controversial works in the mid-fifties, and began to collect and reprint his early poems and childhood memories. Treasure Trove and The Golden City (published posthumously) are devoid of the usual profusion of naked, lissome youths, but instead offer a glimpse into his youthful imagination, and some of his most charming poetry. In the final years of his life he donated his remaining volumes to the national libraries of Britain. He died peacefully at Fair Oak Cottage in Hampshire and was buried next to his parents at the Kingsclere Woodland Church. Chubb’s own assessment of his work conforms to the general critical reaction: I do not necessarily claim to be a great artist or writer; but I claim to be a true spirit– this is a subtler test. Seek me out; but you may not find me. (An Appendix) Works * None of the editions of Chubb’s books exceed more than 200 copies, and some of his lithographed masterworks exist in only 30 or 40 copies, of which a mere 6 or 7 are meticulously hand-colored by Chubb. * The dates and titles of Chubb’s printed works are given below. Early typeset works * 1924 Manhood * 1924 The Sacrifice of Youth * 1925 A Fable of Love & War * 1927 The Cloud & the Voice * 1928 Woodcuts * 1928 The Book of God’s Madness * 1929 An Appendix (duplicated hand-written text) Lithographed texts * 1930 Songs of Mankind * 1931 The Sun Spirit * 1934 The Heavenly Cupid * 1935 Songs Pastoral and Paradisal (illustrated by Vincent Stuart; script by Helen Hinkley) * 1936 Water Cherubs * 1939 The Secret Country Post-war prophetic texts * 1948 The Child of Dawn * 1953 Flames of Sunrise Juvenalia and early romances * 1957 Treasure Trove * 1960 The Golden City Posthumous works * 1965 The Day of St Alban * 1970 Autumn Leaves References and further reading * Cave, Roderick (1960). In Blake’s Tradition: the Press of Ralph Chubb. The American Book Collector. 11 (2), p8-17 * Cave, Roderick (1960). 'Blake’s Mantle’, a Memoir of Ralph Chubb. Book Design and Production. 3 (2), p24-8 * D’Arch Smith, Timothy (1970). Love in Earnest. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. * Rahman, Tariq (1991). Ephebophilia and the Creation of a Spiritual Myth in the Works of Ralph Nicholas Chubb. Journal of Homosexuality. 20 (1-2), p103-127 * Reid, Anthony (1970). Ralph Chubb: The Unknown. Reprinted from The Private Library. 3 (3-4). References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ralph_Chubb

Juan Francisco Manzano (Matanzas, 1797-1856) fue un poeta cubano que nació esclavo durante el periodo colonial. Escribió dos poemarios y su autobiografía, que se publicaron antes de que obtuviera la libertad en 1836. Su Autobiografía constituye el texto más divulgado de la narrativa antiesclavista y se considera un texto clave para comprender el periodo colonial. En 1844 fue víctima de una acusación falsa por supuestamente haber participado en la Conspiración de la Escalera. Fue condenado a prisión y después de salir de la cárcel no volvió a escribir, muriendo en la pobreza en 1856. Juan Francisco Manzano es considerado hoy como uno de los más valiosos e influyentes escritores cubanos del siglo XIX. Infancia Se acepta el año de 1797 como el año de nacimiento de Juan Francisco Manzano en El Molino, una plantación de caña de azúcar cerca de la ciudad de Matanzas. Sus padres eran esclavizados. Su padre era un sastre y su madre, María del Pilar, era una de las esclavizadas preferidas de la señora Beatriz Agustina de Jústiz y Zayas-Bazán, casada con el I marqués de Jústiz de Santa Ana, Manuel José Aparicio del Manzano y Jústiz. Manzano recibió el apellido de sus dueños como era costumbre en esa época. Sus amos le trataban bien, siempre acompañaba a su señora como «un niño de su vejez». De niño recitaba de memoria sermones, el Catecismo, loas y entremeses aprendidos en las misas y representaciones de ópera a las que asistía acompañando a sus amos, que se comportaban benévolamente con él y le permitían corretear por la casa, lo que indica la cierta libertad de la que gozaba Manzano. Desde su adolescencia era conocido en su ambiente como versificador ingenioso, ya que le era fácil resaltar. Sus padrinos eran blancos y el niño esclavizado estaba muy vinculado en general con el mundo de los blancos. Se decía que el niño pasaba más tiempo en los brazos de su señora marquesa que de la propia madre. A pesar del humilde trabajo que ejercía su madre nunca se separaba de ella, solo para dormir. Se le envió a la escuela de su madrina de bautismo enseguida que cumplió los seis años de edad, en dónde lo consideraban «rápido» para aprender. Después de la muerte de su propietaria la marquesa Jústiz de Santa Ana, su propiedad fue transferida a su hija segunda, la marquesa consorte de Prado Ameno, quién abusaba de su poder y le trataba con mucha crueldad. Manzano era maltratado y sufrió frecuentemente varios castigos: era encerrado en una carbonera, pasaba hambre y recibía azotes y golpes. Primeros escritos En 1818, Nicolás de Cárdenas y Manzano, segundo hijo de la marquesa consorte de Prado Ameno,2 lo recibió como sirviente de su casa. Fue entonces cuando Manzano aprendió a leer y escribir. En los libros de su nuevo amo también estudió retórica. Con un permiso –necesario debido a su condición social- pronto publicó sus versos en el volumen lírico Cantos a Lesbia (1821), hoy perdido, al igual que sus nanas y décimas, divulgadas anónimamente en Matanzas . Igual fortuna corrió el poemario Flores pasajeras, compuesto hacia 1830, y también buena parte de la producción que apareció de forma esporádica en periódicos de la época, si bien se salvó parte de ella. Entre los años 1837 y 1838 colaboró con las revistas El Aguinaldo Habanero y El Álbum. Otra obra de Manzano extraviada es la segunda parte de su autobiografía, Apuntes autobiográficos que escribió con su propia y rudimentaria ortografía, ya que se negaba la más elemental instrucción a los esclavos. Esta segunda parte se perdió cuando la conservaba el escritor cubano-español Ramón de Palma, vinculado al Círculo de Domingo del Monte. Manzano escribió la primera parte de su autobiografía en 1839, por iniciativa del activo animador intelectual Domingo del Monte (1804-1853), quien se la había pedido para que formara parte de una serie de alegatos antiesclavistas entregados al comisionado inglés, el abolicionista Richard Robert Madden. References Wikipedia—https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Juan_Francisco_Manzano

